CD40-CD40 ligand (CD154) engagement is required but may not be sufficient for human T helper 1 cell induction of interleukin-2- or interleukin-15-driven, contact-dependent, interleukin-1beta production by monocytes
- PMID: 10692048
- PMCID: PMC2327150
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00948.x
CD40-CD40 ligand (CD154) engagement is required but may not be sufficient for human T helper 1 cell induction of interleukin-2- or interleukin-15-driven, contact-dependent, interleukin-1beta production by monocytes
Abstract
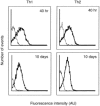
To investigate whether antigen-independent, interleukin-2 (IL-2) or IL-15 activation of polarized T helper (Th) cells would result in contact-dependent activation of monocytes, living Th1 and Th2 cell clones were co-cultured with THP-1 cells or fresh peripheral blood monocytes. Under these conditions IL-1beta production was induced almost exclusively by Th1 cells and was dependent on the presence and dose of IL-2 or IL-15, and on cell-cell contact, as demonstrated by double-chamber cultures. Low levels of IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) were induced by Th1 and higher levels by Th2 cells. IL-10 production was similar in Th1/monocyte and Th2/monocyte co-cultures, thus arguing against preferential down-regulation of IL-1beta production by anti-inflammatory IL-10 in Th2 co-cultures. In addition, IL-4 and IL-10 neutralization did not result in enhanced IL-1beta production in Th2/monocyte co-cultures. Preferential expression on Th1 cells of CD11b correlated with their capacity to induce IL-1beta production by THP-1 cells in the presence of IL-2 or IL-15, but anti-CD11b monoclonal antibody could not inhibit this activity. Blockade of the CD40-CD40 ligand interaction resulted in inhibition of IL-1beta-inducing capacity while IL-1Ra induction was unaffected, a result previously unknown. This differential effect indicates the selective relevance of CD40-CD40 ligand engagement in inflammatory monocyte responses upon activation by T cells. CD40 ligand expression levels did not differ in Th1 and Th2 cell clones, thus indicating that additional, unidentified molecule(s) preferentially expressed by Th1 cells are involved in their IL-1beta induction capacity.
Figures

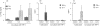

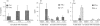
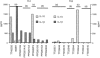

Similar articles
-
Human Th1 cells preferentially induce interleukin (IL)-1beta while Th2 cells induce IL-1 receptor antagonist production upon cell/cell contact with monocytes.Eur J Immunol. 1997 Jan;27(1):171-7. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830270125. Eur J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9022014
-
Th1 cells induce and Th2 inhibit antigen-dependent IL-12 secretion by dendritic cells.Eur J Immunol. 1998 Jun;28(6):2003-16. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199806)28:06<2003::AID-IMMU2003>3.0.CO;2-S. Eur J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9645382
-
Role of the CD40-CD40 ligand interaction in CD4+ T cell contact-dependent activation of monocyte interleukin-1 synthesis.Eur J Immunol. 1994 Dec;24(12):3148-54. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241235. Eur J Immunol. 1994. PMID: 7528671
-
The role of CD40/CD154 interactions in the priming, differentiation, and effector function of helper and cytotoxic T cells.J Leukoc Biol. 1998 Apr;63(4):418-28. doi: 10.1002/jlb.63.4.418. J Leukoc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9544571 Review.
-
CD40 ligand-dependent signaling of bovine B lymphocyte development and differentiation.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1998 May 15;63(1-2):15-20. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(98)00077-4. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1998. PMID: 9656436 Review.
Cited by
-
Differences of the Structure of Immune Regulatory Cell Populations between Cellular Material from Sonographically Detected Focal Thyroid Lesions and Peripheral Blood in Humans.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 20;20(4):918. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040918. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30791564 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of tumour necrosis factor and IL-17 production by leflunomide involves the JAK/STAT pathway.Ann Rheum Dis. 2009 Oct;68(10):1644-50. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.096743. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009. PMID: 18957484 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuating effect of pretreatment with Yiqifumai on lipopolysaccharide-induced intestine injury and survival rate in rat.J Inflamm (Lond). 2011 May 2;8:10. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-8-10. J Inflamm (Lond). 2011. PMID: 21535877 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble CD40 Ligand in Sera of Subjects Exposed to Leishmania infantum Infection Reduces the Parasite Load in Macrophages.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 21;10(10):e0141265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141265. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26488744 Free PMC article.
-
Role of interleukin 15 and interleukin 18 in inflammatory response.Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Nov;61 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):ii100-2. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.suppl_2.ii100. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002. PMID: 12379638 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burger D, Dayer JM. Interactions between T cell plasma membranes and monocytes. In: Miossec P, van den Berg WB, Firestein GS, editors. T Cells in Arthritis. Basel: Birkhäuser Verlag; 1998. p. 111.
-
- Del Prete G, De Carli M, Lammel RM, et al. Th1 and Th2 T-helper cells exert opposite regulatory effects on procoagulant activity and tissue factor production by human monocytes. Blood. 1995;86:250. - PubMed
-
- Chizzolini C, Chicheportiche R, Burger D, Dayer J-M. Human Th1 cells preferentially induce interleukin (IL) -1β while Th2 cells induce IL-1 receptor antagonist production upon cell/cell contact with monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1997;27:171. - PubMed
-
- Sebbag M, Parry SL, Brennan FM, Feldmann M. Cytokine stimulation of T lymphocytes regulates their capacity to induce monocyte production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, but not interleukin-10: possible relevance to pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1997;27:624. - PubMed
-
- McInnes IB, Leung BP, Sturrock RD, Field M, Liew FY. Interleukin-15 mediates T cell-dependent regulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med. 1997;3:189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

