Cloning of gp-340, a putative opsonin receptor for lung surfactant protein D
- PMID: 10485905
- PMCID: PMC17962
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.19.10794
Cloning of gp-340, a putative opsonin receptor for lung surfactant protein D
Abstract
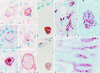
Surfactant protein D (SP-D) is an oligomeric C type lectin that promotes phagocytosis by binding to microbial surface carbohydrates. A 340-kDa glycoprotein (gp-340) has been shown to bind SP-D in the presence of calcium but does so independently of carbohydrate recognition. This protein exists both in a soluble form and in association with the membranes of alveolar macrophages. The primary structure of gp-340 has been established by molecular cloning, which yielded a 7,686-bp cDNA sequence encoding a polypeptide chain of 2, 413 amino acids. The domain organization features 13 scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domains, each separated by an SRCR-interspersed domain, except for SRCRs 4 and 5, which are contiguous. The 13 SRCR domains are followed by two C1r/C1s Uegf Bmp1 domains separated by a 14th SRCR domain and a zona pellucida domain. gp-340 seems to be an alternative spliced form of DMBT1. Reverse transcription-PCR analysis showed that the main sites of synthesis of gp-340 are lung, trachea, salivary gland, small intestine, and stomach. Immunohistochemistry revealed strong staining for gp-340 in alveolar and other tissue macrophages. Immunostaining of the macrophage membrane was either uniform or focal in a way that suggested capping, whereas other macrophages showed strong intracellular staining within the phagosome/phagolysosome compartments. In some macrophages, SP-D and gp-340 were located in the same cellular compartment. Immunoreactive gp-340 was also found in epithelial cells of the small intestine and in the ducts of salivary glands. The distribution of gp-340 in macrophages is compatible with a role as an opsonin receptor for SP-D.
Figures



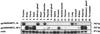
Similar articles
-
Glycoprotein-340 binds surfactant protein-A (SP-A) and stimulates alveolar macrophage migration in an SP-A-independent manner.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999 Apr;20(4):759-68. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.20.4.3439. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10101009
-
Isolation and characterization of a new member of the scavenger receptor superfamily, glycoprotein-340 (gp-340), as a lung surfactant protein-D binding molecule.J Biol Chem. 1997 May 23;272(21):13743-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.21.13743. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9153228
-
Human salivary agglutinin binds to lung surfactant protein-D and is identical with scavenger receptor protein gp-340.Biochem J. 2001 Oct 1;359(Pt 1):243-8. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3590243. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11563989 Free PMC article.
-
Functional roles of the lung surfactant proteins SP-A and SP-D in innate immunity.Immunobiology. 1998 Aug;199(2):200-7. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(98)80027-2. Immunobiology. 1998. PMID: 9777406 Review.
-
Structural aspects of collectins and receptors for collectins.Immunobiology. 1998 Aug;199(2):165-89. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(98)80025-9. Immunobiology. 1998. PMID: 9777404 Review.
Cited by
-
Surfactant protein D is present in human tear fluid and the cornea and inhibits epithelial cell invasion by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Infect Immun. 2005 Apr;73(4):2147-56. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.4.2147-2156.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15784557 Free PMC article.
-
A peptide domain of bovine milk lactoferrin inhibits the interaction between streptococcal surface protein antigen and a salivary agglutinin peptide domain.Infect Immun. 2004 Oct;72(10):6181-4. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.6181-6184.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15385529 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of terminal differentiation in epithelial cells requires polymerization of hensin by galectin 3.J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec 11;151(6):1235-46. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.6.1235. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11121438 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori induces an antimicrobial response in rhesus macaques in a cag pathogenicity island-dependent manner.Gastroenterology. 2008 Apr;134(4):1049-57. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.01.018. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18395086 Free PMC article.
-
HIV envelope binding by macrophage-expressed gp340 promotes HIV-1 infection.J Immunol. 2008 Aug 1;181(3):2065-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.3.2065. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18641344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weis W I, Taylor M E, Drickamer K. Immunol Rev. 1998;163:19–34. - PubMed
-
- Thiel S, Vorup-Jensen T, Stover C M, Schwaeble W, Laursen S B, Poulsen K, Willis A C, Eggleton P, Hansen S, Holmskov U, et al. Nature (London) 1997;386:506–510. - PubMed
-
- Janeway C A., Jr Immunol Today. 1992;13:11–16. - PubMed
-
- Hartshorn K L, Crouch E, White M R, Colamussi M L, Kakkanatt A, Tauber B, Shepherd V, Sastry K N. Am J Physiol. 1998;274:L958–L969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

