Platelet-derived growth factor-mediated signal transduction underlying astrocyte proliferation: site of ethanol action
- PMID: 10559409
- PMCID: PMC6782990
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-22-10014.1999
Platelet-derived growth factor-mediated signal transduction underlying astrocyte proliferation: site of ethanol action
Abstract
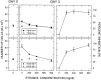
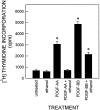
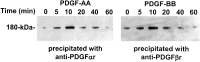
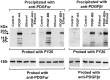
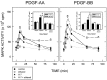
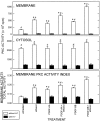
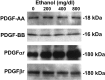
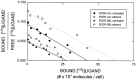
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is a critical regulator of cell proliferation. Because ethanol inhibits cell proliferation in vivo and in vitro, we hypothesize that ethanol-induced inhibition results from differential interference with signal transduction pathways activated by PDGF. Cultured cortical astrocytes were used to examine the effects of ethanol on PDGF-mediated signal transduction, on the expression of two PDGF monomers (A- and B-chains), and on the expression of two PDGF receptor subunits (PDGFalphar and PDGFbetar). PDGF-B chain homodimer (PDGF-BB), and to a lesser extent PDGF-A chain homodimer (PDGF-AA), stimulated the proliferation of astrocytes raised in a serum-free medium. Ethanol attenuated these actions in a concentration-dependent manner. Ethanol inhibited both PDGF-AA- and PDGF-BB-mediated phosphorylation of PDGFalphar, but it had little effect on PDGFbetar autophosphorylation. Likewise, ethanol abolished the association of PDGFalphar to Ras GTPase-activating protein (Ras-GAP), but it did not affect the binding of Ras-GAP to PDGFbetar. PDGF stimulated the activities of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in protein kinase C (PKC) independent and dependent manners. Ethanol inhibited the PKC-independent, acute activation of MAPK; however, it stimulated the PKC-dependent, sustained activation of MAPK. The expression of neither ligand was altered by exposure to ethanol for 3 d. Moreover, such treatment specifically upregulated PDGFalphar expression in a concentration-dependent manner. It did not, however, affect the binding affinity of either receptor. Thus, the signal transduction pathways initiated by PDGF-AA and PDGF-BB were differentially affected by ethanol. This differential vulnerability resulted from the preferential effects of ethanol on PDGFalphar autophosphorylation. Hence, ethanol-induced alterations are transduced through specific receptors of mitogenic growth factors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differences in signal transduction between platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) alpha and beta receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells. PDGF-BB is a potent mitogen, but PDGF-AA promotes only protein synthesis without activation of DNA synthesis.J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30546-52. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 7982973
-
Sodium butyrate inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995 Dec;15(12):2273-83. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.15.12.2273. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995. PMID: 7489253
-
Protein phosphorylation in response to PDGF stimulation in cultured neurons and astrocytes.Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1997 Apr 18;99(2):216-25. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(96)00218-0. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1997. PMID: 9125475
-
Platelet-derived growth factor. Distinct signal transduction pathways associated with migration versus proliferation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Sep 7;766:416-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb26691.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995. PMID: 7486687 Review.
-
Regulatory mechanisms for the expression and activity of platelet-derived growth factor receptor.Acta Biochim Pol. 2003;50(3):647-58. Acta Biochim Pol. 2003. PMID: 14515146 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of ethanol during adolescence on the number of neurons and glia in the medial prefrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala of adult male and female rats.Brain Res. 2012 Jul 23;1466:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.05.023. Epub 2012 May 22. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22627163 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor as a new Therapy for Ischemic Stroke and other Neurologic Diseases: is there any Hope for a Better Outcome?Curr Neuropharmacol. 2015;13(6):836-44. doi: 10.2174/1570159x13666150518235504. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26630962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic ethanol treatment enhances inflammatory mediators and cell death in the brain and in astrocytes.Brain Pathol. 2004 Oct;14(4):365-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2004.tb00079.x. Brain Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15605983 Free PMC article.
-
Acute ethanol intake induces mitogen-activated protein kinase activation, platelet-derived growth factor receptor phosphorylation, and oxidative stress in resistance arteries.J Physiol Biochem. 2014 Jun;70(2):509-23. doi: 10.1007/s13105-014-0331-6. Epub 2014 Apr 15. J Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24733165
-
Cross-talk between phosphatidic acid and ceramide during ethanol-induced apoptosis in astrocytes.BMC Pharmacol. 2005 Feb 4;5:3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2210-5-3. BMC Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15694004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adickes ED, Mollner TJ, Lockwood SK. Closed chamber system for delivery of ethanol to cell cultures. Alcohol Alcohol. 1988;23:377–381. - PubMed
-
- Aloe L, Tirassa P. The effect of long-term alcohol intake on brain NGF-target cells of aged rats. Alcohol. 1992;9:299–304. - PubMed
-
- Baek JK, Heaton MB, Walker DW. Up-regulation of high-affinity neurotrophin receptor, trkB-like protein on Western blots of rat cortex after chronic ethanol treatment. Mol Brain Res. 1996;40:161–164. - PubMed
-
- Bejcek BE, Voravud N, Deuel TF. Biosynthesis and processing of the platelet-derived growth factor type α receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;196:69–78. - PubMed
-
- Bonner JC, Badgett A, Lindroos PM, Osornio-Vargas AR. Transforming growth factor β1 downregulates the platelet-derived growth factor α-receptor subtype on human lung fibroblast in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1995;13:496–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
