Combined effect of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and ionizing radiation in breast cancer therapy
- PMID: 10677530
- PMCID: PMC26508
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.030545097
Combined effect of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and ionizing radiation in breast cancer therapy
Abstract
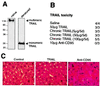
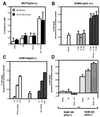
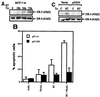
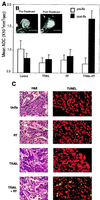
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a potent endogenous activator of the cell death pathway and functions by activating the cell surface death receptors 4 and 5 (DR4 and DR5). TRAIL is nontoxic in vivo and preferentially kills neoplastically transformed cells over normal cells by an undefined mechanism. Radiotherapy is a common treatment for breast cancer as well as many other cancers. Here we demonstrate that ionizing radiation can sensitize breast carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. This synergistic effect is p53-dependent and may be the result of radiation-induced up-regulation of the TRAIL-receptor DR5. Importantly, TRAIL and ionizing radiation have a synergistic effect in the regression of established breast cancer xenografts. Changes in tumor cellularity and extracellular space were monitored in vivo by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (diffusion MRI), a noninvasive technique to produce quantitative images of the apparent mobility of water within a tissue. Increased water mobility was observed in combined TRAIL- and radiation-treated tumors but not in tumors treated with TRAIL or radiation alone. Histological analysis confirmed the loss of cellularity and increased numbers of apoptotic cells in TRAIL- and radiation-treated tumors. Taken together, our results provide support for combining radiation with TRAIL to improve tumor eradication and suggest that efficacy of apoptosis-inducing cancer therapies may be monitored noninvasively, using diffusion MRI.
Figures
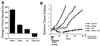
Similar articles
-
The sequential treatment with ionizing radiation followed by TRAIL/Apo-2L reduces tumor growth and induces apoptosis of breast tumor xenografts in nude mice.Int J Oncol. 2004 May;24(5):1133-40. Int J Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15067334
-
Synergistic interactions of chemotherapeutic drugs and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand/Apo-2 ligand on apoptosis and on regression of breast carcinoma in vivo.Cancer Res. 2003 Sep 1;63(17):5390-400. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14500373
-
p53-dependent and -independent regulation of the death receptor KILLER/DR5 gene expression in response to genotoxic stress and tumor necrosis factor alpha.Cancer Res. 1998 Apr 15;58(8):1593-8. Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 9563466
-
Modulation of death receptor pathways in oncology.Drugs Today (Barc). 2003;39 Suppl C:95-109. Drugs Today (Barc). 2003. PMID: 14988748 Review.
-
[Death inducing ligands in combination with ionizing radiation: objective and current knowledge].Strahlenther Onkol. 2003 Mar;179(3):141-51. doi: 10.1007/s00066-003-1047-7. Strahlenther Onkol. 2003. PMID: 12627256 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Drug Development.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1310:187-209. doi: 10.1007/978-981-33-6064-8_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33834438
-
TPL2 kinase is a suppressor of lung carcinogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Apr 16;110(16):E1470-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215938110. Epub 2013 Mar 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23533274 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting TRAIL Death Receptors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers: Challenges and Strategies for Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2022 Nov 22;11(23):3717. doi: 10.3390/cells11233717. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36496977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
2-Deoxy-D-glucose enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells through XBP-1-mediated up-regulation of TRAIL-R2.Mol Cancer. 2009 Dec 14;8:122. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-8-122. Mol Cancer. 2009. PMID: 20003459 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated expression of Fau and MELK is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(4):R60. doi: 10.1186/bcr2350. Epub 2009 Aug 11. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19671159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hortobagyi G N. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:974–984. - PubMed
-
- Hall E. Radiobiology for the Radiologist. Philadelphia: Lippincott; 1988.
-
- Steele G G, McMillan T J, Peacock J H. Int J Radiat Biol. 1998;56:525–537. - PubMed
-
- Bradford J S. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1991;21:1457–1469. - PubMed
-
- Nagata S. Cell. 1997;88:355–365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

