Synaptotagmin VII regulates Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis of lysosomes in fibroblasts
- PMID: 10725327
- PMCID: PMC2174306
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.148.6.1141
Synaptotagmin VII regulates Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis of lysosomes in fibroblasts
Abstract
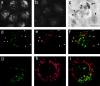
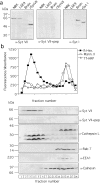
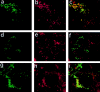
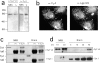
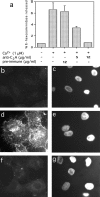
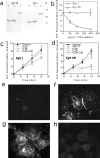
Synaptotagmins (Syts) are transmembrane proteins with two Ca(2+)-binding C(2) domains in their cytosolic region. Syt I, the most widely studied isoform, has been proposed to function as a Ca(2+) sensor in synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Several of the twelve known Syts are expressed primarily in brain, while a few are ubiquitous (Sudhof, T.C., and J. Rizo. 1996. Neuron. 17: 379-388; Butz, S., R. Fernandez-Chacon, F. Schmitz, R. Jahn, and T.C. Sudhof. 1999. J. Biol. Chem. 274:18290-18296). The ubiquitously expressed Syt VII binds syntaxin at free Ca(2+) concentrations ([Ca(2+)]) below 10 microM, whereas other isoforms require 200-500 microM [Ca(2+)] or show no Ca(2+)-dependent syntaxin binding (Li, C., B. Ullrich, Z. Zhang, R.G.W. Anderson, N. Brose, and T.C. Sudhof. 1995. Nature. 375:594-599). We investigated the involvement of Syt VII in the exocytosis of lysosomes, which is triggered in several cell types at 1-5 microM [Ca(2+)] (Rodríguez, A., P. Webster, J. Ortego, and N.W. Andrews. 1997. J. Cell Biol. 137:93-104). Here, we show that Syt VII is localized on dense lysosomes in normal rat kidney (NRK) fibroblasts, and that GFP-tagged Syt VII is targeted to lysosomes after transfection. Recombinant fragments containing the C(2)A domain of Syt VII inhibit Ca(2+)-triggered secretion of beta-hexosaminidase and surface translocation of Lgp120, whereas the C(2)A domain of the neuronal- specific isoform, Syt I, has no effect. Antibodies against the Syt VII C(2)A domain are also inhibitory in both assays, indicating that Syt VII plays a key role in the regulation of Ca(2+)-dependent lysosome exocytosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ca(2+)-dependent and -independent activities of neural and non-neural synaptotagmins.Nature. 1995 Jun 15;375(6532):594-9. doi: 10.1038/375594a0. Nature. 1995. PMID: 7791877
-
Synaptotagmin VII is targeted to dense-core vesicles and regulates their Ca2+ -dependent exocytosis in PC12 cells.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 10;279(50):52677-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409241200. Epub 2004 Sep 28. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15456748
-
Synaptotagmin V is targeted to dense-core vesicles that undergo calcium-dependent exocytosis in PC12 cells.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jul 5;277(27):24499-505. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202767200. Epub 2002 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12006594
-
Synaptotagmin regulates mast cell functions.Immunol Rev. 2001 Feb;179:25-34. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.790103.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11292024 Review.
-
There's more to life than neurotransmission: the regulation of exocytosis by synaptotagmin VII.Trends Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;15(11):626-31. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.09.001. Epub 2005 Sep 15. Trends Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16168654 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytotoxic Granule Trafficking and Fusion in Synaptotagmin7-Deficient Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes.Front Immunol. 2020 May 29;11:1080. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01080. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32547563 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of the Rab27a-dependent trafficking and secretory mechanisms improves lysosomal transport, alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress, and reduces lysosome overload in cystinosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;33(15):2950-62. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00417-13. Epub 2013 May 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23716592 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin-mediated vesicle fusion regulates cell migration.Nat Immunol. 2010 Jun;11(6):495-502. doi: 10.1038/ni.1878. Epub 2010 May 16. Nat Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20473299 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 gp120 Promotes Lysosomal Exocytosis in Human Schwann Cells.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Jul 17;13:329. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00329. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31379513 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+ and synaptotagmin VII-dependent delivery of lysosomal membrane to nascent phagosomes.J Cell Biol. 2006 Sep 25;174(7):997-1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200605004. Epub 2006 Sep 18. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16982801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Black D.L. Splicing in the inner eara common tune, but what are the instruments? Neuron. 1998;20:165–168. - PubMed
-
- Bommert K., Charlton M.P., DeBello W.M., Chin G.J., Betz H., Augustine G.J. Inhibition of neurotransmitter release by C2-domain peptides implicates synaptotagmin in exocytosis. Nature. 1993;363:163–165. - PubMed
-
- Burgoyne R.D., Morgan A. Calcium sensors in regulated exocytosis. Cell Calcium. 1998;24:367–376. - PubMed
-
- Butz S., Fernandez-Chacon R., Schmitz F., Jahn R., Sudhof T.C. The subcellular localizations of atypical synaptotagmins III and VI. Synaptotagmin III is enriched in synapses and synaptic plasma membranes but not in synaptic vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:18290–18296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

