B7 costimulation is critical for antibody class switching and CD8(+) cytotoxic T-lymphocyte generation in the host response to vesicular stomatitis virus
- PMID: 10590107
- PMCID: PMC111529
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.1.203-208.2000
B7 costimulation is critical for antibody class switching and CD8(+) cytotoxic T-lymphocyte generation in the host response to vesicular stomatitis virus
Abstract
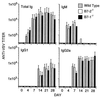
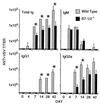
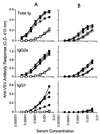
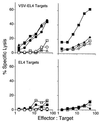
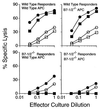
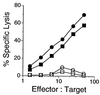
Antibody and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) responses have critical roles in eliminating many viral infections. In addition to stimulation of the T-cell receptor, T cells require costimulatory signals to respond optimally. We evaluated the role of B7 costimulatory molecules (B7-1 and B7-2) in the immune response to viral infection using vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) and mice lacking either B7-1 or B7-2 or both molecules. Mice lacking both B7-1 and B7-2 had essentially no anti-VSV immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) response, decreased IgG2a responses, and normal IgM responses, while mice lacking either B7-1 or B7-2 had unaltered anti-VSV antibody responses compared to wild-type mice. Depletion of CD4(+) cells further reduced the IgG2a response in mice lacking both B7 molecules, suggesting that CD4(-) cells may supply help for IgG2a in the absence of B7 costimulation. The absence of both B7 molecules profoundly reduced generation of both primary and secondary VSV-specific class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-restricted CTL, whereas VSV-specific CTL responses in mice lacking either B7-1 or B7-2 were similar to those of wild-type animals. Class I MHC-restricted CTL in wild-type mice were not dependent on CD4(+) cells, suggesting that the failure of CTL in the absence of B7s is due to a lack of B7 costimulation directly to the CD8(+) CTL. These data demonstrate that B7-1 and B7-2 have critical, overlapping functions in the antibody and CTL responses to this viral infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The roles of MHC class II, CD40, and B7 costimulation in CTL induction by plasmid DNA.J Immunol. 2001 Mar 1;166(5):3061-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.5.3061. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11207256
-
Mechanism of reduced T-cell effector functions and class-switched antibody responses to herpes simplex virus type 2 in the absence of B7 costimulation.J Virol. 2003 Feb;77(4):2426-35. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.4.2426-2435.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12551980 Free PMC article.
-
Either B7 costimulation or IL-2 can elicit generation of primary alloreactive CTL.J Immunol. 2000 Sep 15;165(6):3088-93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.6.3088. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10975820
-
The role of B7 costimulation in T-cell immunity.Immunol Cell Biol. 1999 Aug;77(4):304-11. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1711.1999.00835.x. Immunol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10457196 Review.
-
Emerging mechanisms of immune regulation: the extended B7 family and regulatory T cells.Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6(5):208-14. doi: 10.1186/ar1225. Epub 2004 Aug 5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004. PMID: 15380035 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Control of memory CD8+ T cell differentiation by CD80/CD86-CD28 costimulation and restoration by IL-2 during the recall response.J Immunol. 2008 Jan 15;180(2):1148-57. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.2.1148. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18178855 Free PMC article.
-
B cell-specific expression of B7-2 is required for follicular Th cell function in response to vaccinia virus.J Immunol. 2011 May 1;186(9):5294-303. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100406. Epub 2011 Mar 25. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21441451 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking B7 and CD40 co-stimulatory molecules decreases antiviral T cell activity.Clin Exp Immunol. 2004 Feb;135(2):253-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2003.02363.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14738453 Free PMC article.
-
Differential requirements for CD80/86-CD28 costimulation in primary and memory CD4 T cell responses to vaccinia virus.Cell Immunol. 2011;266(2):130-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2010.09.008. Epub 2010 Oct 30. Cell Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21040905 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of an miR155 inhibitor by anti-CD20 single-chain antibody into B cells reduces the acetylcholine receptor-specific autoantibodies and ameliorates experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2014 May;176(2):207-21. doi: 10.1111/cei.12265. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24387321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachmann M F, Hengartner H, Zinkernagel R M. T helper cell-independent neutralizing B cell response against vesicular stomatitis virus: role of antigen patterns in B cell induction? Eur J Immunol. 1995;25:3445–3451. - PubMed
-
- Borriello F, Sethna M P, Boyd S D, Schweitzer A N, Tivol E A, Jacoby D, Strom T B, Simpson E M, Freeman G J, Sharpe A H. B7-1 and B7-2 have overlapping, critical roles in immunoglobulin class switching and germinal center formation. Immunity. 1997;6:303–313. - PubMed
-
- Borrow P, Tough D F, Eto D, Tishon A, Grewal I S, Sprent J, Flavell R A, Oldstone M B A. CD40 ligand-mediated interactions are involved in the generation of memory CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) but are not required for the maintenance of CTL memory following virus infection. J Virol. 1998;72:7440–7449. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

