Sphingolipid-cholesterol rafts diffuse as small entities in the plasma membrane of mammalian cells
- PMID: 10704449
- PMCID: PMC2174552
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.148.5.997
Sphingolipid-cholesterol rafts diffuse as small entities in the plasma membrane of mammalian cells
Abstract
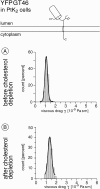
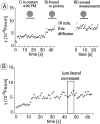
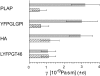
To probe the dynamics and size of lipid rafts in the membrane of living cells, the local diffusion of single membrane proteins was measured. A laser trap was used to confine the motion of a bead bound to a raft protein to a small area (diam < or = 100 nm) and to measure its local diffusion by high resolution single particle tracking. Using protein constructs with identical ectodomains and different membrane regions and vice versa, we demonstrate that this method provides the viscous damping of the membrane domain in the lipid bilayer. When glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) -anchored and transmembrane proteins are raft-associated, their diffusion becomes independent of the type of membrane anchor and is significantly reduced compared with that of nonraft transmembrane proteins. Cholesterol depletion accelerates the diffusion of raft-associated proteins for transmembrane raft proteins to the level of transmembrane nonraft proteins and for GPI-anchored proteins even further. Raft-associated GPI-anchored proteins were never observed to dissociate from the raft within the measurement intervals of up to 10 min. The measurements agree with lipid rafts being cholesterol-stabilized complexes of 26 +/- 13 nm in size diffusing as one entity for minutes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sphingomyelin chain length influences the distribution of GPI-anchored proteins in rafts in supported lipid bilayers.Mol Membr Biol. 2007 May-Jun;24(3):233-42. doi: 10.1080/09687860601127770. Mol Membr Biol. 2007. PMID: 17520480
-
Both sphingolipids and cholesterol participate in the detergent insolubility of alkaline phosphatase, a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein, in mammalian membranes.J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 17;270(11):6254-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.11.6254. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7890763
-
Detergent-insoluble GPI-anchored proteins are apically sorted in fischer rat thyroid cells, but interference with cholesterol or sphingolipids differentially affects detergent insolubility and apical sorting.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Feb;11(2):531-42. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.2.531. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10679012 Free PMC article.
-
The state of lipid rafts: from model membranes to cells.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003;32:257-83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.142439. Epub 2003 Jan 16. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003. PMID: 12543707 Review.
-
Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle.Science. 2010 Jan 1;327(5961):46-50. doi: 10.1126/science.1174621. Science. 2010. PMID: 20044567 Review.
Cited by
-
Microtubule motors power plasma membrane tubulation in clathrin-independent endocytosis.Traffic. 2015 Jun;16(6):572-90. doi: 10.1111/tra.12269. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Traffic. 2015. PMID: 25690058 Free PMC article.
-
JAK2-V617F-mediated signalling is dependent on lipid rafts and statins inhibit JAK2-V617F-dependent cell growth.Br J Haematol. 2013 Jan;160(2):177-87. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12103. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Br J Haematol. 2013. PMID: 23157224 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and application of a new optical probe for membrane lipid domains.Biophys J. 2006 Apr 1;90(7):2563-75. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.072884. Epub 2006 Jan 13. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16415047 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the topography of cellular membrane domains by combined atomic force microscopy/fluorescence imaging.Biophys J. 2006 Apr 1;90(7):2404-13. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.073692. Epub 2006 Jan 13. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16415053 Free PMC article.
-
Phase behavior and nanoscale structure of phospholipid membranes incorporated with acylated C14-peptides.Biophys J. 2005 Oct;89(4):2494-503. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.060756. Epub 2005 Aug 12. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 16100273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartlett M.S. On the theoretical specification of sampling properties of autocorrelated time series. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1946;8:B27–B34.
-
- Blasie J.K., Worthington C.R. Molecular localization of frog retinal receptor photopigment by electron microscopy and low-angle X-ray diffraction. J. Mol. Biol. 1969;39:407–416. - PubMed
-
- Brown D.A., Rose J.K. Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins to glycolipid-enriched membrane subdomains during transport to the apical cell surface. Cell. 1992;68:533–544. - PubMed
-
- Brown D.A., London E. Structure of detergent-resistant membrane domainsdoes phase separation occur in biological membranes? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 1997;240:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Brown D.A., London E. Functions of lipid rafts in biological membranes. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1998;14:111–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

