Effects of human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early proteins in controlling the cell cycle and inhibiting apoptosis: studies with ts13 cells
- PMID: 10074130
- PMCID: PMC104040
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.4.2825-2831.1999
Effects of human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early proteins in controlling the cell cycle and inhibiting apoptosis: studies with ts13 cells
Abstract
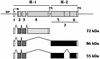
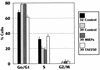
The major immediate-early (MIE) gene of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) encodes several MIE proteins (MIEPs) produced as a result of alternative splicing and polyadenylation of the primary transcript. Previously we demonstrated that the HCMV MIEPs expressed from the entire MIE gene could rescue the temperature-sensitive (ts) transcriptional defect in the ts13 cell line. This defect is caused by a ts mutation in TAFII250, the 250-kDa TATA binding protein-associated factor (TAF). These and other data suggested that the MIEPs perform a TAF-like function in complex with the basal transcription factor TFIID. In addition to the transcriptional defect, the ts mutation in ts13 cells results in a defect in cell cycle progression which ultimately leads to apoptosis. Since all of these defects can be rescued by wild-type TAFII250, we asked whether the MIEPs could rescue the cell cycle defect and/or affect the progression to apoptosis. We have found that the MIEPs, expressed from the entire MIE gene, do not rescue the cell cycle block in ts13 cells grown at the nonpermissive temperature. However, despite the maintenance of the cell cycle block, the ts13 cells which express the MIEPs are resistant to apoptosis. MIEP mutants, which have previously been shown to be defective in rescuing the ts transcriptional defect, maintained the ability to inhibit apoptosis. Hence, the MIEP functions which affect transcription appear to be separable from the functions which inhibit apoptosis. We discuss these data in the light of the HCMV life cycle and the possibility that the MIEPs promote cellular transformation by a "hit-and-run" mechanism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early proteins and simian virus 40 large T antigen can inhibit apoptosis through activation of the phosphatidylinositide 3'-OH kinase pathway and the cellular kinase Akt.J Virol. 2002 Apr;76(8):3731-8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.8.3731-3738.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11907212 Free PMC article.
-
TAF-like functions of human cytomegalovirus immediate-early proteins.J Virol. 1997 Oct;71(10):7227-39. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.10.7227-7239.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9311796 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Oncogenic Alleles Induces Multiple Blocks to Human Cytomegalovirus Infection.J Virol. 2016 Apr 14;90(9):4346-4356. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00179-16. Print 2016 May. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26889030 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene expression.Intervirology. 1996;39(5-6):331-42. doi: 10.1159/000150504. Intervirology. 1996. PMID: 9130043 Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus latency is associated with the state of differentiation of the host cells: an in vitro model in teratocarcinoma cells.Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2005;52(3-4):397-406. doi: 10.1556/AMicr.52.2005.3-4.11. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2005. PMID: 16400879 Review.
Cited by
-
HCMV Infection and Apoptosis: How Do Monocytes Survive HCMV Infection?Viruses. 2018 Sep 29;10(10):533. doi: 10.3390/v10100533. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30274264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence that the human cytomegalovirus IE2-86 protein binds mdm2 and facilitates mdm2 degradation.J Virol. 2006 Apr;80(8):3833-43. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.8.3833-3843.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16571800 Free PMC article.
-
The human cytomegalovirus immediate early 2 protein dissociates cellular DNA synthesis from cyclin-dependent kinase activation.EMBO J. 2001 Mar 1;20(5):1086-98. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.5.1086. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11230132 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus protein pUL38 induces ATF4 expression, inhibits persistent JNK phosphorylation, and suppresses endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death.J Virol. 2009 Apr;83(8):3463-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02307-08. Epub 2009 Feb 4. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19193809 Free PMC article.
-
The human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein can block cell cycle progression after inducing transition into the S phase of permissive cells.J Virol. 2000 Aug;74(15):7108-18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.15.7108-7118.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10888651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baracchini E, Glezer E, Fish K, Stenberg R M, Nelson J A, Ghazal P. An isoform variant of the cytomegalovirus immediate-early auto repressor functions as a transcriptional activator. Virology. 1992;188:518–529. - PubMed
-
- Biegalke B J, Geballe A P. Sequence requirements for activation of the HIV-1 LTR by human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1991;183:381–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

