Sensitivity of an epstein-barr virus-positive tumor line, Daudi, to alpha interferon correlates with expression of a GC-rich viral transcript
- PMID: 10523619
- PMCID: PMC84724
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.11.7305
Sensitivity of an epstein-barr virus-positive tumor line, Daudi, to alpha interferon correlates with expression of a GC-rich viral transcript
Abstract
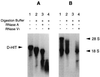
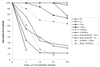
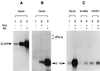
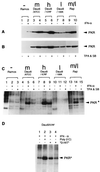
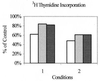
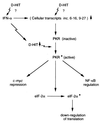
The exquisite sensitivity of the Burkitt's lymphoma (BL)-derived cell line Daudi to type I interferons has not previously been explained. Here we show that expression of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) transcript, designated D-HIT (Y. Gao et al., J. Virol. 71:84-94, 1997), correlates with the sensitivity of different Daudi cell isolates (or that of other EBV-carrying cells, where known) to alpha interferon (IFN-alpha). D-HIT, transcribed from a GC-rich repetitive region (IR4) of the viral genome, is highly structured, responding to RNase digestion in a manner akin to double-stranded RNA. Comparing EBV-carrying BL cell lines with differing responses to IFN-alpha, we found the protein levels of the dsRNA-activated kinase, PKR, to be similar, whereas the levels of the autophosphorylated active form of PKR varied in a manner that correlated with endogenous levels of D-HIT expression. In a classical in vitro kinase assay, addition of either poly(I)-poly(C) or an in vitro-transcribed D-HIT homolog stimulated the autophosphorylation activity of PKR from IFN-alpha-treated cells in both EBV-positive and EBV-negative B lymphocytes. By transfection experiments, these RNAs were shown to reduce cell proliferation and to sensitize otherwise relatively insensitive Raji cells to IFN-alpha. The data lead to a model wherein the D-HIT viral RNA also serves as a possible transcriptional activator of IFN-alpha or cellular genes regulated by this cytokine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus RNA confers resistance to interferon-alpha-induced apoptosis in Burkitt's lymphoma.EMBO J. 2002 Mar 1;21(5):954-65. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.5.954. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 11867523 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of an exceptionally high-level, nontranslated, Epstein-Barr virus-encoded polyadenylated transcript in the Burkitt's lymphoma line Daudi.J Virol. 1997 Jan;71(1):84-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.1.84-94.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 8985326 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of genes for the Epstein-Barr virus small RNAs EBER-1 and EBER-2 in Daudi Burkitt's lymphoma cells: effects of interferon treatment.J Gen Virol. 1992 Dec;73 ( Pt 12):3169-75. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-12-3169. J Gen Virol. 1992. PMID: 1335024
-
The role of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs (EBERs) in oncogenesis.Rev Med Virol. 2002 Sep-Oct;12(5):321-6. doi: 10.1002/rmv.363. Rev Med Virol. 2002. PMID: 12211044 Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of antibodies against Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 for detection of cellular proteins with monomethylated arginine residues that are potentially involved in viral transformation.Arch Virol. 2024 Nov 8;169(12):241. doi: 10.1007/s00705-024-06172-7. Arch Virol. 2024. PMID: 39514105 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity: frameshift mechanisms alter coding of a gene (Epstein-Barr virus LF3 gene) that contains multiple 102-base-pair direct sequence repeats.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Mar;23(6):2192-201. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.6.2192-2201.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12612089 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of two related viral early genes in Epstein-Barr virus-associated tumors.J Virol. 2000 Mar;74(6):2793-803. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.6.2793-2803.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10684296 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune modulation in EBV infection.Herpesviridae. 2011 Jan 5;2(1):1. doi: 10.1186/2042-4280-2-1. Herpesviridae. 2011. PMID: 21429244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams A, Lidin B, Strander H, Cantell K. Spontaneous interferon production and Epstein-Barr virus antigen expression in human lymphoid cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1975;28:219–223. - PubMed
-
- Adams A, Strander H, Cantell K. Sensitivity of the Epstein-Barr virus transformed human lymphoid cell lines to interferon. J Gen Virol. 1975;28:207–217. - PubMed
-
- Blomhoff H K, Davies C, Ruud E, Funderud S, Godal T. Distinct effects of γ interferon on human B-lymphocyte precursor cell lines. Scand J Immunol. 1985;22:611–617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
