Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infectivity by the ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
- PMID: 10074203
- PMCID: PMC104113
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.4.3460-3466.1999
Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infectivity by the ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
Abstract
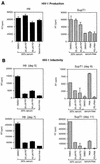
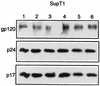
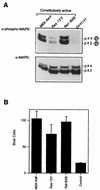
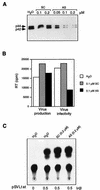
ERK1 and ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) play a critical role in regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation in response to mitogens and other extracellular stimuli. Mitogens and cytokines that activate MAPK in T cells have been shown to activate human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) replication. Little is known about the signal transduction pathways that activate HIV-1 replication in T cells upon activation by extracellular stimulation. Here, we report that activation of MAPK through the Ras/Raf/MEK signaling pathway enhances the infectivity of HIV-1 virions. Virus infectivity was enhanced by treatment of cells with MAPK stimulators, such as serum and phorbol myristate acetate, as well as by coexpression of constitutively activated Ras, Raf, or MEK (MAPK kinase) in the absence of extracellular stimulation. Treatment of cells with PD 098059, a specific inhibitor of MAPK activation, or with a MAPK antisense oligonucleotide reduced the infectivity of HIV-1 virions without significantly affecting virus production or the levels of virion-associated Gag and Env proteins. MAPK has been shown to regulate HIV-1 infectivity by phosphorylating Vif (X. Yang and D. Gabuzda, J. Biol. Chem. 273:29879-29887, 1998). However, MAPK activation enhanced virus infectivity in some cells lines that do not require Vif function. The HIV-1 Rev, Tat, p17(Gag), and Nef proteins were directly phosphorylated by MAPK in vitro, suggesting that other HIV-1 proteins are potential substrates for MAPK phosphorylation. These results suggest that activation of the ERK MAPK pathway plays a role in HIV-1 replication by enhancing the infectivity of HIV-1 virions through Vif-dependent as well as Vif-independent mechanisms. MAPK activation in producer cells may contribute to the activation of HIV-1 replication when T cells are activated by mitogens and other extracellular stimuli.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Signaling through the P38 and ERK pathways: a common link between HIV replication and the immune response.Immunol Res. 2010 Dec;48(1-3):99-109. doi: 10.1007/s12026-010-8170-1. Immunol Res. 2010. PMID: 20725863 Review.
-
ERK MAP kinase links cytokine signals to activation of latent HIV-1 infection by stimulating a cooperative interaction of AP-1 and NF-kappaB.J Biol Chem. 1999 Sep 24;274(39):27981-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.39.27981. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10488148
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylates and regulates the HIV-1 Vif protein.J Biol Chem. 1998 Nov 6;273(45):29879-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.45.29879. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9792705
-
Modulation of HIV-1 infectivity by MAPK, a virion-associated kinase.EMBO J. 1998 May 1;17(9):2607-18. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.9.2607. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9564043 Free PMC article.
-
ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Mar;19(3):1997-2007. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8454. Epub 2020 Jan 15. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32104259 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HIV Genome-Wide Protein Associations: a Review of 30 Years of Research.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Jun 29;80(3):679-731. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00065-15. Print 2016 Sep. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27357278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Up-regulation of hepatitis C virus replication and production by inhibition of MEK/ERK signaling.PLoS One. 2009 Oct 16;4(10):e7498. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007498. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19834602 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of coronavirus replication by inhibition of the MEK signaling pathway.J Virol. 2007 Jan;81(2):446-56. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01705-06. Epub 2006 Nov 1. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17079328 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic characterization of HIV-modulated membrane receptors, kinases and signaling proteins involved in novel angiogenic pathways.J Transl Med. 2009 Aug 27;7:75. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-7-75. J Transl Med. 2009. PMID: 19712456 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling through the P38 and ERK pathways: a common link between HIV replication and the immune response.Immunol Res. 2010 Dec;48(1-3):99-109. doi: 10.1007/s12026-010-8170-1. Immunol Res. 2010. PMID: 20725863 Review.
References
-
- Alessi D R, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley D T, Saltiel P. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
-
- Bandres J C, Luria S, Ratner L. Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus nef protein by phosphorylation. Virology. 1994;201:157–161. - PubMed
-
- Bodéus M, Marie-Cardine A, Bougeret C, Ramos-Morales F, Benarous R. In vitro binding and phosphorylation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef protein by serine/threonine protein kinase. J Gen Virol. 1995;76:1337–1344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

