Regulation of fas ligand expression during activation-induced cell death in T cells by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
- PMID: 10727463
- PMCID: PMC2193110
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.191.6.1017
Regulation of fas ligand expression during activation-induced cell death in T cells by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
Abstract
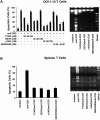
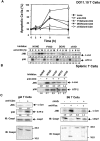
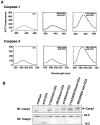
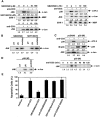
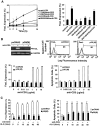
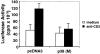
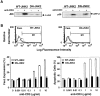
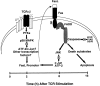
Activation-induced cell death (AICD) is a mechanism of peripheral T cell tolerance that depends upon an interaction between Fas and Fas ligand (FasL). Although c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) may be involved in apoptosis in various cell types, the mode of regulation of FasL expression during AICD in T cells by these two MAPKs is incompletely understood. To investigate the regulatory roles of these two MAPKs, we analyzed the kinetics of TCR-induced p38 MAPK and JNK activity and their regulation of FasL expression and AICD. We report that both JNK and p38 MAPK regulate AICD in T cells. Our data suggest a novel model of T cell AICD in which p38 MAPK acts early to initiate FasL expression and the Fas-mediated activation of caspases. Subsequently, caspases stimulate JNK to further upregulate FasL expression. Thus, p38 MAPK and downstream JNK converge to regulate FasL expression at different times after T cell receptor stimulation to elicit maximum AICD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T cell receptor ligation triggers novel nonapoptotic cell death pathways that are Fas-independent or Fas-dependent.J Immunol. 2002 Dec 1;169(11):6218-30. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.11.6218. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12444127
-
Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in activation-induced apoptosis of T cells.Immunology. 1999 May;97(1):26-35. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00756.x. Immunology. 1999. PMID: 10447711 Free PMC article.
-
Role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation and Fas-Fas ligand interaction in morphine-induced macrophage apoptosis.J Immunol. 2002 Apr 15;168(8):4025-33. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.8.4025. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11937560
-
Antigen-induced T cell death is regulated by CD4 expression.Int Rev Immunol. 2001 Oct;20(5):535-46. doi: 10.3109/08830180109045577. Int Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11890611 Review.
-
Mechanism of activation-induced cell death of T cells and regulation of FasL expression.Crit Rev Immunol. 2014;34(4):301-14. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.2014009988. Crit Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24941158 Review.
Cited by
-
Temporal Profile of Brain Gene Expression After Prey Catching Conditioning in an Anuran Amphibian.Front Neurosci. 2020 Jan 14;13:1407. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01407. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31992968 Free PMC article.
-
MK2 and Fas receptor contribute to the severity of CNS demyelination.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 25;9(6):e100363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100363. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24964076 Free PMC article.
-
Amifostine Analog, DRDE-30, Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Apr 24;9:394. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00394. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29740320 Free PMC article.
-
Squamous cell carcinoma antigen suppresses radiation-induced cell death.Br J Cancer. 2001 Mar 23;84(6):851-8. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.2000.1683. Br J Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11259103 Free PMC article.
-
NFATc1 is a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma and induces tumor cell apoptosis by activating the FasL-mediated extrinsic signaling pathway.Cancer Med. 2018 Sep;7(9):4701-4717. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1716. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 30085405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nagata S. Apoptosis by death factor. Cell. 1997;88:355–365. - PubMed
-
- Green D.R., Scott D.W. Activation-induced apoptosis in lymphocytes. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1994;6:476–487. - PubMed
-
- Russell J.H. Activation-induced death of mature T cells in the regulation of immune responses. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1995;7:382–388. - PubMed
-
- Brunner T., Mogil R.J., LaFrace D., Yoo N.J., Mahboubl A., Echeverri F., Martin S.J., Force W.R., Lynch D.H., Ware C.F. Cell-autonomous Fas (CD95)/Fas-ligand interaction mediates activation-induced apoptosis in T-cell hybridomas. Nature. 1995;373:441–444. - PubMed
-
- Dhein J., Walczak H., Baumler C., Debatin K.-M., Krammer P.H. Autocrine T-cell suicide mediated by APO-1/(Fas/CD95) Nature. 1995;373:438–441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

