A role for Tlg1p in the transport of proteins within the Golgi apparatus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 10397773
- PMCID: PMC25462
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.7.2407
A role for Tlg1p in the transport of proteins within the Golgi apparatus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
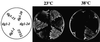
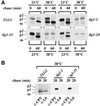
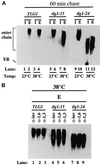
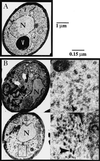
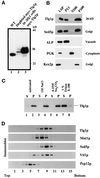
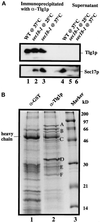
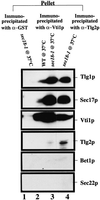
Members of the syntaxin protein family participate in the docking-fusion step of several intracellular vesicular transport events. Tlg1p has been identified as a nonessential protein required for efficient endocytosis as well as the maintenance of normal levels of trans-Golgi network proteins. In this study we independently describe Tlg1p as an essential protein required for cell viability. Depletion of Tlg1p in vivo causes a defect in the transport of the vacuolar protein carboxypeptidase Y through the early Golgi. Temperature-sensitive (ts) mutants of Tlg1p also accumulate the endoplasmic reticulum/cis-Golgi form of carboxypeptidase Y at the nonpermissive temperature (38 degrees C) and exhibit underglycosylation of secreted invertase. Overexpression of Tlg1p complements the growth defect of vti1-11 at the nonpermissive temperature, whereas incomplete complementation was observed with vti1-1, further suggesting a role for Tlg1p in the Golgi apparatus. Overexpression of Sed5p decreases the viability of tlg1 ts mutants compared with wild-type cells, suggesting that tlg1 ts mutants are more susceptible to elevated levels of Sed5p. Tlg1p is able to bind His6-tagged Sec17p (yeast alpha-SNAP) in a dose-dependent manner and enters into a SNARE complex with Vti1p, Tlg2p, and Vps45p. Morphological analyses by electron microscopy reveal that cells depleted of Tlg1p or tlg1 ts mutants incubated at the restrictive temperature accumulate 40- to 50-nm vesicles and experience fragmentation of the vacuole.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of a novel yeast SNARE protein implicated in Golgi retrograde traffic.Mol Biol Cell. 1997 Dec;8(12):2659-76. doi: 10.1091/mbc.8.12.2659. Mol Biol Cell. 1997. PMID: 9398683 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast v-SNARE Vti1p mediates two vesicle transport pathways through interactions with the t-SNAREs Sed5p and Pep12p.J Cell Biol. 1997 Jun 30;137(7):1511-24. doi: 10.1083/jcb.137.7.1511. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9199167 Free PMC article.
-
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae v-SNARE Vti1p is required for multiple membrane transport pathways to the vacuole.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Jun;10(6):1719-32. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.6.1719. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10359592 Free PMC article.
-
SNAREs and membrane fusion in the Golgi apparatus.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Aug 14;1404(1-2):9-31. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(98)00044-5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9714710 Review.
-
Proteins involved in vesicular transport and membrane fusion.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):615-20. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90031-s. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991. PMID: 1772655 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin-regulated trafficking of GLUT4 requires ubiquitination.Traffic. 2010 Nov;11(11):1445-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01113.x. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 20854370 Free PMC article.
-
The complexity of vesicle transport factors in plants examined by orthology search.PLoS One. 2014 May 20;9(5):e97745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097745. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24844592 Free PMC article.
-
The Tlg SNARE complex is required for TGN homotypic fusion.J Cell Biol. 2001 Dec 10;155(6):969-78. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200104093. Epub 2001 Dec 10. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11739408 Free PMC article.
-
Components of the SNARE-containing regulon are co-regulated in root cells undergoing defense.Plant Signal Behav. 2017 Feb;12(2):e1274481. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2016.1274481. Plant Signal Behav. 2017. PMID: 28010187 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Lipidation: Occurrence, Mechanisms, Biological Functions, and Enabling Technologies.Chem Rev. 2018 Feb 14;118(3):919-988. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00750. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Chem Rev. 2018. PMID: 29292991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abeliovich H, Grote E, Novick P, Ferro-Novick S. Tlg2p, a yeast syntaxin homolog that resides on the Golgi and endocytic structures. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:11719–11727. - PubMed
-
- Banfield DK, Lewis MJ, Pelham HRB. A SNARE-like protein required for traffic through the Golgi complex. Nature. 1995;375:806–809. - PubMed
-
- Berber G, Dumont J, Gilliquet V, Bolle P-A, Higler F. The YDp plasmids, a uniform set of vectors bearing a versatile gene disruption cassettes for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1991;7:475–477. - PubMed
-
- Bock JB, Lin RC, Scheller RH. A new syntaxin family member implicated in targeting of intracellular transport vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:17961–17965. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

