Effects of roundabout on growth cone dynamics, filopodial length, and growth cone morphology at the midline and throughout the neuropile
- PMID: 10479692
- PMCID: PMC6782466
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-18-07901.1999
Effects of roundabout on growth cone dynamics, filopodial length, and growth cone morphology at the midline and throughout the neuropile
Abstract
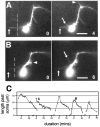
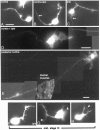
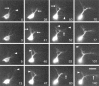
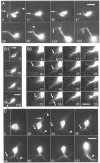
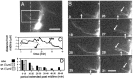
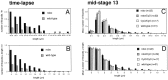
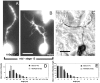
roundabout (robo) encodes an axon guidance receptor that controls midline crossing in the Drosophila CNS. In robo mutants, axons that normally project ipsilaterally can cross and recross the midline. Growth cones expressing Robo are believed to be repelled from the midline by the interaction of Robo and its ligand Slit, an extracellular protein expressed by the midline glia. To help understand the cellular basis for the midline repulsion mediated by Robo, we used time-lapse observations to compare the growth cone behavior of the ipsilaterally projecting motorneuron RP2 in robo and wild-type embyros. In wild-type embryos, filopodia can project across the midline but are quickly retracted. In robo mutants, medial filopodia can remain extended for longer periods and can develop into contralateral branches. In many cases RP2 produces both ipsilateral and contralateral branches, both of which can extend into the periphery. The growth cone also exhibits longer filopodia and more extensive branching both at the midline and throughout the neuropile. Cell injections in fixed stage 13 embryos confirmed and quantified these results for both RP2 and the interneuron pCC. The results suggest that Robo both repels growth cones at the midline and inhibits branching throughout the neuropile by promoting filopodial retraction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Axon pathfinding proceeds normally despite disrupted growth cone decisions at CNS midline.Development. 2000 May;127(10):2001-9. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.10.2001. Development. 2000. PMID: 10769225
-
Drosophila neurexin IV interacts with Roundabout and is required for repulsive midline axon guidance.J Neurosci. 2010 Apr 21;30(16):5653-67. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6187-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20410118 Free PMC article.
-
Robo recruitment of the Wave regulatory complex plays an essential and conserved role in midline repulsion.Elife. 2021 Apr 12;10:e64474. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64474. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33843588 Free PMC article.
-
[Current progress in functions of axon guidance molecule Robo and underlying molecular mechanism].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2014 Jun 25;66(3):373-85. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2014. PMID: 24964856 Review. Chinese.
-
Roundabout receptors.Adv Neurobiol. 2014;8:133-64. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-8090-7_7. Adv Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 25300136 Review.
Cited by
-
A frazzled/DCC-dependent transcriptional switch regulates midline axon guidance.Science. 2009 May 15;324(5929):944-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1171320. Epub 2009 Mar 26. Science. 2009. PMID: 19325078 Free PMC article.
-
Labeling of single cells in the central nervous system of Drosophila melanogaster.J Vis Exp. 2013 Mar 4;(73):e50150. doi: 10.3791/50150. J Vis Exp. 2013. PMID: 23486245 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila as a genetic and cellular model for studies on axonal growth.Neural Dev. 2007 May 2;2:9. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-2-9. Neural Dev. 2007. PMID: 17475018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteolytic cleavage of Slit by the Tolkin protease converts an axon repulsion cue to an axon growth cue in vivo.Development. 2020 Oct 29;147(20):dev196055. doi: 10.1242/dev.196055. Development. 2020. PMID: 32994163 Free PMC article.
-
Dscam1 Forms a Complex with Robo1 and the N-Terminal Fragment of Slit to Promote the Growth of Longitudinal Axons.PLoS Biol. 2016 Sep 21;14(9):e1002560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002560. eCollection 2016 Sep. PLoS Biol. 2016. PMID: 27654876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bentley D, O’Connor TP. Cytoskeletal events in growth cone steering. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1994;4:43–48. - PubMed
-
- Brose K, Bland KS, Wang KH, Arnott D, Henzel W, Goodman CS, Tessier-Lavigne M, Kidd T. Slit proteins bind Robo receptors and have an evolutionarily conserved role in repulsive axon guidance. Cell. 1999;96:795–806. - PubMed
-
- Fan J, Raper JA. Localized collapsing cues can steer growth cones without inducing their full collapse. Neuron. 1995;14:263–274. - PubMed
-
- Gertler FB, Comer AR, Juang J, Ahern SM, Clark MJ, Liebl EC, Hoffmann FM. enabled, a dosage-sensitive suppressor of mutations in the Drosophila Abl tyrosine kinase, encodes an Abl substrate with SH3 domain-binding properties. Genes Dev. 1995;9:521–533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
