Differential roles of IL-1 and TNF-alpha on graft-versus-host disease and graft versus leukemia
- PMID: 10449438
- PMCID: PMC408528
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI6896
Differential roles of IL-1 and TNF-alpha on graft-versus-host disease and graft versus leukemia
Abstract
We demonstrate an increase in graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after experimental bone marrow transplant (BMT) when cyclophosphamide (Cy) is added to an otherwise well-tolerated dose (900 cGy) of total body irradiation (TBI). Donor T cell expansion on day +13 was increased after conditioning with Cy/TBI compared with Cy or TBI alone, although cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) function was not altered. Histological analysis of the gastrointestinal tract demonstrated synergistic damage by Cy/TBI and allogeneic donor cells, which permitted increased translocation of LPS into the systemic circulation. TNF-alpha and IL-1 production in response to LPS was increased in BMT recipients after Cy/TBI conditioning. Neutralization of IL-1 significantly reduced serum LPS levels and GVHD mortality, but it did not affect donor CTL activity. By contrast, neutralization of TNF-alpha did not prevent GVHD mortality but did impair CTL activity after BMT. When P815 leukemia cells were added to the bone marrow inoculum, allogeneic BMT recipients given the TNF-alpha inhibitor relapsed at a significantly faster rate than those given the IL-1 inhibitor. To confirm that the role of TNF-alpha in graft versus leukemia (GVL) was due to effects on donor T cells, cohorts of animals were transplanted with T cells from either wild-type mice or p55 TNF-alpha receptor-deficient mice. Recipients of TNF-alpha p55 receptor-deficient T cells demonstrated a significant impairment in donor CTL activity after BMT and an increased rate of leukemic relapse compared with recipients of wild-type T cells. These data highlight the importance of conditioning in GVHD pathophysiology, and demonstrate that TNF-alpha is critical to GVL mediated by donor T cells, whereas IL-1 is not.
Figures
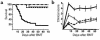
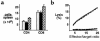
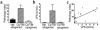
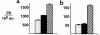
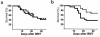
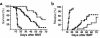
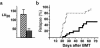
Similar articles
-
TNF receptor p55 controls early acute graft-versus-host disease.J Immunol. 1997 Jun 1;158(11):5185-90. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9164935
-
[Effects of immature dendritic cells genetically modified to express sTNFR I on graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation mice].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Feb;33(2):88-93. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22730654 Chinese.
-
Lymphohematopoietic graft-vs.-host reactions can be induced without graft-vs.-host disease in murine mixed chimeras established with a cyclophosphamide-based nonmyeloablative conditioning regimen.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 1999;5(3):133-43. doi: 10.1053/bbmt.1999.v5.pm10392959. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 1999. PMID: 10392959
-
Protective conditioning against GVHD and graft rejection after combined organ and hematopoietic cell transplantation.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008 Jan-Feb;40(1):48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2007.06.019. Epub 2007 Sep 10. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008. PMID: 17827036 Review.
-
Alloreactivity and the predictive value of anti-recipient specific interleukin 2 producing helper T lymphocyte precursor frequencies for alloreactivity after bone marrow transplantation.Dan Med Bull. 2002 May;49(2):89-108. Dan Med Bull. 2002. PMID: 12064093 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in the treatment of graft-versus-host disease.Clin Med Res. 2004 Nov;2(4):243-52. doi: 10.3121/cmr.2.4.243. Clin Med Res. 2004. PMID: 15931364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal graft-versus-host disease: mechanisms and management.Drugs. 2003;63(1):1-15. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363010-00001. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12487619 Review.
-
Bone marrow deficient in IFN-{gamma} signaling selectively reverses GVHD-associated immunosuppression and enhances a tumor-specific GVT effect.Blood. 2009 May 14;113(20):5002-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-11-187385. Epub 2009 Mar 3. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19258593 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of GVHD while sparing GVL effect by targeting Th1 and Th17 transcription factor T-bet and RORγt in mice.Blood. 2011 Nov 3;118(18):5011-20. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-340315. Epub 2011 Aug 19. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21856864 Free PMC article.
-
Human peripheral blood leucocyte non-obese diabetic-severe combined immunodeficiency interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain gene mouse model of xenogeneic graft-versus-host-like disease and the role of host major histocompatibility complex.Clin Exp Immunol. 2009 Jul;157(1):104-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.03933.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19659776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Truitt, R., Johnson, B., and McCabe, C. 1997. Graft versus leukemia. Marcel Dekker Inc. New York, NY. 385–424.
-
- Krenger W, Hill G, Ferrara J. Cytokine cascades in acute graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation. 1997;64:553–558. - PubMed
-
- Kichian K, Nestel FP, Kim D, Ponka P, Lapp WS. IL-12 p40 messenger RNA expression in target organs during acute graft-versus-host disease. J Immunol. 1996;157:2851–2856. - PubMed
-
- Hill GR, Krenger W, Ferrara JLM. The role of cytokines in acute graft-versus-host disease. Cytokines Cell Mol Ther. 1997;3:257–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

