Yeast HOS3 forms a novel trichostatin A-insensitive homodimer with intrinsic histone deacetylase activity
- PMID: 10535926
- PMCID: PMC22921
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.22.12356
Yeast HOS3 forms a novel trichostatin A-insensitive homodimer with intrinsic histone deacetylase activity
Abstract
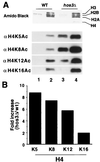
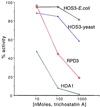
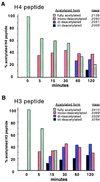
Histone deacetylases such as human HDAC1 and yeast RPD3 are trichostatin A (TSA)-sensitive enzymes that are members of large, multiprotein complexes. These contain specialized subunits that help target the catalytic protein to histones at the appropriate DNA regulatory element, where the enzyme represses transcription. To date, no deacetylase catalytic subunits have been shown to have intrinsic activity, suggesting that noncatalytic subunits of the deacetylase complex are required for their enzymatic function. In this paper we describe a novel yeast histone deacetylase HOS3 that is relatively insensitive to the histone deacetylase inhibitor TSA, forms a homodimer when expressed ectopically both in yeast and Escherichia coli, and has intrinsic activity when produced in the bacterium. Most HOS3 protein can be found associated with a larger complex in partially purified yeast nuclear extracts, arguing that the HOS3 homodimer may be dissociated from a very large nuclear structure during purification. We also demonstrate, using a combination of mass spectrometry, tandem mass spectrometry, and proteolytic digestion, that recombinant HOS3 has a distinct specificity in vitro for histone H4 sites K5 and K8, H3 sites K14 and K23, H2A site K7, and H2B site K11. We propose that while factors that interact with HOS3 may sequester the catalytic subunit at specific cellular sites, they are not required for HOS3 histone deacetylase activity.
Figures
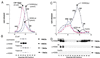

Similar articles
-
HDA1 and RPD3 are members of distinct yeast histone deacetylase complexes that regulate silencing and transcription.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Dec 10;93(25):14503-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.25.14503. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8962081 Free PMC article.
-
phd1+, a histone deacetylase gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe, is required for the meiotic cell cycle and resistance to trichostatin A.FEBS Lett. 1998 Oct 2;436(2):193-6. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(98)01124-7. FEBS Lett. 1998. PMID: 9781677
-
HDA2 and HDA3 are related proteins that interact with and are essential for the activity of the yeast histone deacetylase HDA1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 10;98(8):4391-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.081560698. Epub 2001 Apr 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11287668 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional studies of the yeast class II Hda1 histone deacetylase complex.J Mol Biol. 2009 Aug 28;391(4):744-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.06.059. Epub 2009 Jun 30. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19573535
-
The origin and utility of histone deacetylases.FEBS Lett. 1997 Dec 15;419(2-3):157-60. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(97)01423-3. FEBS Lett. 1997. PMID: 9428625 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone deacetylase inhibition as an alternative strategy against invasive aspergillosis.Front Microbiol. 2015 Feb 16;6:96. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00096. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25762988 Free PMC article.
-
The complex underpinnings of genetic background effects.Nat Commun. 2018 Sep 17;9(1):3548. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06023-5. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30224702 Free PMC article.
-
Application of mass spectrometry to the identification and quantification of histone post-translational modifications.J Cell Biochem. 2004 Jul 1;92(4):691-700. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20106. J Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15211567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Genomes of Three Uneven Siblings: Footprints of the Lifestyles of Three Trichoderma Species.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Feb 10;80(1):205-327. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00040-15. Print 2016 Mar. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26864432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ssn6-Tup1 interacts with class I histone deacetylases required for repression.Genes Dev. 2000 Nov 1;14(21):2737-44. doi: 10.1101/gad.829100. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 11069890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carmen A A, Rundlett S E, Grunstein M. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:15837–15844. - PubMed
-
- Taunton J, Hassig C A, Schreiber S L. Science. 1996;272:408–411. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Iratni R, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Reinberg D. Cell. 1997;89:357–364. - PubMed
-
- Laherty C D, Yang W M, Sun J M, Davie J R, Seto E, Eisenman R N. Cell. 1997;89:349–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

