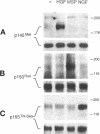
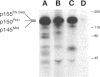
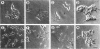
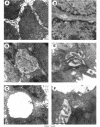
Abstract
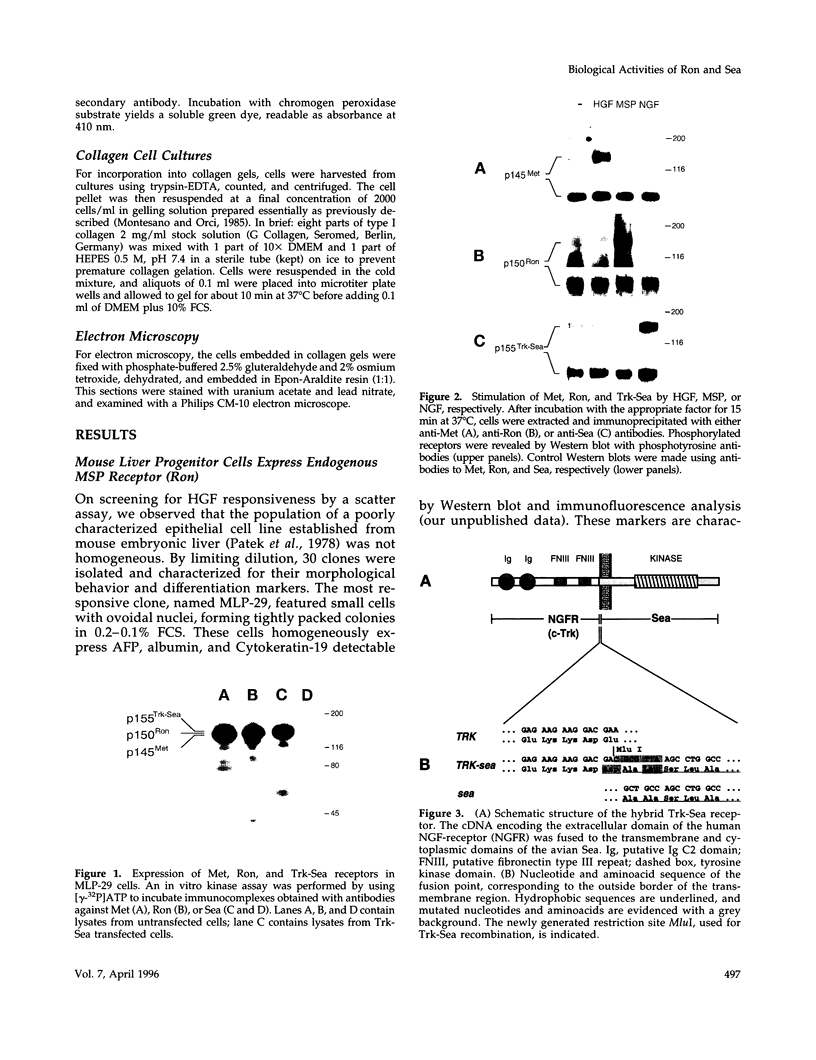
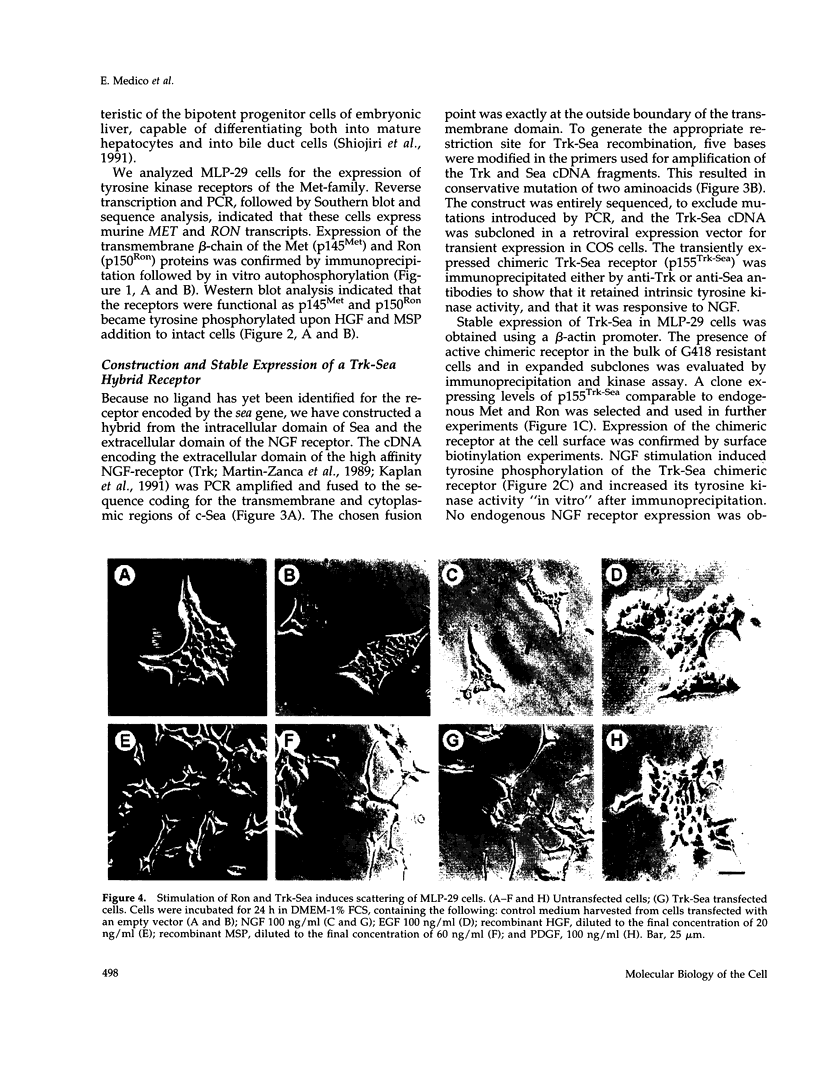
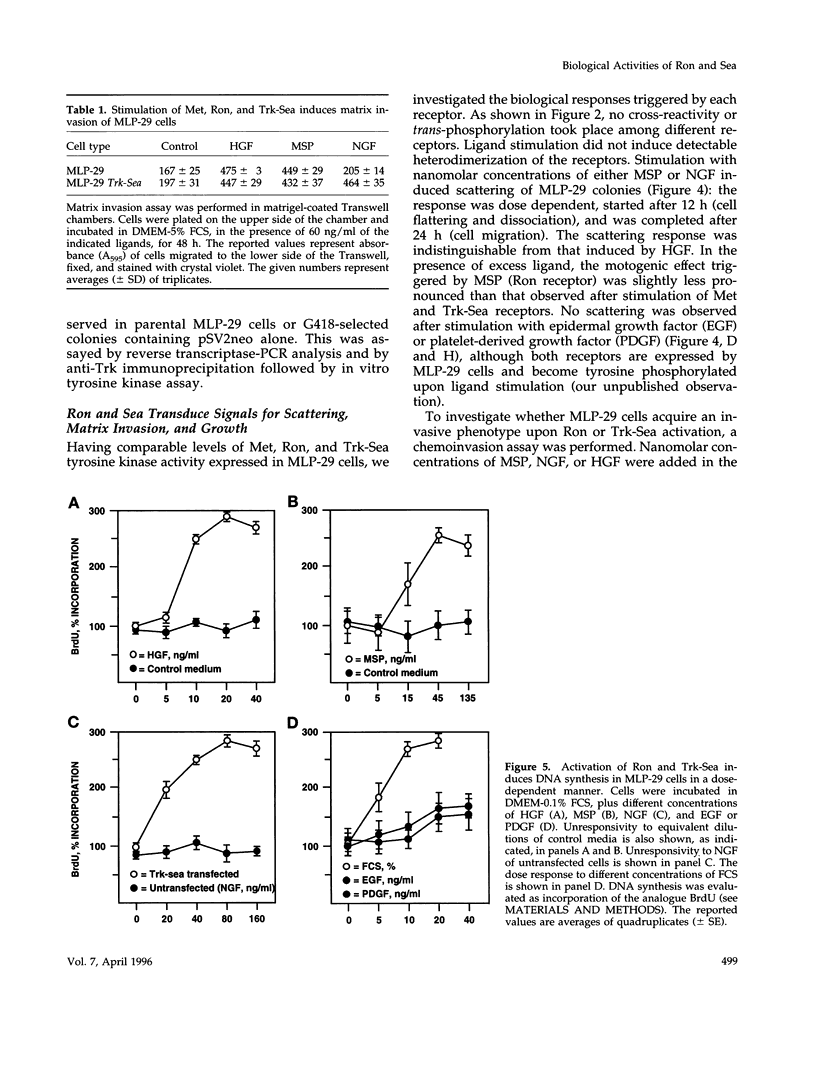
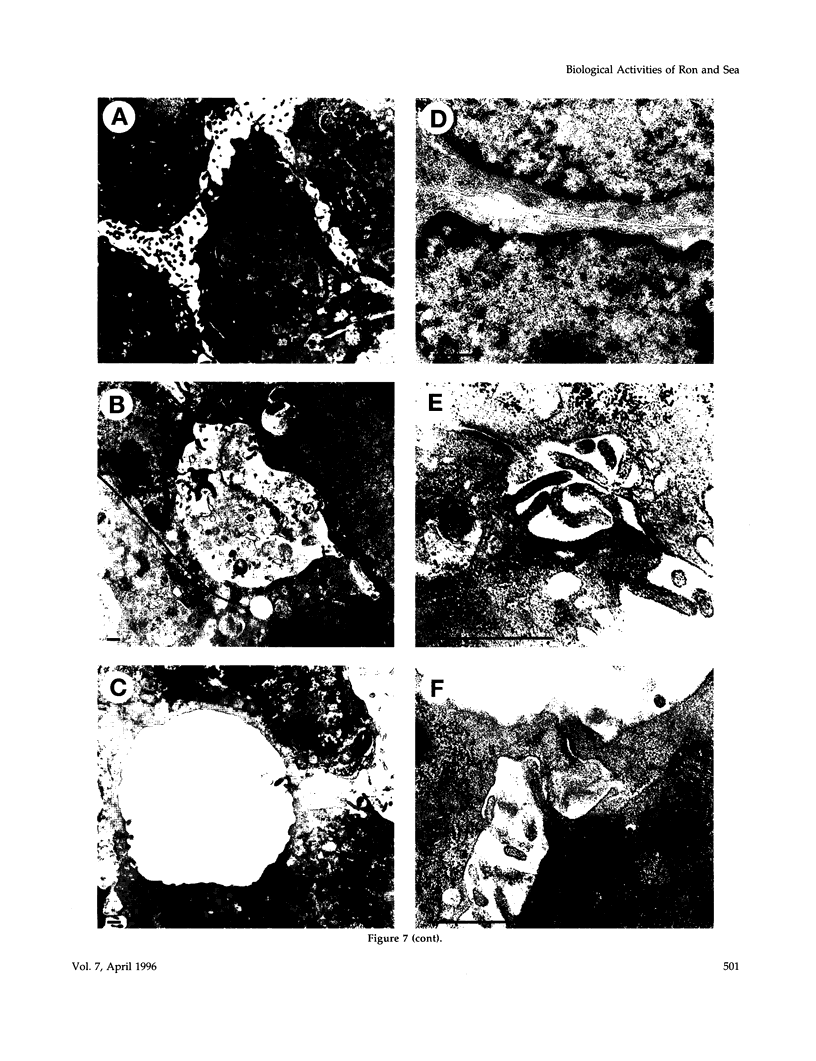
The mammalian RON and the avian sea genes encode tyrosine kinase receptors of poorly characterized biological functions. We recently identified macrophage-stimulating protein as the ligand for Ron; no ligand has yet been found for Sea. In this work we investigated the biological response to macrophage-stimulating protein in mouse liver progenitor cells expressing Ron. These cells were also transfected with a chimeric cDNA encoding the cytoplasmic domain of Sea, fused to the extracellular domain of Trk (nerve growth factor receptor). In the presence of nanomolar concentrations of the respective ligands, both receptors induced cell "scattering", extracellular matrix invasion, and DNA synthesis. When liver progenitor cells were grown in a tri-dimensional type-I collagen matrix, ligand-induced stimulation of either Ron or Sea induced sprouting of branched cell cords, evolving into ductular-like tubules. The motogenic, mitogenic, and morphogenic responses were also elicited by triggering the structurally related hepatocyte growth factor receptor (Met) but not epidermal growth factor or platelet-derived growth factor receptors. These data show that Ron, Sea, and Met belong to a receptor subfamily that elicits a distinctive biological response in epithelial cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Faletto D. L., Chan A. M., Kmiecik T. E., Vande Woude G. F., Aaronson S. A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.1846706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S. The basics of basal transcription by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Di Renzo M. F., Ziche M., Bocchietto E., Olivero M., Naldini L., Gaudino G., Tamagnone L., Coffer A., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor is a potent angiogenic factor which stimulates endothelial cell motility and growth. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):629–641. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T. Signalling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:453–481. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudino G., Avantaggiato V., Follenzi A., Acampora D., Simeone A., Comoglio P. M. The proto-oncogene RON is involved in development of epithelial, bone and neuro-endocrine tissues. Oncogene. 