Orphan receptor COUP-TF is required for induction of retinoic acid receptor beta, growth inhibition, and apoptosis by retinoic acid in cancer cells
- PMID: 10629053
- PMCID: PMC85213
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.3.957-970.2000
Orphan receptor COUP-TF is required for induction of retinoic acid receptor beta, growth inhibition, and apoptosis by retinoic acid in cancer cells
Abstract
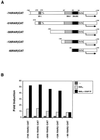
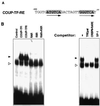
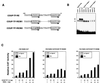
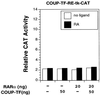
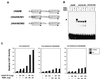
Retinoic acid receptor beta (RARbeta) plays a critical role in mediating the anticancer effects of retinoids. Expression of RARbeta is highly induced by retinoic acid (RA) through a RA response element (betaRARE) that is activated by heterodimers of RARs and retinoid X receptors (RXRs). However, RARbeta induction is often lost in cancer cells despite expression of RARs and RXRs. In this study, we provide evidence that orphan receptor COUP-TF is required for induction of RARbeta expression, growth inhibition, and apoptosis by RA in cancer cells. Expression of COUP-TF correlates with RARbeta induction in a variety of cancer cell lines. In addition, stable expression of COUP-TF in COUP-TF-negative cancer cells restores induction of RARbeta expression, growth inhibition, and apoptosis by RA, whereas inhibition of COUP-TF by expression of COUP-TF antisense RNA represses the RA effects. In a transient transfection assay, COUP-TF strongly induced transcriptional activity of the RARbeta promoter in a RA- and RARalpha-dependent manner. By mutation analysis, we demonstrate that the effect of COUP-TF requires its binding to a DR-8 element present in the RARbeta promoter. The binding of COUP-TF to the DR-8 element synergistically increases the RA-dependent RARalpha transactivation function by enhancing the interaction of RARalpha with its coactivator CREB binding protein. These results demonstrate that COUP-TF, by serving as an accessory protein for RARalpha to induce RARbeta expression, plays a critical role in regulating the anticancer activities of retinoids.
Figures
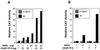

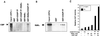
Similar articles
-
Regulation of retinoic acid-induced inhibition of AP-1 activity by orphan receptor chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter-transcription factor.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 14;277(24):21414-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M201885200. Epub 2002 Apr 4. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11934895
-
Modulation of retinoic acid sensitivity in lung cancer cells through dynamic balance of orphan receptors nur77 and COUP-TF and their heterodimerization.EMBO J. 1997 Apr 1;16(7):1656-69. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.7.1656. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9130711 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic balance between ARP-1/COUP-TFII, EAR-3/COUP-TFI, and retinoic acid receptor:retinoid X receptor heterodimers regulates Oct-3/4 expression in embryonal carcinoma cells.Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;15(2):1034-48. doi: 10.1128/MCB.15.2.1034. Mol Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7823919 Free PMC article.
-
F9 embryocarcinoma cells: a cell autonomous model to study the functional selectivity of RARs and RXRs in retinoid signaling.Histol Histopathol. 2001 Jul;16(3):909-22. doi: 10.14670/HH-16.909. Histol Histopathol. 2001. PMID: 11510982 Review.
-
Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter-transcription factors and their regulation.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996 Jan;56(1-6 Spec No):81-5. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(95)00225-1. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8603050 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of nucleolin as a COUP-TFII coactivator of retinoic acid receptor β transcription in breast cancer cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e38278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038278. Epub 2012 May 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22693611 Free PMC article.
-
Rere controls retinoic acid signalling and somite bilateral symmetry.Nature. 2010 Feb 18;463(7283):953-7. doi: 10.1038/nature08763. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20164929
-
Tumor-suppressive activity of retinoic acid receptor-beta in cancer.Cancer Lett. 2007 Aug 8;253(1):14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2006.11.019. Epub 2006 Dec 22. Cancer Lett. 2007. PMID: 17188427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic analyses of the cytotoxic effects of compound 11a, a putative synthetic agonist of photoreceptor-specific nuclear receptor (PNR), in cancer cell lines.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 16;8(9):e75198. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075198. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24066170 Free PMC article.
-
Computational analysis of mRNA expression profiling in the inner ear reveals candidate transcription factors associated with proliferation, differentiation, and deafness.Hum Genomics. 2018 Jun 22;12(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s40246-018-0161-7. Hum Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29929553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berard J, Laboune F, Mukuna M, Masse S, Kothary R, Bradley W E C. Lung tumors in mice expressing an antisense RARβ2 transgene. FASEB J. 1996;10:1091–1097. - PubMed
-
- Campbell M J, Park S, Uskokovic M R, Dawson M I, Koeffler H P. Expression of retinoic acid receptor-beta sensitizes prostate cancer cells to growth inhibition mediated by combinations of retinoids and a 19-nor hexafluoride vitamin D3 analog. Endocrinology. 1998;139:1972–1980. - PubMed
-
- Cooney A J, Tsai S Y, O'Malley B W, Tsai M-J. Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor (COUP-TF) dimers bind to different GGTCA response elements, allowing COUP-TF to repress hormonal induction of the vitamin D3, thyroid hormone, and retinoic acid receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992;12:4153–4163. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dejean A, Bougueleret L, Grzeschik K-H, Tiollais P. Hepatitis B virus DNA integration in a sequence homologous to c-erb-A and steroid receptor genes in a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1991;322:70–72. - PubMed
-
- de The H, Vivanco-Ruiz M M, Tiollais P, Stunnenberg H, Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor β gene. Nature. 1990;343:177–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
