Epstein-Barr virus suppresses a G(2)/M checkpoint activated by genotoxins
- PMID: 10648620
- PMCID: PMC85280
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.4.1344-1360.2000
Epstein-Barr virus suppresses a G(2)/M checkpoint activated by genotoxins
Abstract
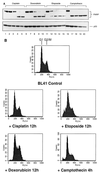
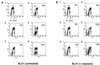
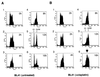
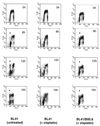
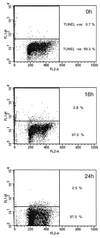
Several Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-negative Burkitt lymphoma-derived cell lines (for example, BL41 and Ramos) are extremely sensitive to genotoxic drugs despite being functionally null for the tumor suppressor p53. They rapidly undergo apoptosis, largely from G(2)/M of the cell cycle. 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine labeling experiments showed that although the treated cells can pass through S phase, they are unable to complete cell division, suggesting that a G(2)/M checkpoint is activated. Surprisingly, latent infection of these genotoxin-sensitive cells with EBV protects them from both apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, allowing them to complete the division cycle. However, a comparison with EBV-immortalized B-lymphoblastoid cell lines (which have functional p53) showed that EBV does not block apoptosis per se but rather abrogates the activation of, or signalling from, the checkpoint in G(2)/M. Furthermore, analyses of BL41 and Ramos cells latently infected with P3HR1 mutant virus, which expresses only a subset of the latent viral genes, showed that LMP-1, the main antiapoptotic latent protein encoded by EBV, is not involved in the protection afforded here by viral infection. This conclusion was confirmed by analysis of clones of BL41 stably expressing LMP-1 from a transfected plasmid, which respond like the parental cell line. Although steady-state levels of Bcl-2 and related proteins varied between BL41 lines and clones, they did not change significantly during apoptosis, nor was the level of any of these anti- or proapoptotic proteins predictive of the outcome of treatment. We have demonstrated that a subset of EBV latent gene products can inactivate a cell cycle checkpoint for monitoring the fidelity and timing of cell division and therefore genomic integrity. This is likely to be important in EBV-associated growth transformation of B cells and perhaps tumorigenesis. Furthermore, this study suggests that EBV will be a unique tool for investigating the intimate relationship between cell cycle regulation and apoptosis.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 oncogene deletions: correlations with malignancy in Epstein-Barr virus--associated lymphoproliferative disorders and malignant lymphomas.Blood. 1996 Jul 1;88(1):242-51. Blood. 1996. PMID: 8704180
-
Epstein-barr virus-induced resistance to drugs that activate the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint in Burkitt's lymphoma cells.J Virol. 2007 Jan;81(1):248-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01096-06. Epub 2006 Oct 11. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17035311 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression on the apoptosis-inducing effects of cortisone and 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine (2-CDA) in B-cell lines.Cytokines Mol Ther. 1996 Mar;2(1):21-8. Cytokines Mol Ther. 1996. PMID: 9384686
-
EBV and Apoptosis: The Viral Master Regulator of Cell Fate?Viruses. 2017 Nov 13;9(11):339. doi: 10.3390/v9110339. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 29137176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt's lymphoma.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001;258:141-51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56515-1_9. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11443859 Review.
Cited by
-
At a crossroads: human DNA tumor viruses and the host DNA damage response.Future Virol. 2011 Jul;6(7):813-830. doi: 10.2217/fvl.11.55. Future Virol. 2011. PMID: 21927617 Free PMC article.
-
EBV and human microRNAs co-target oncogenic and apoptotic viral and human genes during latency.EMBO J. 2012 May 2;31(9):2207-21. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.63. Epub 2012 Mar 30. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22473208 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2) gene deletion is consistently linked with EBNA3A, -3B, and -3C expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells and with increased resistance to apoptosis.J Virol. 2005 Aug;79(16):10709-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.16.10709-10717.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16051863 Free PMC article.
-
Viral-Targeted Strategies Against EBV-Associated Lymphoproliferative Diseases.Front Oncol. 2019 Feb 26;9:81. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00081. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30873380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular virology of Epstein-Barr virus.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2001 Apr 29;356(1408):437-59. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2000.0781. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2001. PMID: 11313004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
