The yeast GRD20 gene is required for protein sorting in the trans-Golgi network/endosomal system and for polarization of the actin cytoskeleton
- PMID: 10588657
- PMCID: PMC25757
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.12.4263
The yeast GRD20 gene is required for protein sorting in the trans-Golgi network/endosomal system and for polarization of the actin cytoskeleton
Abstract
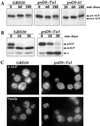
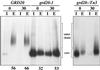
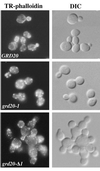
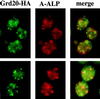
The proper localization of resident membrane proteins to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) involves mechanisms for both TGN retention and retrieval from post-TGN compartments. In this study we report identification of a new gene, GRD20, involved in protein sorting in the TGN/endosomal system of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A strain carrying a transposon insertion allele of GRD20 exhibited rapid vacuolar degradation of the resident TGN endoprotease Kex2p and aberrantly secreted approximately 50% of the soluble vacuolar hydrolase carboxypeptidase Y. The Kex2p mislocalization and carboxypeptidase Y missorting phenotypes were exhibited rapidly after loss of Grd20p function in grd20 temperature-sensitive mutant strains, indicating that Grd20p plays a direct role in these processes. Surprisingly, little if any vacuolar degradation was observed for the TGN membrane proteins A-ALP and Vps10p, underscoring a difference in trafficking patterns for these proteins compared with that of Kex2p. A grd20 null mutant strain exhibited extremely slow growth and a defect in polarization of the actin cytoskeleton, and these two phenotypes were invariably linked in a collection of randomly mutagenized grd20 alleles. GRD20 encodes a hydrophilic protein that partially associates with the TGN. The discovery of GRD20 suggests a link between the cytoskeleton and function of the yeast TGN.
Figures

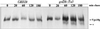
Similar articles
-
SOI1 encodes a novel, conserved protein that promotes TGN-endosomal cycling of Kex2p and other membrane proteins by modulating the function of two TGN localization signals.J Cell Biol. 1997 Oct 6;139(1):23-36. doi: 10.1083/jcb.139.1.23. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9314526 Free PMC article.
-
Retrieval of resident late-Golgi membrane proteins from the prevacuolar compartment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is dependent on the function of Grd19p.J Cell Biol. 1998 Feb 9;140(3):577-90. doi: 10.1083/jcb.140.3.577. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9456318 Free PMC article.
-
Allele-specific suppression of a defective trans-Golgi network (TGN) localization signal in Kex2p identifies three genes involved in localization of TGN transmembrane proteins.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Nov;16(11):6208-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.11.6208. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8887651 Free PMC article.
-
Bi-cycling the furin pathway: from TGN localization to pathogen activation and embryogenesis.Trends Cell Biol. 1999 Jan;9(1):28-35. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(98)01382-8. Trends Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10087614 Review.
-
Sorting in the endosomal system in yeast and animal cells.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000 Aug;12(4):457-66. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00117-4. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10873832 Review.
Cited by
-
Maintaining order: COG complex controls Golgi trafficking, processing, and sorting.FEBS Lett. 2019 Sep;593(17):2466-2487. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13570. Epub 2019 Aug 16. FEBS Lett. 2019. PMID: 31381138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Target silencing of components of the conserved oligomeric Golgi complex impairs HIV-1 replication.Virus Res. 2014 Nov 4;192:92-102. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.08.015. Epub 2014 Aug 30. Virus Res. 2014. PMID: 25179963 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydia trachomatis hijacks intra-Golgi COG complex-dependent vesicle trafficking pathway.Cell Microbiol. 2012 May;14(5):656-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01747.x. Epub 2012 Feb 15. Cell Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22233276 Free PMC article.
-
Actin acting at the Golgi.Histochem Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;140(3):347-60. doi: 10.1007/s00418-013-1115-8. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23807268 Review.
-
Role of vesicle tethering factors in the ER-Golgi membrane traffic.FEBS Lett. 2009 Dec 3;583(23):3770-83. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.083. Epub 2009 Nov 1. FEBS Lett. 2009. PMID: 19887069 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amberg D, Basart E, Botstein D. Defining protein interactions with yeast actin in vivo. Struct Biol. 1995;2:28–35. - PubMed
-
- Armatruda JF, Cannon JF, Tatchell K, Hug C, Cooper JA. Disruption of the actin cytoskeleton in yeast capping protein mutants. Nature. 1990;344:352–354. - PubMed
-
- Beck KA, Buchanan JA, Nelson WJ. Golgi membrane skeleton: identification, localization and oligomerization of a 195 kDa isoform associated with the Golgi complex. J Cell Sci. 1997;110:1239–1249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

