Two distinct mechanisms drive protein translocation across the mitochondrial outer membrane in the late step of the cytochrome b(2) import pathway
- PMID: 10518525
- PMCID: PMC18361
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.21.11770
Two distinct mechanisms drive protein translocation across the mitochondrial outer membrane in the late step of the cytochrome b(2) import pathway
Abstract
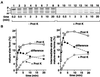
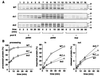
The import of cytochrome b(2) into mitochondria consists of two steps. The translocation of the first part of the presequence across the inner membrane is coupled with the translocation of the tightly folded heme-binding domain across the outer membrane and requires a membrane potential DeltaPsi and the functions of mitochondrial Hsp70 (mHsp70) in the matrix. Once the heme-binding domain has passed the outer membrane, the translocation of the rest of the polypeptide chain across the outer membrane becomes independent of DeltaPsi and mHsp70. Here we analyzed the late DeltaPsi- and mHsp70-independent step in the transport of cytochrome b(2) fusion proteins into the intermembrane space (IMS). The import of the cytochrome b(2) fusion proteins containing two protein domains linked by a spacer segment into mitochondria was arrested at a stage at which one domain folded on each side of the outer membrane, along the pathway that is consistent with the stop-transfer model. The mature-size form of the translocation intermediate could move across the outer membrane in both directions, and the stabilization of the protein domain in the IMS promoted the forward translocation. On the other hand, the intermediate-size form of the translocation intermediate, which retains the anchorage to the inner membrane, was transported into the IMS independently of the stability of the protein domain in the IMS. These results suggest that two distinct mechanisms, the Brownian ratchet and the anchor diffusion mechanisms, can operate for the transmembrane movement of the mature-size form and the intermediate-size form, respectively, of cytochrome b(2) species.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Import of cytochrome b2 to the mitochondrial intermembrane space: the tightly folded heme-binding domain makes import dependent upon matrix ATP.Protein Sci. 1993 Nov;2(11):1901-17. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560021112. Protein Sci. 1993. PMID: 8268801 Free PMC article.
-
The requirement of matrix ATP for the import of precursor proteins into the mitochondrial matrix and intermembrane space.Eur J Biochem. 1994 Feb 15;220(1):9-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18593.x. Eur J Biochem. 1994. PMID: 8119302
-
Cytochromes c1 and b2 are sorted to the intermembrane space of yeast mitochondria by a stop-transfer mechanism.Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):809-22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90292-k. Cell. 1992. PMID: 1350514
-
Import and insertion of proteins into the mitochondrial outer membrane.Eur J Biochem. 1995 Jan 15;227(1-2):9-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20354.x. Eur J Biochem. 1995. PMID: 7851447 Review.
-
Protein Translocation into the Intermembrane Space and Matrix of Mitochondria: Mechanisms and Driving Forces.Front Mol Biosci. 2017 Dec 7;4:83. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2017.00083. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Biosci. 2017. PMID: 29270408 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gene delivery to mitochondria by targeting modified adenoassociated virus suppresses Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy in a mouse model.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 May 15;109(20):E1238-47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1119577109. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22523243 Free PMC article.
-
Mdm35p imports Ups proteins into the mitochondrial intermembrane space by functional complex formation.EMBO J. 2010 Sep 1;29(17):2875-87. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.149. Epub 2010 Jul 9. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20622808 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the membrane potential in mitochondrial protein unfolding and import.Sci Rep. 2019 May 21;9(1):7637. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44152-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31114030 Free PMC article.
-
Trypanosoma brucei: differential requirement of membrane potential for import of proteins into mitochondria in two developmental stages.Exp Parasitol. 2008 Mar;118(3):420-33. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2007.10.008. Epub 2007 Oct 15. Exp Parasitol. 2008. PMID: 18021773 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Mitochondria-Targeted Gene Delivery.Molecules. 2018 Sep 11;23(9):2316. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092316. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30208599 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hanein D, Matlack K E S, Jungnickel B, Plath K, Kalies K-U, Miller K R, Rapoport T A, Akey C W. Cell. 1996;87:721–732. - PubMed
-
- Künkele K-P, Heins S, Dembowski M, Nargang F E, Benz R, Thieffry M, Walz J, Lill R, Nussberger S, Neupert W. Cell. 1998;93:1009–1019. - PubMed
-
- Meyer T H, Ménétret J-F, Breitling R, Miller K R, Akey C W, Rapoport T A. J Mol Biol. 1999;285:1789–1800. - PubMed
-
- Hartl F-U, Neupert W. Science. 1990;247:930–938. - PubMed
-
- Glick B S, Beasley E M, Schatz G. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992;17:453–459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

