Radiation-induced release of transforming growth factor alpha activates the epidermal growth factor receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in carcinoma cells, leading to increased proliferation and protection from radiation-induced cell death
- PMID: 10436007
- PMCID: PMC25480
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.8.2493
Radiation-induced release of transforming growth factor alpha activates the epidermal growth factor receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in carcinoma cells, leading to increased proliferation and protection from radiation-induced cell death
Abstract
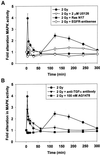
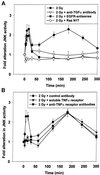
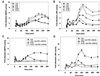
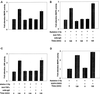
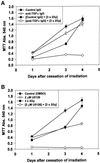
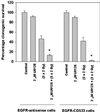
Exposure of A431 squamous and MDA-MB-231 mammary carcinoma cells to ionizing radiation has been associated with short transient increases in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) pathways. Irradiation (2 Gy) of A431 and MDA-MB-231 cells caused immediate primary activations (0-10 min) of the EGFR and the MAPK and JNK pathways, which were surprisingly followed by later prolonged secondary activations (90-240 min). Primary and secondary activation of the EGFR was abolished by molecular inhibition of EGFR function. The primary and secondary activation of the MAPK pathway was abolished by molecular inhibition of either EGFR or Ras function. In contrast, molecular inhibition of EGFR function abolished the secondary but not the primary activation of the JNK pathway. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor function by use of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies blunted primary activation of the JNK pathway. Addition of a neutralizing monoclonal antibody versus transforming growth factor alpha (TGFalpha) had no effect on the primary activation of either the EGFR or the MAPK and JNK pathways after irradiation but abolished the secondary activation of EGFR, MAPK, and JNK. Irradiation of cells increased pro-TGFalpha cleavage 120-180 min after exposure. In agreement with radiation-induced release of a soluble factor, activation of the EGFR and the MAPK and JNK pathways could be induced in nonirradiated cells by the transfer of media from irradiated cells 120 min after irradiation. The ability of the transferred media to cause MAPK and JNK activation was blocked when media were incubated with a neutralizing antibody to TGFalpha. Thus radiation causes primary and secondary activation of the EGFR and the MAPK and JNK pathways in autocrine-regulated carcinoma cells. Secondary activation of the EGFR and the MAPK and JNK pathways is dependent on radiation-induced cleavage and autocrine action of TGFalpha. Neutralization of TGFalpha function by an anti-TGFalpha antibody or inhibition of MAPK function by MEK1/2 inhibitors (PD98059 and U0126) radiosensitized A431 and MDA-MB-231 cells after irradiation in apoptosis, 3-[4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), and clonogenic assays. These data demonstrate that disruption of the TGFalpha-EGFR-MAPK signaling module represents a strategy to decrease carcinoma cell growth and survival after irradiation.
Figures



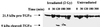
Similar articles
-
Dominant negative EGFR-CD533 and inhibition of MAPK modify JNK1 activation and enhance radiation toxicity of human mammary carcinoma cells.Oncogene. 1999 Aug 19;18(33):4756-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202849. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10467423
-
Ionizing radiation-induced mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase activation in DU145 prostate carcinoma cells: MAP kinase inhibition enhances radiation-induced cell killing and G2/M-phase arrest.Radiat Res. 2000 Apr;153(4):371-83. doi: 10.1667/0033-7587(2000)153[0371:irimap]2.0.co;2. Radiat Res. 2000. PMID: 10760996
-
Inhibition of the mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade potentiates cell killing by low dose ionizing radiation in A431 human squamous carcinoma cells.Oncogene. 1998 May 28;16(21):2787-96. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201802. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9652746
-
Stress and radiation-induced activation of multiple intracellular signaling pathways.Radiat Res. 2003 Mar;159(3):283-300. doi: 10.1667/0033-7587(2003)159[0283:sariao]2.0.co;2. Radiat Res. 2003. PMID: 12600231 Review.
-
Xmrks the Spot: Fish Models for Investigating Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling in Cancer Research.Cells. 2021 May 7;10(5):1132. doi: 10.3390/cells10051132. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34067095 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphorylation of TRIP13 at Y56 induces radiation resistance but sensitizes head and neck cancer to cetuximab.Mol Ther. 2022 Jan 5;30(1):468-484. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.06.009. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Mol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34111559 Free PMC article.
-
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in head and neck cancer: its role and treatment implications.Radiat Oncol. 2006 May 2;1:11. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-1-11. Radiat Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16722544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deoxycholic acid (DCA) causes ligand-independent activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and FAS receptor in primary hepatocytes: inhibition of EGFR/mitogen-activated protein kinase-signaling module enhances DCA-induced apoptosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Sep;12(9):2629-45. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.9.2629. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11553704 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of combined modality radiotherapy of orthotopic human squamous cell carcinomas in Nu/Nu mice using cetuximab, tirapazamine and MnSOD-plasmid liposome gene therapy.In Vivo. 2010 Jan-Feb;24(1):1-8. In Vivo. 2010. PMID: 20133969 Free PMC article.
-
National Cancer Institute (NCI) state of the science: Targeted radiosensitizers in colorectal cancer.Cancer. 2019 Aug 15;125(16):2732-2746. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32150. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31017664 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbott DW, Holt J. Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 activation is essential for progression through the G2/M checkpoint arrest in cells exposed to ionizing radiation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:2732–2742. - PubMed
-
- Auer KL, Ishac E, Seth P, Coffey RJ, DePinho R, Fisher PB, Dent P. Prolonged activation of the mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase pathway promotes DNA synthesis in primary hepatocytes from p21Cip-1/WAF1 knock out mice, but not in hepatocytes from p16INK4a knock out mice. Biochem J. 1998b;336:551–560. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balaban N, Moni J, Shannon M, Dang L, Murphy E, Goldkorn T. The effect of ionizing radiation on signal transduction: antibodies to EGF receptor sensitize A431 cells to radiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1314:147–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

