F-actin stabilization increases tension cost during contraction of permeabilized airway smooth muscle in dogs
- PMID: 10457068
- PMCID: PMC2269509
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0527m.x
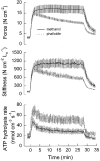
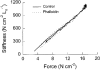
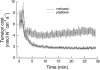
F-actin stabilization increases tension cost during contraction of permeabilized airway smooth muscle in dogs
Abstract
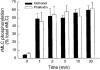
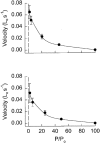
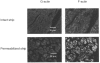
1. Dynamic actin reorganization involving actin polymerization and depolymerization may play an important functional role in smooth muscle. 2. This study tested the hypothesis that F-actin stabilization by phalloidin increases tension cost (i.e. ATP hydrolysis rate per unit of isometric force) during Ca2+-induced activation of Triton X-100-permeabilized canine tracheal smooth muscle. 3. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) hydrolysis rate was quantified using an enzyme-coupled NADH fluorometric technique, regulatory myosin light chain (rMLC) phosphorylation was measured by Western blot analysis, and maximum unloaded shortening velocity (Vmax) was estimated by interpolation of the force-velocity relationship to zero load during isotonic loading. 4. Maximal activation with 10 microM free Ca2+ induced sustained increases in isometric force, stiffness, and rMLC phosphorylation. However, the increase in ATP hydrolysis rate initially reached peak values, but then declined to steady-state levels above that of the unstimulated muscle. Thus, tension cost decreased throughout steady-state isometric force. 5. Following incubation of permeabilized strips with 50 microM phalloidin for 1 h, the increases in isometric force and stiffness were not sustained despite a sustained increase in rMLC phosphorylation. Also, after an initial decline, tension cost increased throughout activation. Phalloidin had no effect on Vmax during steady-state isometric force or on rMLC phosphorylation. 6. These findings suggest that dynamic reorganization of actin is necessary for optimal energy utilization during contraction of permeabilized airway smooth muscle.
Figures
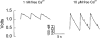

Similar articles
-
ATP hydrolysis during contraction of permeabilized airway smooth muscle.Am J Physiol. 1999 Aug;277(2):L334-42. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1999.277.2.L334. Am J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10444528
-
Halothane inhibits agonist-induced potentiation of rMLC phosphorylation in permeabilized airway smooth muscle.Am J Physiol. 1997 Jul;273(1 Pt 1):L80-5. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1997.273.1.L80. Am J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9252543
-
TNFα enhances force generation in airway smooth muscle.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):L994-L1002. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00550.2016. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28385814 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and tuning of smooth muscle myosin.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 Nov;158(5 Pt 3):S95-9. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.158.supplement_2.13tac400. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. PMID: 9817731 Review.
-
The biophysics and biochemistry of smooth muscle contraction.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;70(4):515-31. doi: 10.1139/y92-067. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992. PMID: 1498719 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacometabolomics of Asthma as a Road Map to Precision Medicine.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2023;277:247-273. doi: 10.1007/164_2022_615. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36271166 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoskeletal remodeling slows cross-bridge cycling and ATP hydrolysis rates in airway smooth muscle.Physiol Rep. 2020 Aug;8(16):e14561. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14561. Physiol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32812390 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying TNFα-induced enhancement of force generation in airway smooth muscle.Physiol Rep. 2019 Sep;7(17):e14220. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14220. Physiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31512410 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of non-phosphorylatable paxillin mutants in canine tracheal smooth muscle inhibits tension development.J Physiol. 2003 Nov 15;553(Pt 1):21-35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.045047. Epub 2003 Aug 29. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12949231 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and dynamics of the actin-based smooth muscle contractile and cytoskeletal apparatus.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2012 Dec;33(6):461-9. doi: 10.1007/s10974-012-9283-z. Epub 2012 Feb 7. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2012. PMID: 22311558 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adler KB, Krill J, Alberghini TV, Evans JN. Effect of cytochalasin D on smooth muscle contraction. Cell Motility. 1983;3:545–551. - PubMed
-
- Aktories K, Barmann M, Ohishi I, Tsuyama S, Jakobs KH, Habermann E. Botulinum C2 toxin ADP-ribosylates actin. Nature. 1986;322:390–392. - PubMed
-
- Berdiev BK, Prat AG, Cantiello HF, Ausiello DA, Fuller CM, Jovov B, Benos DJ, Ismailov II. Regulation of epithelial sodium channels by short actin filaments. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996;271:17704–17710. - PubMed
-
- Boels PJ, Pfitzer G. Relaxant effect of phalloidin on Triton-skinned microvascular and other smooth muscle preparations. Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility. 1992;13:71–80. - PubMed
-
- Brenner B. Mechanical approaches to elucidation of the crossbridge cycle. Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility. 1985;6:659–668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

