Espin contains an additional actin-binding site in its N terminus and is a major actin-bundling protein of the Sertoli cell-spermatid ectoplasmic specialization junctional plaque
- PMID: 10588661
- PMCID: PMC25761
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.12.4327
Espin contains an additional actin-binding site in its N terminus and is a major actin-bundling protein of the Sertoli cell-spermatid ectoplasmic specialization junctional plaque
Abstract
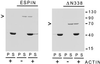
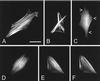
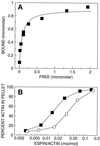
The espins are actin-binding and -bundling proteins localized to parallel actin bundles. The 837-amino-acid "espin" of Sertoli cell-spermatid junctions (ectoplasmic specializations) and the 253-amino-acid "small espin" of brush border microvilli are splice isoforms that share a C-terminal 116-amino-acid actin-bundling module but contain different N termini. To investigate the roles of espin and its extended N terminus, we examined the actin-binding and -bundling properties of espin constructs and the stoichiometry and developmental accumulation of espin within the ectoplasmic specialization. An espin construct bound to F-actin with an approximately threefold higher affinity (K(d) = approximately 70 nM) than small espin and was approximately 2.5 times more efficient at forming bundles. The increased affinity appeared to be due to an additional actin-binding site in the N terminus of espin. This additional actin-binding site bound to F-actin with a K(d) of approximately 1 microM, decorated actin stress fiber-like structures in transfected cells, and was mapped to a peptide between the two proline-rich peptides in the N terminus of espin. Espin was detected at approximately 4-5 x 10(6) copies per ectoplasmic specialization, or approximately 1 espin per 20 actin monomers and accumulated there coincident with the formation of parallel actin bundles during spermiogenesis. These results suggest that espin is a major actin-bundling protein of the Sertoli cell-spermatid ectoplasmic specialization.
Figures



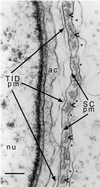
Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of espin, an actin-binding protein localized to the F-actin-rich junctional plaques of Sertoli cell ectoplasmic specializations.J Cell Sci. 1996 Jun;109 ( Pt 6):1229-39. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.6.1229. J Cell Sci. 1996. PMID: 8799813
-
Small espin: a third actin-bundling protein and potential forked protein ortholog in brush border microvilli.J Cell Biol. 1998 Oct 5;143(1):107-19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.1.107. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9763424 Free PMC article.
-
Sertoli cell ectoplasmic specializations in the seminiferous epithelium of the testosterone-suppressed adult rat.Biol Reprod. 2000 Jul;63(1):99-108. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod63.1.99. Biol Reprod. 2000. PMID: 10859247
-
Plastins regulate ectoplasmic specialization via its actin bundling activity on microfilaments in the rat testis.Asian J Androl. 2016 Sep-Oct;18(5):716-22. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.166583. Asian J Androl. 2016. PMID: 26608945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tubulobulbar complex: cytoskeletal remodeling to release spermatozoa.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2012 Apr 17;10:27. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-10-27. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22510523 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural polymorphism of the actin-espin system: a prototypical system of filaments and linkers in stereocilia.Phys Rev Lett. 2007 Feb 2;98(5):058105. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.058105. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Phys Rev Lett. 2007. PMID: 17358907 Free PMC article.
-
Inframe deletion of human ESPN is associated with deafness, vestibulopathy and vision impairment.J Med Genet. 2018 Jul;55(7):479-488. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2017-105221. Epub 2018 Mar 23. J Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 29572253 Free PMC article.
-
The deaf jerker mouse has a mutation in the gene encoding the espin actin-bundling proteins of hair cell stereocilia and lacks espins.Cell. 2000 Aug 4;102(3):377-85. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00042-8. Cell. 2000. PMID: 10975527 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted wild-type and jerker espins reveal a novel, WH2-domain-dependent way to make actin bundles in cells.J Cell Sci. 2006 Apr 15;119(Pt 8):1655-65. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02869. Epub 2006 Mar 28. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 16569662 Free PMC article.
-
Actin cross-linkers and the shape of stereocilia.Biophys J. 2010 Oct 20;99(8):2423-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.07.065. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20959082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alicea HA, Mooseker MS. Characterization of villin from the intestinal brush border of the rat, and comparative analysis with avian villin. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1988;9:60–72. - PubMed
-
- Bartles JR, Wierda A, Zheng L. Identification and characterization of espin, an actin-binding protein localized to the F-actin-rich junctional plaques of Sertoli cell ectoplasmic specializations. J Cell Sci. 1996;109:1229–1239. - PubMed
-
- Bryan J, Kane RE. Separation and interaction of the major components of sea urchin actin gel. J Mol Biol. 1978;125:207–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

