Poly(A)-binding protein I of Leishmania: functional analysis and localisation in trypanosomatid parasites
- PMID: 10666465
- PMCID: PMC102622
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/28.5.1211
Poly(A)-binding protein I of Leishmania: functional analysis and localisation in trypanosomatid parasites
Abstract
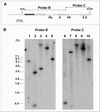
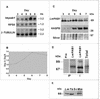
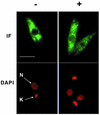
Regulation of gene expression in trypanosomatid parasites is predominantly post-transcriptional. Primary transcripts are trans-spliced and polyadenylated to generate mature mRNAs and transcript stability is a major factor controlling stage-specific gene expression. Degenerate PCR has been used to clone the gene encoding the Leishmania homologue of poly(A)-binding protein (Lm PAB1), as an approach to the identification of trans-acting factors involved in this atypical mode of eukaryotic gene expression. lmpab1 is a single copy gene encoding a 63 kDa protein which shares major structural features but only 35-40% amino acid identity with other PAB1 sequences, including those of other trypanosomatids. Lm PAB1 is expressed at constant levels during parasite differentiation and is phosphorylated in vivo. It is localised predominantly in the cytoplasm but inhibition of transcription with actinomycin D also reveals diffuse localisation in the nucleus. Lm PAB1 binds poly(A) with high specificity and affinity but fails to complement a null mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. These properties are indicative of functional divergence in vivo.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of novel proteins and mRNAs differentially bound to the Leishmania Poly(A) Binding Proteins reveals a direct association between PABP1, the RNA-binding protein RBP23 and mRNAs encoding ribosomal proteins.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Oct 27;15(10):e0009899. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009899. eCollection 2021 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34705820 Free PMC article.
-
The unique Leishmania EIF4E4 N-terminus is a target for multiple phosphorylation events and participates in critical interactions required for translation initiation.RNA Biol. 2015;12(11):1209-21. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1086865. Epub 2015 Sep 4. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26338184 Free PMC article.
-
A novel form of actin in Leishmania: molecular characterisation, subcellular localisation and association with subpellicular microtubules.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2004 Mar;134(1):105-14. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2003.11.008. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2004. PMID: 14747148
-
Biogenesis, maintenance and dynamics of glycosomes in trypanosomatid parasites.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1863(5):1038-48. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.09.015. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26384872 Review.
-
Chitin binding protein as a possible RNA binding protein in Leishmania parasites.Pathog Dis. 2020 Feb 1;78(1):ftaa007. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftaa007. Pathog Dis. 2020. PMID: 32053190 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolutionary changes in the Leishmania eIF4F complex involve variations in the eIF4E-eIF4G interactions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jun;37(10):3243-53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp190. Epub 2009 Mar 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19321500 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation and interactions associated with the control of the Leishmania Poly-A Binding Protein 1 (PABP1) function during translation initiation.RNA Biol. 2018;15(6):739-755. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2018.1445958. Epub 2018 Mar 23. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 29569995 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Functional Characterization of ssDNA Aptamers that Specifically Bind Leishmania infantum PABP.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 12;10(10):e0140048. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140048. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26457419 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of a poly(A) binding protein and two proteins with cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation in Crithidia fasciculata mRNA cycling sequence binding protein II.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Oct;3(5):1185-97. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.5.1185-1197.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 15470247 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that poly(A) binding protein has an evolutionarily conserved function in facilitating mRNA biogenesis and export.RNA. 2003 Dec;9(12):1476-90. doi: 10.1261/rna.5128903. RNA. 2003. PMID: 14624004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ullu E., Tschudi,C. and Gunzl,A. (1996) In Smith,D.F. and Parsons,M. (eds), Molecular Biology of Parasitic Protozoa. IRL Press, Oxford, UK, pp. 115–133.
-
- LeBowitz J.H., Smith,H.Q., Rusche,L. and Beverley,S.M. (1993) Genes Dev., 7, 996–1007. - PubMed
-
- Matthews K.R., Tschudi,C. and Ullu,E. (1994) Genes Dev., 15, 491–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

