A functional genetic screen identifies regions at the C-terminal tail and death-domain of death-associated protein kinase that are critical for its proapoptotic activity
- PMID: 10677501
- PMCID: PMC26476
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.020519497
A functional genetic screen identifies regions at the C-terminal tail and death-domain of death-associated protein kinase that are critical for its proapoptotic activity
Abstract
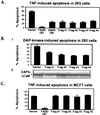
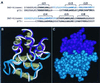
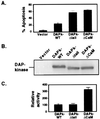
Death-associated protein kinase (DAP-kinase) is a Ca(+2)/calmodulin-regulated serine/threonine kinase with a multidomain structure that participates in apoptosis induced by a variety of signals. To identify regions in this protein that are critical for its proapoptotic activity, we performed a genetic screen on the basis of functional selection of short DAP-kinase-derived fragments that could protect cells from apoptosis by acting in a dominant-negative manner. We expressed a library of randomly fragmented DAP-kinase cDNA in HeLa cells and treated these cells with IFN-gamma to induce apoptosis. Functional cDNA fragments were recovered from cells that survived the selection, and those in the sense orientation were examined further in a secondary screen for their ability to protect cells from DAP-kinase-dependent tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis. We isolated four biologically active peptides that mapped to the ankyrin repeats, the "linker" region, the death domain, and the C-terminal tail of DAP-kinase. Molecular modeling of the complete death domain provided a structural basis for the function of the death-domain-derived fragment by suggesting that the protective fragment constitutes a distinct substructure. The last fragment, spanning the C-terminal serine-rich tail, defined a new regulatory region. Ectopic expression of the tail peptide (17 amino acids) inhibited the function of DAP-kinase, whereas removal of this region from the complete protein caused enhancement of the killing activity, indicating that the C-terminal tail normally plays a negative regulatory role. Altogether, this unbiased screen highlighted functionally important regions in the protein and revealed an additional level of regulation of DAP-kinase apoptotic function that does not affect the catalytic activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DAP-kinase: from functional gene cloning to establishment of its role in apoptosis and cancer.Cell Death Differ. 2001 Jan;8(1):6-15. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400794. Cell Death Differ. 2001. PMID: 11313698 Review.
-
Death associated proteins (DAPs): from gene identification to the analysis of their apoptotic and tumor suppressive functions.Oncogene. 1998 Dec 24;17(25):3331-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202588. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9916995 Review.
-
DAP-kinase is a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent, cytoskeletal-associated protein kinase, with cell death-inducing functions that depend on its catalytic activity.EMBO J. 1997 Mar 3;16(5):998-1008. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.5.998. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9118961 Free PMC article.
-
DAP kinase links the control of apoptosis to metastasis.Nature. 1997 Nov 13;390(6656):180-4. doi: 10.1038/36599. Nature. 1997. PMID: 9367156
-
Autophosphorylation restrains the apoptotic activity of DRP-1 kinase by controlling dimerization and calmodulin binding.EMBO J. 2001 Mar 1;20(5):1099-113. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.5.1099. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11230133 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
DAPK1-p53 interaction converges necrotic and apoptotic pathways of ischemic neuronal death.J Neurosci. 2014 May 7;34(19):6546-56. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5119-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24806680 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of TNNI3K, a cardiac-specific MAPKKK, promotes cardiac dysfunction.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013 Jan;54:101-11. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.10.004. Epub 2012 Oct 16. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23085512 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a new form of death-associated protein kinase that promotes cell survival.J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 26;276(43):39667-78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101886200. Epub 2001 Aug 2. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11485996 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional signals transduced by DAPK-ERK interaction promote the apoptotic effect of DAPK.EMBO J. 2005 Jan 26;24(2):294-304. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600510. Epub 2004 Dec 16. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 15616583 Free PMC article.
-
Par-4 is an essential downstream target of DAP-like kinase (Dlk) in Dlk/Par-4-mediated apoptosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Sep;20(18):4010-20. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-02-0173. Epub 2009 Jul 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19625447 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

