Trafficking of Shigella lipopolysaccharide in polarized intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 10330399
- PMCID: PMC2133196
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.145.4.689
Trafficking of Shigella lipopolysaccharide in polarized intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
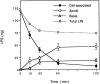
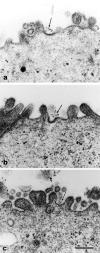
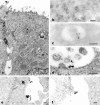
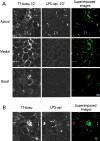
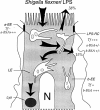
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) at the apical surface of polarized intestinal epithelial cells was previously shown to be transported from the apical to the basolateral pole of the epithelium (Beatty, W.L., and P.J. Sansonetti. 1997. Infect. Immun. 65:4395-4404). The present study was designed to elucidate the transcytotic pathway of LPS and to characterize the endocytic compartments involved in this process. Confocal and electron microscopic analyses revealed that LPS internalized at the apical surface became rapidly distributed within endosomal compartments accessible to basolaterally internalized transferrin. This compartment largely excluded fluid-phase markers added at either pole. Access to the basolateral side of the epithelium subsequent to trafficking to basolateral endosomes occurred via exocytosis into the paracellular space beneath the intercellular tight junctions. LPS appeared to exploit other endocytic routes with much of the internalized LPS recycled to the original apical membrane. In addition, analysis of LPS in association with markers of the endocytic network revealed that some LPS was sent to late endosomal and lysosomal compartments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Shigella flexneri Interactions with the Basolateral Membrane Domain of Polarized Model Intestinal Epithelium: Role of Lipopolysaccharide in Cell Invasion and in Activation of the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase ERK.Infect Immun. 2002 Mar;70(3):1150-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.3.1150-1158.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 11854195 Free PMC article.
-
Basolateral to apical transcytosis in polarized cells is indirect and involves BFA and trimeric G protein sensitive passage through the apical endosome.J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):83-100. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.83. J Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 7905002 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-mediated transcytosis of IgA in MDCK cells is via apical recycling endosomes.J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(1):67-86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.1.67. J Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 8138576 Free PMC article.
-
Sorting of membrane and fluid at the apical pole of polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Jun;11(6):2131-50. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.6.2131. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10848634 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between lipopolysaccharide and the intestinal epithelium.J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2004 May 1;224(9):1446-52. doi: 10.2460/javma.2004.224.1446. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2004. PMID: 15124884 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-8 controls bacterial transepithelial translocation at the cost of epithelial destruction in experimental shigellosis.Infect Immun. 1999 Mar;67(3):1471-80. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.3.1471-1480.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10024597 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharides transport during fat absorption in rodent small intestine.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Jun 1;318(6):G1070-G1087. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00079.2020. Epub 2020 May 11. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32390462 Free PMC article.
-
Endotoxin-induced alterations of adipose tissue function: a pathway to bovine metabolic stress.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Apr 6;15(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s40104-024-01013-8. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38581064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular recognition of lipopolysaccharide by toll-like receptor 4 in intestinal epithelial cells.J Exp Med. 2003 Oct 20;198(8):1225-35. doi: 10.1084/jem.20022194. J Exp Med. 2003. PMID: 14568981 Free PMC article.
-
Proinflammatory signal transduction pathway induced by Shigella flexneri porins in caco-2 cells.Braz J Microbiol. 2009 Jul;40(3):701-13. doi: 10.1590/S1517-838220090003000036. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Braz J Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 24031417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aracil FM, Bosch MA, Municio AM. Influence of E. colilipopolysaccharide binding to rat alveolar type II cells on their functional properties. Mol Cell Biochem. 1985;68:59–66. - PubMed