1995 Dec 21;11(12):2627–2637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudino G., Follenzi A., Naldini L., Collesi C., Santoro M., Gallo K. A., Godowski P. J., Comoglio P. M. RON is a heterodimeric tyrosine kinase receptor activated by the HGF homologue MSP. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3524–3532. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherardi E., Gray J., Stoker M., Perryman M., Furlong R. Purification of scatter factor, a fibroblast-derived basic protein that modulates epithelial interactions and movement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5844–5848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherardi E., Sharpe M., Lane K., Sirulnik A., Stoker M. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF), the c-met receptor and the behaviour of epithelial cells. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1993;47:163–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano S., Ponzetto C., Di Renzo M. F., Cooper C. S., Comoglio P. M. Tyrosine kinase receptor indistinguishable from the c-met protein. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):155–156. doi: 10.1038/339155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano S., Zhen Z., Medico E., Gaudino G., Galimi F., Comoglio P. M. Transfer of motogenic and invasive response to scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor by transfection of human MET protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):649–653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gohda E., Tsubouchi H., Nakayama H., Hirono S., Sakiyama O., Takahashi K., Miyazaki H., Hashimoto S., Daikuhara Y. Purification and partial characterization of hepatocyte growth factor from plasma of a patient with fulminant hepatic failure. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):414–419. doi: 10.1172/JCI113334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani A., Gramaglia D., Cantley L. C., Comoglio P. M. The tyrosine-phosphorylated hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor associates with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22087–22090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani A., Gramaglia D., dalla Zonca P., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor stimulates the Ras-guanine nucleotide exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9165–9168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halaban R., Rubin J. S., Funasaka Y., Cobb M., Boulton T., Faletto D., Rosen E., Chan A., Yoko K., White W. Met and hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor signal transduction in normal melanocytes and melanoma cells. Oncogene. 1992 Nov;7(11):2195–2206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. C., Burns K. D., Alattar M., Homma T., Nakamura T. Hepatocyte growth factor stimulates phosphoinositide hydrolysis and mitogenesis in cultured renal epithelial cells. Life Sci. 1993;52(13):1091–1100. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90430-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann G., Weidner K. M., Schwarz H., Birchmeier W. The motility signal of scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor mediated through the receptor tyrosine kinase met requires intracellular action of Ras. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 2;269(35):21936–21939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J. The sea oncogene of the avian erythroblastosis virus S13. Pathol Immunopathol Res. 1987;6(5-6):390–399. doi: 10.1159/000157065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff J. L., Jelinek M. A., Borgman C. A., Lansing T. J., Parsons J. T. The protooncogene c-sea encodes a transmembrane protein-tyrosine kinase related to the Met/hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6140–6144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwama A., Okano K., Sudo T., Matsuda Y., Suda T. Molecular cloning of a novel receptor tyrosine kinase gene, STK, derived from enriched hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 1994 Jun 1;83(11):3160–3169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan M., Zhang G. H., Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G., Myoken Y., McKeehan W. L., Stevens J. I. Hepatocyte growth factor/hepatopoietin A stimulates the growth of rat kidney proximal tubule epithelial cells (RPTE), rat nonparenchymal liver cells, human melanoma cells, mouse keratinocytes and stimulates anchorage-independent growth of SV-40 transformed RPTE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 15;174(1):331–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90524-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F. The trk proto-oncogene product: a signal transducing receptor for nerve growth factor. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.1850549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Ohi H., Sugimura M., Shinohara H., Fujii T., Terao T. Inhibition of in vitro ovarian cancer cell invasion by modulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and cathepsin B. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 1;52(13):3610–3614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard E. J., Skeel A. H. Enhancement of spreading, phagocytosis and chemotaxis by macrophage stimulating protein (MSP). Adv Exp Med Biol. 1979;121B:181–194. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8914-9_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Oskam R., Mitra G., Copeland T., Barbacid M. Molecular and biochemical characterization of the human trk proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):24–33. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa K., Tsubouchi H., Naka D., Takahashi K., Okigaki M., Arakaki N., Nakayama H., Hirono S., Sakiyama O., Takahashi K. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human hepatocyte growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 15;163(2):967–973. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92316-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Matsumoto K., Nakamura T., Orci L. Identification of a fibroblast-derived epithelial morphogen as hepatocyte growth factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Orci L. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters induce angiogenesis in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):469–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuchi A., Takeichi M. Cell binding function of E-cadherin is regulated by the cytoplasmic domain. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3679–3684. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03249.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Nishizawa T., Hagiya M., Seki T., Shimonishi M., Sugimura A., Tashiro K., Shimizu S. Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):440–443. doi: 10.1038/342440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Teramoto H., Ichihara A. Purification and characterization of a growth factor from rat platelets for mature parenchymal hepatocytes in primary cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6489–6493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Vigna E., Bardelli A., Follenzi A., Galimi F., Comoglio P. M. Biological activation of pro-HGF (hepatocyte growth factor) by urokinase is controlled by a stoichiometric reaction. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):603–611. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Vigna E., Narsimhan R. P., Gaudino G., Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G. K., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) stimulates the tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor encoded by the proto-oncogene c-MET. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):501–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M., Dean M., Kaul K., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Vande Woude G. Sequence of MET protooncogene cDNA has features characteristic of the tyrosine kinase family of growth-factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6379–6383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patek P. Q., Collins J. L., Cohn M. Transformed cell lines susceptible or resistant to in vivo surveillance against tumorigenesis. