A highly selective CC chemokine receptor (CCR)8 antagonist encoded by the poxvirus molluscum contagiosum
- PMID: 10620615
- PMCID: PMC2195798
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.191.1.171
A highly selective CC chemokine receptor (CCR)8 antagonist encoded by the poxvirus molluscum contagiosum
Abstract
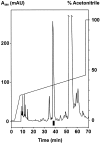
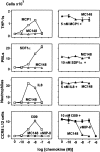
The MC148 CC chemokine from the human poxvirus molluscum contagiosum (MCV) was probed in parallel with viral macrophage inflammatory protein (vMIP)-II encoded by human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8) in 16 classified human chemokine receptors. In competition binding using radiolabeled endogenous chemokines as well as radiolabeled MC148, MC148 bound with high affinity only to CCR8. In calcium mobilization assays, MC148 had no effect on its own on any of the chemokine receptors, but in a dose-dependent manner blocked the stimulatory effect of the endogenous I-309 chemokine on CCR8 without affecting chemokine-induced signaling of any other receptor. In contrast, vMIP-II acted as an antagonist on 10 of the 16 chemokine receptors, covering all four classes: XCR, CCR, CXCR, and CX(3)CR. In chemotaxis assays, MC148 specifically blocked the I-309-induced response but, for example, not stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, or interleukin 8-induced chemotaxis. We thus concluded that the two viruses choose two different ways to block the chemokine system: HHV8 encodes the broad-spectrum chemokine antagonist vMIP-II, whereas MCV encodes a highly selective CCR8 antagonist, MC148, conceivably to interfere with monocyte invasion and dendritic cell function. Because of its pharmacological selectivity, the MC148 protein could be a useful tool in the delineation of the role played by CCR8 and its endogenous ligand, I-309.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MC148 encoded by human molluscum contagiosum poxvirus is an antagonist for human but not murine CCR8.J Leukoc Biol. 2001 Aug;70(2):277-82. J Leukoc Biol. 2001. PMID: 11493620
-
The herpesvirus 8-encoded chemokine vMIP-II, but not the poxvirus-encoded chemokine MC148, inhibits the CCR10 receptor.Eur J Immunol. 2001 Apr;31(4):1217-20. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200104)31:4<1217::aid-immu1217>3.0.co;2-s. Eur J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11298347
-
Broad spectrum chemokine antagonistic activity of a human poxvirus chemokine homolog.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 May 26;95(11):6403-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6403. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9600978 Free PMC article.
-
Virally encoded chemokines and chemokine receptors in the role of viral infections.Contrib Microbiol. 2003;10:232-52. doi: 10.1159/000068138. Contrib Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12530329 Review.
-
vCCL2/vMIP-II, the viral master KEYmokine.J Leukoc Biol. 2016 Jun;99(6):893-900. doi: 10.1189/jlb.2MR0815-383R. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Leukoc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26701133 Review.
Cited by
-
The chemokine receptor CCR5: multi-faceted hook for HIV-1.Retrovirology. 2024 Jan 23;21(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12977-024-00634-1. Retrovirology. 2024. PMID: 38263120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The non-ELR CXC chemokine encoded by human cytomegalovirus UL146 genotype 5 contains a C-terminal β-hairpin and induces neutrophil migration as a selective CXCR2 agonist.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Mar 10;18(3):e1010355. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010355. eCollection 2022 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35271688 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular machinations: chemokine signals in host-pathogen interactions.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001 Oct;14(4):821-35, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/CMR.14.4.821-835.2001. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11585787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role for the conserved N-terminal cysteines in the anti-chemokine activities by the chemokine-like protein MC148R1 encoded by Molluscum contagiosum virus.Virology. 2011 Sep 1;417(2):449-56. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.07.001. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Virology. 2011. PMID: 21802105 Free PMC article.
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. [corrected]. LXXXIX. Update on the extended family of chemokine receptors and introducing a new nomenclature for atypical chemokine receptors.Pharmacol Rev. 2013 Nov 11;66(1):1-79. doi: 10.1124/pr.113.007724. Print 2014. Pharmacol Rev. 2013. PMID: 24218476 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Viac J., Chardonnet Y. Immunocompetent cells and epithelial cell modifications in molluscum contagiosum. J. Cutan. Pathol. 1990;17:202–205 . - PubMed
-
- Heng M.C., Steuer M.E., Levy A., McMahon S., Richman M., Allen S.G., Blackhart B. Lack of host cellular immune response in eruptive molluscum contagiosum. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 1989;11:248–254 . - PubMed
-
- Bhawan J., Dayal Y., Bhan A.K. Langerhans cells in molluscum contagiosum, verruca vulgaris, plantar wart, and condyloma acuminatum. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1986;15:645–649 . - PubMed
-
- Senkevich T.G., Bugert J.J., Sisler J.R., Koonin E.V., Darai G., Moss B. Genome sequence of a human tumorigenic poxvirusprediction of specific host response-evasion genes. Science. 1996;273:813–816 . - PubMed
-
- Baggiolini M. Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature. 1998;392:565–568 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

