Cationic microparticles: A potent delivery system for DNA vaccines
- PMID: 10639162
- PMCID: PMC15413
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.2.811
Cationic microparticles: A potent delivery system for DNA vaccines
Abstract
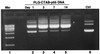
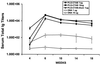
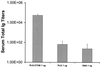
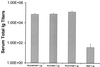
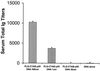
An approach involving the preparation of biodegradable microparticles with a cationic surface was developed to improve the delivery of adsorbed DNA into antigen-presenting cells after i.m. injection. The microparticles released intact and functional DNA over 2 weeks in vitro. In addition, the microparticles induced higher levels of marker gene expression in vivo. After i.m. immunization, the microparticles induced significantly enhanced serum antibody responses in comparison to naked DNA. Moreover, the level of antibodies induced by the microparticles was significantly enhanced by the addition of a vaccine adjuvant, aluminum phosphate. In addition, in contrast to naked DNA, the cationic microparticles induced potent cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses at a low dose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cationic microparticles are a potent delivery system for a HCV DNA vaccine.Vaccine. 2004 Dec 16;23(5):672-80. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.06.037. Vaccine. 2004. PMID: 15542189
-
Controlled release of PEI/DNA complexes from PLGA microspheres as a potent delivery system to enhance immune response to HIV vaccine DNA prime/MVA boost regime.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008 Mar;68(3):589-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2007.09.006. Epub 2007 Sep 21. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008. PMID: 17950586
-
Enhancing efficacy of HIV gag DNA vaccine by local delivery of GM-CSF in murine and macaque models.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2006 Jun;26(6):380-9. doi: 10.1089/jir.2006.26.380. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2006. PMID: 16734558 Free PMC article.
-
Polylactide-co-glycolide microparticles with surface adsorbed antigens as vaccine delivery systems.Curr Drug Deliv. 2006 Jan;3(1):115-20. doi: 10.2174/156720106775197565. Curr Drug Deliv. 2006. PMID: 16472100 Review.
-
Microparticles and nanoparticles as delivery systems for DNA vaccines.Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2003;20(2-3):103-37. doi: 10.1615/critrevtherdrugcarriersyst.v20.i23.10. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2003. PMID: 14584521 Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of broad and potent anti-human immunodeficiency virus immune responses in rhesus macaques by priming with a DNA vaccine and boosting with protein-adsorbed polylactide coglycolide microparticles.J Virol. 2003 May;77(10):6087-92. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.10.6087-6092.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12719603 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradable particles as vaccine delivery systems: size matters.AAPS J. 2013 Jan;15(1):85-94. doi: 10.1208/s12248-012-9418-6. Epub 2012 Oct 10. AAPS J. 2013. PMID: 23054976 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of three innovative bacterin vaccines against experimental infection with Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae.Vet Res. 2019 Nov 8;50(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s13567-019-0709-0. Vet Res. 2019. PMID: 31703726 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in vaccine adjuvants.Pharm Res. 2002 Jun;19(6):715-28. doi: 10.1023/a:1016104910582. Pharm Res. 2002. PMID: 12134940 Review.
-
Vaccines: all things considered.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2006 Aug;13(8):821-9. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00152-06. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16893980 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wolff J A, Malone R W, Williams P, Chong W, Acsadi G, Jani A, Felgner P L. Science. 1990;247:1465–1468. - PubMed
-
- Ulmer J B, Donnelly J J, Parker S E, Rhodes G H, Felgner P L, Dwarki V J, Gromkowski S H, Deck R R, De Witt C M, Friedman A, et al. Science. 1993;258:1745–1749. - PubMed
-
- Donnelly J J, Ulmer J B, Liu M A. Life Sci. 1997;60:163–172. - PubMed
-
- Calarota S, Bratt G, Nordlund S, Hinkula J, Leandersson A-C, Sandstrom E, Wahren B. Lancet. 1998;351:1320–1325. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

