Human immunodeficiency virus type 1-induced hematopoietic inhibition is independent of productive infection of progenitor cells in vivo
- PMID: 10516015
- PMCID: PMC112941
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.11.9089-9097.1999
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1-induced hematopoietic inhibition is independent of productive infection of progenitor cells in vivo
Abstract
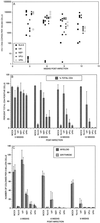
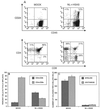
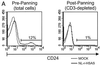
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected individuals exhibit a variety of hematopoietic dysfunctions. The SCID-hu mouse (severe combined immunodeficient mouse transplanted with human fetal thymus and liver tissues) can be used to model the loss of human hematopoietic precursor cell function following HIV infection and has a distinct advantage in that data can be obtained in the absence of confounding factors often seen in infected humans. In this study, we establish that HIV type 1 (HIV-1) bearing a reporter gene inserted into the viral vpr gene is highly aggressive in depleting human myeloid and erythroid colony-forming precursor activity in vivo. Human CD34(+) progenitor cells can be efficiently recovered from infected implants yet do not express the viral reporter gene, despite severe functional defects. Our results indicate that HIV-1 infection alone leads to hematopoietic inhibition in vivo; however, this effect is due to indirect mechanisms rather than to direct infection of CD34(+) cells in vivo.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeting c-Mpl for revival of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-induced hematopoietic inhibition when CD34+ progenitor cells are re-engrafted into a fresh stromal microenvironment in vivo.J Virol. 2004 Oct;78(20):11385-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.20.11385-11392.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15452260 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-based anti-HIV-1 gene therapeutic constructs in SCID-hu mouse model.Mol Ther. 2002 Dec;6(6):770-82. doi: 10.1006/mthe.2002.0800. Mol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12498773
-
Human immunodeficiency virus inhibits multilineage hematopoiesis in vivo.J Virol. 1998 Jun;72(6):5121-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.6.5121-5127.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9573283 Free PMC article.
-
Cytopenias in HIV infection: mechanisms and alleviation of hematopoietic inhibition.Curr HIV Res. 2004 Jul;2(3):275-82. doi: 10.2174/1570162043351282. Curr HIV Res. 2004. PMID: 15279591 Review.
-
Could Nef and Vpr proteins contribute to disease progression by promoting depletion of bystander cells and prolonged survival of HIV-infected cells?Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Jan 27;267(3):677-85. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1708. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. PMID: 10673351 Review.
Cited by
-
The utilization of humanized mouse models for the study of human retroviral infections.Retrovirology. 2009 Aug 12;6:76. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-6-76. Retrovirology. 2009. PMID: 19674458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early and persistent bone marrow hematopoiesis defect in simian/human immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques despite efficient reduction of viremia by highly active antiretroviral therapy during primary infection.J Virol. 2001 Dec;75(23):11594-602. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.23.11594-11602.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11689641 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Killer Cell Receptor NKG2A/HLA-E Interaction Dependent Differential Thymopoiesis of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells Influences the Outcome of HIV Infection.J Stem Cells. 2007;2(4):237-248. J Stem Cells. 2007. PMID: 19005583 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA target homeobox messenger RNA in HIV induced hematopoietic inhibition.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Apr 24;12:1382789. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1382789. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38721526 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell transplantation in HIV-infected patients.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2009 Jan;4(1):11-5. doi: 10.1097/COH.0b013e32831a6fc9. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2009. PMID: 19339935 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aldrovandi G M, Feuer G, Gao L, Kristeva M, Chen I S Y, Jamieson B, Zack J A. HIV-1 infection of the SCID-hu mouse: an animal model for virus pathogenesis. Nature. 1993;363:732–736. - PubMed
-
- Bijl J, van Oostveen J W, Kreike M, Rieger E, van der Raaij-Helmer L M, Walboomers J M, Corte G, Boncinelli E, van den Brule A J, Meijer C J. Expression of HOXC4, HOXC5, and HOXC6 in human lymphoid cell lines, leukemias, and benign and malignant lymphoid tissue. Blood. 1996;87:1737–1745. - PubMed
-
- Bonyhadi M L, Rabin L, Salimi S, Brown D A, Kosek J, McCune J M, Kaneshima H. HIV induces thymus depletion in vivo. Nature. 1993;363:728–732. - PubMed
-
- Burstein Y, Rashbaum W K, Hatch W C, Calvelli T, Golodner M, Soeiro R, Lyman W D. Alterations in human fetal hematopoiesis are associated with maternal HIV infection. Pediatr Res. 1992;32:155–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

