Endogenous oxidative DNA base modifications analysed with repair enzymes and GC/MS technique
- PMID: 10684948
- PMCID: PMC111057
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/28.6.e16
Endogenous oxidative DNA base modifications analysed with repair enzymes and GC/MS technique
Abstract
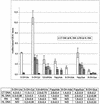
GC/MS technique was used to identify endogenous levels of oxidatively modified DNA bases. To avoid possible artefact formation we used Fpg and Endo III endonucleases instead of acid hydrolysis to liberate the base products from unmodified DNA samples. Several different DNA preparations were used: (i) commercial calf thymus DNA, (ii) DNA isolated from rat liver, (iii) DNA isolated from human lymphocytes and (iv) nuclei isolated from rat liver. In all DNA samples used in our assays the most efficiently removed bases by Fpg protein are FapyG and FapyA although 8-oxoG was also detected in all preparations. The amount of 8-oxoG in human lymphocytes and in rat liver DNA was 3 and 2 per 10(7)bases, respectively. It is reasonable to postulate that the presented method is one of the techniques which should be used to reveal the enigma of endogenous, oxidative DNA damage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DNA oxidation products determined with repair endonucleases in mammalian cells: types, basal levels and influence of cell proliferation.Free Radic Res. 1998 Dec;29(6):585-94. doi: 10.1080/10715769800300631. Free Radic Res. 1998. PMID: 10098463
-
Substrate specificity of the Escherichia coli Fpg protein (formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase): excision of purine lesions in DNA produced by ionizing radiation or photosensitization.Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):106-10. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a016. Biochemistry. 1992. PMID: 1731864
-
Oxidative base damage to DNA: specificity of base excision repair enzymes.Mutat Res. 2000 Apr;462(2-3):121-8. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5742(00)00022-3. Mutat Res. 2000. PMID: 10767623 Review.
-
DNA substrates containing defined oxidative base lesions and their application to study substrate specificities of base excision repair enzymes.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001;68:207-21. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(01)68101-7. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11554298 Review.
-
Recognition and kinetics for excision of a base lesion within clustered DNA damage by the Escherichia coli proteins Fpg and Nth.Biochemistry. 2001 May 15;40(19):5738-46. doi: 10.1021/bi002605d. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11341839
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of a human DNA glycosylase for repair of modified bases in oxidatively damaged DNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Mar 19;99(6):3523-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.062053799. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11904416 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter dependent RNA polymerase II bypass of the epimerizable DNA lesion, Fapy•dG and 8-Oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jul 22;52(13):7437-7446. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae529. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38908029 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanism of RNA Polymerase II Transcriptional Mutagenesis by the Epimerizable DNA Lesion, Fapy·dG.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Mar 6;146(9):6274-6282. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c14476. Epub 2024 Feb 23. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38393762
-
Oxidative damage DNA: 8-oxoGua and 8-oxodG as molecular markers of cancer.Med Sci Monit. 2011 Jun;17(6):CR329-33. doi: 10.12659/msm.881805. Med Sci Monit. 2011. PMID: 21629187 Free PMC article.
-
The DNA repair function of CUX1 contributes to radioresistance.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 21;8(12):19021-19038. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14875. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28147323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feig D.I., Reid,T.M. and Loeb,L.A. (1994) Cancer Res., 54, 1890–1894. - PubMed
-
- Floyd R.A. (1990) Carcinogenesis, 11, 1447–1450. - PubMed
-
- Olinski R., Zastawny,T.H., Foksinski,M., Barecki,A. and Dizdaroglu,M. (1995) Free Rad. Biol. Med., 4, 807–813. - PubMed
-
- Olinski R., Jaruga,P., Foksinski,M., Bialkowski,K. and Tujakowski,J. (1997) Mol. Pharmacol., 52, 882–885. - PubMed
-
- Cadet J., D’Ham,C., Douki,T., Pouget,J.-P., Ravant,J.-L. and Sauvagio,S. (1998) Free Rad. Res., 29, 541–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous