Impaired glucose homeostasis and neonatal mortality in hepatocyte nuclear factor 3alpha-deficient mice
- PMID: 10468578
- PMCID: PMC17858
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.18.10152
Impaired glucose homeostasis and neonatal mortality in hepatocyte nuclear factor 3alpha-deficient mice
Abstract
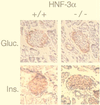
Hepatocyte nuclear factors 3 (HNF-3) belong to an evolutionarily conserved family of transcription factors that are critical for diverse biological processes such as development, differentiation, and metabolism. To study the physiological role of HNF-3alpha, we generated mice that lack HNF-3alpha by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Mice homozygous for a null mutation in the HNF-3alpha gene develop a complex phenotype that is characterized by abnormal feeding behavior, progressive starvation, persistent hypoglycemia, hypotriglyceridemia, wasting, and neonatal mortality between days 2 and 14. Hypoglycemia in HNF-3alpha-null mice leads to physiological counter-regulatory responses in glucocorticoid and growth hormone production and an inhibition of insulin secretion but fails to stimulate glucagon secretion. Glucagon-producing pancreatic alpha cells develop normally in HNF-3alpha-/- mice, but proglucagon mRNA levels are reduced 50%. Furthermore, the transcriptional levels of neuropeptide Y are also significantly reduced shortly after birth, implying a direct role of HNF-3alpha in the expression of these genes. In contrast, mRNA levels were increased in HNF-3 target genes phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphophatase, insulin growth factor binding protein-1, and hexokinase I of HNF-3alpha-null mice. Mice lacking one or both HNF-3alpha alleles also show impaired insulin secretion and glucose intolerance after an intraperitoneal glucose challenge, indicating that pancreatic beta-cell function is also compromised. Our results indicate that HNF-3alpha plays a critical role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis and in pancreatic islet function.
Figures
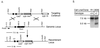


Similar articles
-
Regulation of a transcription factor network required for differentiation and metabolism.Science. 1998 Jul 31;281(5377):692-5. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5377.692. Science. 1998. PMID: 9685261
-
Profound defects in pancreatic beta-cell function in mice with combined heterozygous mutations in Pdx-1, Hnf-1alpha, and Hnf-3beta.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Mar 19;99(6):3818-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.062605899. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11904435 Free PMC article.
-
The human HNF-3 genes: cloning, partial sequence and mutation screening in patients with impaired glucose homeostasis.Hum Hered. 2000 Nov-Dec;50(6):370-81. doi: 10.1159/000022943. Hum Hered. 2000. PMID: 10899756
-
The hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 (HNF3 or FOXA) family in metabolism.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2000 Sep;11(7):281-5. doi: 10.1016/s1043-2760(00)00271-x. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2000. PMID: 10920385 Review.
-
Transcription factors Brn-3α and TRIM16 in cancers, association with hormone reception.Heliyon. 2019 Aug 16;5(8):e02090. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02090. eCollection 2019 Aug. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31463379 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hnf1b controls pancreas morphogenesis and the generation of Ngn3+ endocrine progenitors.Development. 2015 Mar 1;142(5):871-82. doi: 10.1242/dev.110759. Development. 2015. PMID: 25715395 Free PMC article.
-
Foxa1 and Foxa2 in thymic epithelial cells (TEC) regulate medullary TEC and regulatory T-cell maturation.J Autoimmun. 2018 Sep;93:131-138. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Jul 27. J Autoimmun. 2018. PMID: 30061015 Free PMC article.
-
Association of levels of fasting glucose and insulin with rare variants at the chromosome 11p11.2-MADD locus: Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology (CHARGE) Consortium Targeted Sequencing Study.Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2014 Jun;7(3):374-382. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.113.000169. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2014. PMID: 24951664 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of FOXA1/2 is essential for the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer.Cancer Res. 2010 Mar 1;70(5):2115-25. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2979. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20160041 Free PMC article.
-
Differential gene expression between neuropeptide Y expressing neurons of the dorsomedial nucleus of the hypothalamus and the arcuate nucleus: microarray analysis study.Brain Res. 2010 Sep 2;1350:139-50. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.03.082. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20380814 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

