Factors influencing T-cell turnover in HIV-1-seropositive patients
- PMID: 10712441
- PMCID: PMC377453
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI8647
Factors influencing T-cell turnover in HIV-1-seropositive patients
Abstract
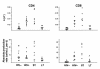
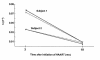
HIV-1 disease is associated with pathological effects on T-cell production, destruction, and distribution. Using the deuterated (2H) glucose method for endogenous labeling, we have analyzed host factors that influence T-cell turnover in HIV-1-uninfected and -infected humans. In untreated HIV-1 disease, the average half life of circulating T cells was diminished without compensatory increases in cell production. Within 12 weeks of the initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), the absolute production rates of circulating T cells increased, and normal half-lives and production rates were restored by 12-36 months. Interpatient heterogeneity in the absolute degree of turnover correlated with the relative proportion of naive- and memory/effector-phenotype T cells in each of the CD4+ and CD8+ populations. The half-lives of naive-phenotype T cells ranged from 116-365 days (fractional replacement rates of 0.19-0.60% per day), whereas memory/effector-phenotype T cells persisted with half-lives from 22-79 days (fractional replacement rates of 0.87-3.14% per day). Naive-phenotype T cells were more abundant, and the half-life of total T cells was prolonged in individuals with abundant thymic tissue, as assessed by computed tomography. Such interpatient variation in T-cell kinetics may be reflective of differences in functional immune reconstitution after treatment for HIV-1 disease.
Figures
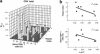
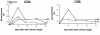
Comment in
-
Normal physiology and HIV pathophysiology of human T-cell dynamics.J Clin Invest. 2000 Mar;105(5):565-6. doi: 10.1172/JCI9478. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 10712427 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
HIV-1-infected children on HAART: immunologic features of three different levels of viral suppression.Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2007 Jan 15;72(1):14-21. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.20152. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2007. PMID: 17041945 Clinical Trial.
-
Directly measured kinetics of circulating T lymphocytes in normal and HIV-1-infected humans.Nat Med. 1999 Jan;5(1):83-9. doi: 10.1038/4772. Nat Med. 1999. PMID: 9883844
-
Normalization of CD4+ cell numbers and reduced levels of memory CD8+ cells in blood and tonsillar tissue after highly active antiretroviral therapy in early HIV type-1 infection.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 Feb 10;16(3):191-201. doi: 10.1089/088922200309287. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000. PMID: 10710207
-
Thymic function in HIV-infection.Dan Med J. 2013 Apr;60(4):B4622. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23651726 Review.
-
Measurement of T-cell kinetics: recent methodologic advances.Immunol Today. 1999 Oct;20(10):438-41. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5699(99)01529-7. Immunol Today. 1999. PMID: 10500289 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Genetic absence of PD-1 promotes accumulation of terminally differentiated exhausted CD8+ T cells.J Exp Med. 2015 Jun 29;212(7):1125-37. doi: 10.1084/jem.20142237. Epub 2015 Jun 1. J Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26034050 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis and treatment of HIV infection.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012 Aug-Oct;23(4-5):207-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.05.007. Epub 2012 Jun 26. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012. PMID: 22738931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qualitative differences between naïve and memory T cells.Immunology. 2002 Jun;106(2):127-38. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2002.01447.x. Immunology. 2002. PMID: 12047742 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Exogenous interleukin-2 administration corrects the cell cycle perturbation of lymphocytes from human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals.J Virol. 2001 Nov;75(22):10843-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.22.10843-10855.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11602725 Free PMC article.
-
MyD88-dependent immune activation mediated by human immunodeficiency virus type 1-encoded Toll-like receptor ligands.J Virol. 2007 Aug;81(15):8180-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00421-07. Epub 2007 May 16. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17507480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ho DD, et al. Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature. 1995;373:123–126. - PubMed
-
- Wei X, et al. Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Nature. 1995;373:117–122. - PubMed
-
- Mohri H, Bonhoeffer S, Monard S, Perelson AS, Ho DD. Rapid turnover of T lymphocytes in SIV-infected rhesus macaques. Science. 1998;279:1223–1227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

