Three-dimensional visualization of transcription sites and their association with splicing factor-rich nuclear speckles
- PMID: 10444064
- PMCID: PMC2150559
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.146.3.543
Three-dimensional visualization of transcription sites and their association with splicing factor-rich nuclear speckles
Abstract
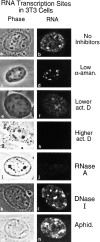
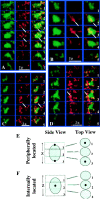
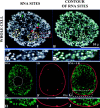
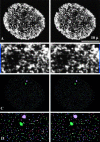
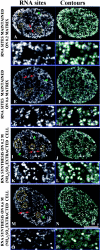
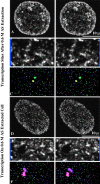
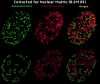
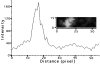
Transcription sites are detected by labeling nascent transcripts with BrUTP in permeabilized 3T3 mouse fibroblasts followed by laser scanning confocal microscopy. Inhibition and enzyme digestion studies confirm that the labeled sites are from RNA transcripts and that RNA polymerase I (RP I) and II (RP II) are responsible for nucleolar and extranucleolar transcription, respectively. An average of 2,000 sites are detected per nucleus with over 90% in the extranucleolar compartment where they are arranged in clusters and three-dimensional networklike arrays. The number of transcription sites, their three-dimensional organization and arrangement into functional zones (Wei et al. 1998) is strikingly maintained after extraction for nuclear matrix. Significant levels of total RP II mediated transcription sites (45%) were associated with splicing factor-rich nuclear speckles even though the speckles occupied <10% of the total extranucleolar space. Moreover, the vast majority of nuclear speckles (>90%) had moderate to high levels of associated transcription activity. Transcription sites were found along the periphery as well as inside the speckles themselves. These spatial relations were confirmed in optical sections through individual speckles and after in vivo labeling of nascent transcripts. Our results demonstrate that nuclear speckles and their surrounding regions are major sites of RP II-mediated transcription in the cell nucleus, and support the view that both speckle- and nonspeckle-associated regions of the nucleus contain sites for the coordination of transcription and splicing processes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fluorescent labeling of nascent RNA reveals transcription by RNA polymerase II in domains scattered throughout the nucleus.J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(2):283-93. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.2.283. J Cell Biol. 1993. PMID: 8320255 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear pre-mRNA compartmentalization: trafficking of released transcripts to splicing factor reservoirs.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Feb;11(2):497-510. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.2.497. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10679009 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear matrix bound fibroblast growth factor receptor is associated with splicing factor rich and transcriptionally active nuclear speckles.J Cell Biochem. 2003 Nov 1;90(4):856-69. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10672. J Cell Biochem. 2003. PMID: 14587039
-
The localization of sites containing nascent RNA and splicing factors.Exp Cell Res. 1996 Dec 15;229(2):201-3. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.0360. Exp Cell Res. 1996. PMID: 8986598 Review.
-
Nuclear speckles: a model for nuclear organelles.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Aug;4(8):605-12. doi: 10.1038/nrm1172. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12923522 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in imaging the interphase nucleus using thin cryosections.Histochem Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;128(2):97-104. doi: 10.1007/s00418-007-0310-x. Epub 2007 Jul 17. Histochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17636315 Review.
-
Analyses of in vivo interaction and mobility of two spliceosomal proteins using FRAP and BiFC.PLoS One. 2008 Apr 16;3(4):e1953. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001953. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18414657 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring RNA transcription and turnover in vivo by using click chemistry.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Oct 14;105(41):15779-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808480105. Epub 2008 Oct 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18840688 Free PMC article.
-
Control of protein synthesis through mRNA pseudouridylation by dyskerin.Sci Adv. 2023 Jul 28;9(30):eadg1805. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg1805. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37506213 Free PMC article.
-
The genome and the nucleus: a marriage made by evolution. Genome organisation and nuclear architecture.Chromosoma. 2005 Sep;114(4):212-29. doi: 10.1007/s00412-005-0016-6. Epub 2005 Oct 15. Chromosoma. 2005. PMID: 16133352 Review.
References
-
- Bauren G., Wieslander E. Splicing of Balbiani ring 1 gene pre-mRNA occurs simultaneously with transcription. Cell. 1994;76:183–192. - PubMed
-
- Belgrader, P., A.J. Siegel, and R. Berezney. 1991. A comprehensive study on the isolation and characterization of the HeLa S3 nuclear matrix. 98:281–291. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Arie N., Lancet D., Taylor C., Khen M., Walker N., Ledbetter D.H., Carrozzo R., Patel K., Sheer D., Lehrach H., North M.A. Olfactory receptor gene cluster on human chromosome17possible duplication of an ancestral receptor repertoire. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1994;3:229–235. - PubMed
-
- Berezney R. Visualizing DNA replication sites in the cell nucleus. Semin. Cell Biol. 1991;2:103–115. - PubMed
-
- Berezney R., Jeon K.W. Nuclear MatrixStructural and Functional Organization 1995. Academic Press, Inc; Orlando, FL: pp. 1,047

