Fundamental signals that regulate eosinophil homing to the gastrointestinal tract
- PMID: 10377178
- PMCID: PMC408388
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI6560
Fundamental signals that regulate eosinophil homing to the gastrointestinal tract
Abstract
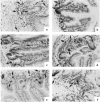
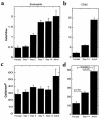
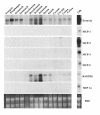
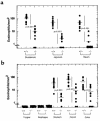
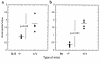
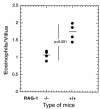
The histological identification of increased eosinophils in the gastrointestinal tract occurs in numerous clinical disorders; however, there is a limited understanding of the mechanisms regulating eosinophil trafficking into this mucosal surface. The results presented in this study characterize the processes regulating eosinophil homing into the gastrointestinal tract at baseline. Eosinophils were found to be present in the lamina propria of 19-day-old embryos and germ-free adult mice at concentrations comparable to those present in non-germ-free adult mice. Furthermore, eosinophil gastrointestinal levels were not altered by increasing circulating eosinophils after pulmonary allergen challenge. Gastrointestinal eosinophil levels were partially reduced in mice deficient in recombinase activating gene-1 (RAG-1), IL-5, or the beta common chain (betac), but these reductions paralleled reductions in circulating eosinophils. In contrast, mice deficient in eotaxin had a marked reduction in gastrointestinal eosinophils but normal levels of eosinophils in the hematopoietic compartments. Furthermore, eotaxin was important for regulating eosinophil levels, even in the presence of high levels of IL-5. These investigations demonstrate eosinophil homing into the gastrointestinal tract during embryonic development occurring independently of viable intestinal flora. Furthermore, eotaxin is identified as the primary regulator of eosinophil gastrointestinal homing under homeostatic states, and may therefore have a fundamental role in innate immune responses.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gastrointestinal eosinophils.Immunol Rev. 2001 Feb;179:139-55. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.790114.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11292017 Review.
-
Peyer's patch eosinophils: identification, characterization, and regulation by mucosal allergen exposure, interleukin-5, and eotaxin.Blood. 2000 Aug 15;96(4):1538-44. Blood. 2000. PMID: 10942403
-
Relationship between interleukin-5 and eotaxin in regulating blood and tissue eosinophilia in mice.J Clin Invest. 1997 Mar 1;99(5):1064-71. doi: 10.1172/JCI119234. J Clin Invest. 1997. PMID: 9062365 Free PMC article.
-
Murine eotaxin-2: a constitutive eosinophil chemokine induced by allergen challenge and IL-4 overexpression.J Immunol. 2000 Nov 15;165(10):5839-46. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.10.5839. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11067944
-
Elemental signals regulating eosinophil accumulation in the lung.Immunol Rev. 2001 Feb;179:173-81. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.790117.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11292021 Review.
Cited by
-
Granulocyte Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor-Activated Eosinophils Promote Interleukin-23 Driven Chronic Colitis.Immunity. 2015 Jul 21;43(1):187-99. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.07.008. Immunity. 2015. PMID: 26200014 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic concepts in adult and paediatric eosinophilic oesophagitis.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Dec;9(12):697-704. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2012.182. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 23007477 Review.
-
Negative regulation of eosinophil recruitment to the lung by the chemokine monokine induced by IFN-gamma (Mig, CXCL9).Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Feb 17;101(7):1987-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308544100. Epub 2004 Feb 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14769916 Free PMC article.
-
Gene targeting of chemokines and their receptors.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2000;22(4):417-32. doi: 10.1007/s002810000055. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2000. PMID: 11155444 Review. No abstract available.
-
Eosinophils in the gastrointestinal tract and their role in the pathogenesis of major colorectal disorders.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jul 21;25(27):3503-3526. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3503. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31367153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gleich GJ, Adolphson CR. The eosinophilic leukocyte: structure and function. Adv Immunol. 1986;39:177–253. - PubMed
-
- Weller PF. The immunobiology of eosinophils. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1110–1118. - PubMed
-
- Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilia. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1592–1600. - PubMed
-
- Furuta GT, Ackerman SJ, Wershil BK. The role of the eosinophil in gastrointestinal diseases. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 1995;1995:541–547.
-
- Sanderson CJ. Interleukin-5, eosinophils, and disease. Blood. 1992;79:3101–3109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

