Signaling by proinflammatory cytokines: oligomerization of TRAF2 and TRAF6 is sufficient for JNK and IKK activation and target gene induction via an amino-terminal effector domain
- PMID: 10346818
- PMCID: PMC316725
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.13.10.1297
Signaling by proinflammatory cytokines: oligomerization of TRAF2 and TRAF6 is sufficient for JNK and IKK activation and target gene induction via an amino-terminal effector domain
Abstract
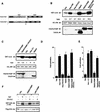
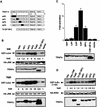
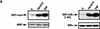
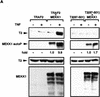
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF-alpha) stimulate transcription factors AP-1 and NF-kappaB through activation of the MAP kinases JNK and p38 and the IkappaB kinase (IKK), respectively. The TNF-alpha and IL-1 signals are transduced through TRAF2 and TRAF6, respectively. Overexpressed TRAF2 or TRAF6 activate JNK, p38, or IKK in the absence of extracellular stimulation. By replacing the carboxy-terminal TRAF domain of TRAF2 and TRAF6 with repeats of the immunophilin FKBP12, we demonstrate that their effector domains are composed of their amino-terminal Zn and RING fingers. Oligomerization of the TRAF2 effector domain results in specific binding to MEKK1, a protein kinase capable of JNK, p38, and IKK activation, and induction of TNF-alpha and IL-1 responsive genes. TNF-alpha also enhances the binding of native TRAF2 to MEKK1 and stimulates the kinase activity of the latter. Thus, TNF-alpha and IL-1 signaling is based on oligomerization of TRAF2 and TRAF6 leading to activation of effector kinases.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Requirement of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF)6 in interleukin 17 signal transduction.J Exp Med. 2000 Apr 3;191(7):1233-40. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.7.1233. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 10748240 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappa B-inducing kinase is a common mediator of IL-17-, TNF-alpha-, and IL-1 beta-induced chemokine promoter activation in intestinal epithelial cells.J Immunol. 1999 May 1;162(9):5337-44. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10228009
-
Differential requirements for tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor family proteins in CD40-mediated induction of NF-kappaB and Jun N-terminal kinase activation.J Biol Chem. 1999 Aug 6;274(32):22414-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.32.22414. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10428814
-
Activation of NF-kappaB by RANK requires tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6 and NF-kappaB-inducing kinase. Identification of a novel TRAF6 interaction motif.J Biol Chem. 1999 Mar 19;274(12):7724-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.12.7724. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10075662
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
Cited by
-
TRAF6-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase activation differentially regulates the production of interleukin-12 by macrophages in response to Toxoplasma gondii.Infect Immun. 2004 Oct;72(10):5662-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.5662-5667.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15385464 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF2-MLK3 interaction is essential for TNF-alpha-induced MLK3 activation.Cell Res. 2010 Jan;20(1):89-98. doi: 10.1038/cr.2009.125. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 19918265 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF)6 in interleukin 17 signal transduction.J Exp Med. 2000 Apr 3;191(7):1233-40. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.7.1233. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 10748240 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF2 exerts its antiapoptotic effect by regulating the expression of Krüppel-like factor LKLF.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Aug;23(16):5849-56. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.16.5849-5856.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12897154 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kappaB pathways by a Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K15 membrane protein.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(17):9346-58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9346-9358.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12915550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arch RH, Gedrich RW, Thompson CB. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs)—A family of adapter proteins that regulates life and death. Genes & Dev. 1998;12:2821–2830. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle PA, Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ, Karin M. Nuclear factor-κB—A pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. New Engl J Med. 1997;336:1066–1071. - PubMed
-
- Beg AA, Baldwin AS., Jr The IκB proteins: Multifunctional regulators of Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Genes & Dev. 1993;7:2064–2070. - PubMed
-
- Blank JL, Gerwins P, Elliott EM, Sather S, Johnson GL. Molecular cloning of mitogen-activated protein/ERK kinase kinases (MEKK) 2 and 3. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:5361–5368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
