Thrombin receptor mediated signals induce expressions of interleukin 6 and granulocyte colony stimulating factor via NF-kappa B activation in synovial fibroblasts
- PMID: 10343541
- PMCID: PMC1752754
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.58.1.55
Thrombin receptor mediated signals induce expressions of interleukin 6 and granulocyte colony stimulating factor via NF-kappa B activation in synovial fibroblasts
Abstract
Objective: To clarify the mechanism of thrombin receptor mediated signal transduction and the induction of cytokines by thrombin stimulation in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts.
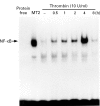
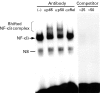
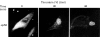
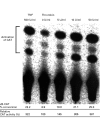
Methods: Cytokines were measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in the supernatants of cultured rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts stimulated by thrombin. To assess the mechanism of thrombin receptor mediated signal transduction in the rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts, electrophoretic mobility gel shift assay (EMSA), immunoglobulin kappa-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) assay, and immunostaining for NF-kappa B subunit molecule was performed.
Results: Thrombin stimulation activated the inducible transcription factor NF-kappa B, and then induced subsequent expressions of interleukin 6 (IL6) and granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) in the cells.
Conclusion: Thrombin receptor mediated signal transduction could induce the expressions of IL6 and G-CSF, and increase inflammatory events in the cavum articulare via NF-kappa B activation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Amplification of the synovial inflammatory response through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor kappaB using ligation of CD40 on CD14+ synovial cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Jul;50(7):2167-77. doi: 10.1002/art.20340. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. PMID: 15248214
-
Alteration of the cellular response to interleukin-1 beta by SV40 large T antigen in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts.Arch Virol. 1999;144(2):317-27. doi: 10.1007/s007050050506. Arch Virol. 1999. PMID: 10470256
-
Thrombin stimulates cell proliferation in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes in nuclear factor-kappaB activation and protein kinase C mediated pathway.J Rheumatol. 2000 Dec;27(12):2777-85. J Rheumatol. 2000. PMID: 11128663
-
Activation of synoviocytes.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2000 May;12(3):186-94. doi: 10.1097/00002281-200005000-00005. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2000. PMID: 10803747 Review.
-
Cytokine activation of transcription.Genet Eng (N Y). 2001;23:35-44. doi: 10.1007/0-306-47572-3_3. Genet Eng (N Y). 2001. PMID: 11570105 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Tissue factor as a proinflammatory agent.Arthritis Res. 2002;4(3):190-5. doi: 10.1186/ar405. Epub 2002 Jan 10. Arthritis Res. 2002. PMID: 12010569 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct functions of activated protein C differentially attenuate acute kidney injury.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Feb;20(2):267-77. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008030294. Epub 2008 Dec 17. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19092124 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombin induces heme oxygenase-1 expression in human synovial fibroblasts through protease-activated receptor signaling pathways.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 Apr 27;14(2):R91. doi: 10.1186/ar3815. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22541814 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the peptide C4b-binding protein beta in the arthritic joint.Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Oct;65(10):1279-85. doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.052118. Epub 2006 May 5. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. PMID: 16679431 Free PMC article.
-
Small GTP-binding protein Rho-mediated signaling promotes proliferation of rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(3):R476-84. doi: 10.1186/ar1694. Epub 2005 Feb 18. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 15899034 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
