Synaptotagmin II negatively regulates Ca2+-triggered exocytosis of lysosomes in mast cells
- PMID: 10330444
- PMCID: PMC2193646
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.10.1649
Synaptotagmin II negatively regulates Ca2+-triggered exocytosis of lysosomes in mast cells
Abstract
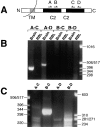
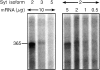
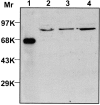
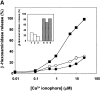
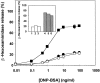
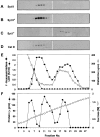
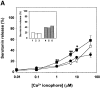
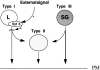
Synaptotagmins (Syts) I and II are believed to act as Ca2+ sensors in the control of neurotransmission. Here we demonstrate that mast cells express Syt II in their lysosomal fraction. We further show that activation of mast cells by either aggregation of FcepsilonRI or by Ca2+ ionophores results in exocytosis of lysosomes, in addition to the well documented exocytosis of their secretory granules. Syt II directly regulates lysosomal exocytosis, whereby overexpression of Syt II inhibited Ca2+-triggered release of the lysosomal processed form of cathepsin D, whereas suppression of Syt II expression markedly potentiated this release. These findings provide evidence for a novel function of Syt II in negatively regulating Ca2+-triggered exocytosis of lysosomes, and suggest that Syt II-regulated secretion from lysosomes may play an important role in mast cell biology.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Synaptotagmin regulates mast cell functions.Immunol Rev. 2001 Feb;179:25-34. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.790103.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11292024 Review.
-
Ca2+-dependent exocytosis in mast cells is stimulated by the Ca2+ sensor, synaptotagmin I.J Immunol. 1998 Nov 15;161(10):5120-3. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9820478
-
Synaptotagmin II negatively regulates MHC class II presentation by mast cells.Mol Immunol. 2002 Sep;38(16-18):1347-52. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00086-x. Mol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12217406
-
Synaptotagmin VII regulates Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis of lysosomes in fibroblasts.J Cell Biol. 2000 Mar 20;148(6):1141-49. doi: 10.1083/jcb.148.6.1141. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10725327 Free PMC article.
-
The mast cell: where endocytosis and regulated exocytosis meet.Immunol Rev. 2007 Jun;217:292-303. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2007.00516.x. Immunol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17498067 Review.
Cited by
-
Mast cells: a unique source of renin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Sep 14;101(37):13607-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403208101. Epub 2004 Sep 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15342908 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin VII restricts fusion pore expansion during lysosomal exocytosis.PLoS Biol. 2004 Aug;2(8):E233. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020233. Epub 2004 Jun 29. PLoS Biol. 2004. PMID: 15226824 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble N-Ethylmaleimide-Sensitive Factor Attachment Protein Receptor-Derived Peptides for Regulation of Mast Cell Degranulation.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 11;9:725. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00725. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29696021 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormalities caused by carbohydrate alterations in Ibeta6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-deficient mice.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Sep;25(17):7828-38. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.17.7828-7838.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16107727 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian diaphanous-related formin 1 (mDia1) coordinates mast cell migration and secretion through its actin-nucleating activity.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Oct;144(4):1074-1090. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.06.028. Epub 2019 Jul 3. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31279009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stevens RL, Austen KF. Recent advance in the cellular and molecular biology of mast cells. Immunol Today. 1989;10:381–385. - PubMed
-
- Galli SJ, Gordon JR, Wershil BK. Cytokine production by mast cells and basophils. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991;3:865–872. - PubMed
-
- Metcalfe DD, Kaliner M, Donlon MA. The mast cell. Crit Rev Immunol. 1981;3:23–74. - PubMed
-
- Malaviya R, Ikeda T, Ross E, Abraham SN. Mast cell modulation of neutrophil influx and bacterial clearance at sites of infection through TNF-alpha. Nature. 1996;381:77–80. - PubMed
-
- Prodeus AP, Zhou X, Maurer M, Galli SJ, Carroll MC. Impaired mast cell-dependent natural immunity in complement C3-deficient mice. Nature. 1997;390:172–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

