The Drosophila caspase DRONC is regulated by DIAP1
- PMID: 10675329
- PMCID: PMC305598
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.4.598
The Drosophila caspase DRONC is regulated by DIAP1
Abstract
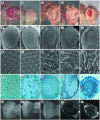
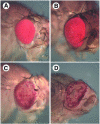
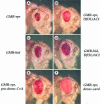
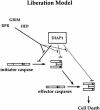
We have isolated the recently identified Drosophila caspase DRONC through its interaction with the effector caspase drICE. Ectopic expression of DRONC induces cell death in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, mammalian fibroblasts and the developing Drosophila eye. The caspase inhibitor p35 fails to rescue DRONC-induced cell death in vivo and is not cleaved by DRONC in vitro, making DRONC the first identified p35-resistant caspase. The DRONC pro-domain interacts with Drosphila inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1 (DIAP1), and co-expression of DIAP1 in the developing Drosophila eye completely reverts the eye ablation phenotype induced by pro-DRONC expression. In contrast, DIAP1 fails to rescue eye ablation induced by DRONC lacking the pro-domain, indicating that interaction of DIAP1 with the pro-domain of DRONC is required for suppression of DRONC-mediated cell death. Heterozygosity at the diap1 locus enhances the pro-DRONC eye phenotype, consistent with a role for endogenous DIAP1 in suppression of DRONC activation. Both heterozygosity at the dronc locus and expression of dominant-negative DRONC mutants suppress the eye phenotype caused by reaper (RPR) and head involution defective (HID), consistent with the idea that DRONC functions in the RPR and HID pathway.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Systematic in vivo RNAi analysis of putative components of the Drosophila cell death machinery.Cell Death Differ. 2006 Oct;13(10):1663-74. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401868. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Cell Death Differ. 2006. PMID: 16485033
-
The CARD-carrying caspase Dronc is essential for most, but not all, developmental cell death in Drosophila.Development. 2005 May;132(9):2125-34. doi: 10.1242/dev.01790. Epub 2005 Mar 30. Development. 2005. PMID: 15800001 Free PMC article.
-
Jafrac2 is an IAP antagonist that promotes cell death by liberating Dronc from DIAP1.EMBO J. 2002 Oct 1;21(19):5118-29. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf530. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 12356728 Free PMC article.
-
An emerging blueprint for apoptosis in Drosophila.Trends Cell Biol. 1999 Nov;9(11):435-40. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(99)01646-3. Trends Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10511707 Review.
-
Drosophila caspases as guardians of host-microbe interactions.Cell Death Differ. 2023 Feb;30(2):227-236. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01038-4. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Cell Death Differ. 2023. PMID: 35810247 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CasExpress reveals widespread and diverse patterns of cell survival of caspase-3 activation during development in vivo.Elife. 2016 Apr 8;5:e10936. doi: 10.7554/eLife.10936. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27058168 Free PMC article.
-
Ecdysone-induced expression of the caspase DRONC during hormone-dependent programmed cell death in Drosophila is regulated by Broad-Complex.J Cell Biol. 2002 Jun 10;157(6):985-95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200201034. Epub 2002 Jun 3. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12045184 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic regulation of Drosophila apoptosis through inhibitory phosphorylation of Dronc.EMBO J. 2010 Sep 15;29(18):3196-207. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.191. Epub 2010 Aug 10. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20700104 Free PMC article.
-
The effector caspases drICE and dcp-1 have partially overlapping functions in the apoptotic pathway in Drosophila.Cell Death Differ. 2006 Oct;13(10):1697-706. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401920. Epub 2006 Apr 28. Cell Death Differ. 2006. PMID: 16645642 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved metabolic energy production pathways govern Eiger/TNF-induced nonapoptotic cell death.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Nov 22;108(47):18977-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1103242108. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 22065747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrams J.M., White, K., Fessler, L.I. and Steller, H. (1993) Programmed cell death during Drosophila embryogenesis. Development, 117, 29–43. - PubMed
-
- Alnemri E.S. (1997) Mammalian cell death proteases: a family of highly conserved aspartate specific cysteine proteases. J. Cell. Biochem., 64, 33–42. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M. (1989) Drosophila: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
-
- Basler K., Christen, B. and Hafen, E. (1991) Ligand-independent activation of the sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase changes the fate of cells in the developing Drosophila eye. Cell, 64, 1069–1081. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