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):510–511. doi: 10.1038/276510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Schlessingert J. SH2 and SH3 domains. Curr Biol. 1993 Jul 1;3(7):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90350-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci G., Giordano S., Zhen Z., Salcini A. E., Lanfrancone L., Bardelli A., Panayotou G., Waterfield M. D., Ponzetto C., Pelicci P. G. The motogenic and mitogenic responses to HGF are amplified by the Shc adaptor protein. Oncogene. 1995 Apr 20;10(8):1631–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Bardelli A., Maina F., Longati P., Panayotou G., Dhand R., Waterfield M. D., Comoglio P. M. A novel recognition motif for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding mediates its association with the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4600–4608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronsin C., Muscatelli F., Mattei M. G., Breathnach R. A novel putative receptor protein tyrosine kinase of the met family. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1195–1202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. S., Chan A. M., Bottaro D. P., Burgess W. H., Taylor W. G., Cech A. C., Hirschfield D. W., Wong J., Miki T., Finch P. W. A broad-spectrum human lung fibroblast-derived mitogen is a variant of hepatocyte growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):415–419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90177-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiojiri N., Lemire J. M., Fausto N. Cell lineages and oval cell progenitors in rat liver development. Cancer Res. 1991 May 15;51(10):2611–2620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeel A., Yoshimura T., Showalter S. D., Tanaka S., Appella E., Leonard E. J. Macrophage stimulating protein: purification, partial amino acid sequence, and cellular activity. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1227–1234. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker M., Gherardi E., Perryman M., Gray J. Scatter factor is a fibroblast-derived modulator of epithelial cell mobility. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):239–242. doi: 10.1038/327239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. H., Cox G. W., Yoshimura T., Sheffler L. A., Skeel A., Leonard E. J. Macrophage-stimulating protein inhibits induction of nitric oxide production by endotoxin- or cytokine-stimulated mouse macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14027–14031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. H., Iwama A., Skeel A., Suda T., Leonard E. J. The murine stk gene product, a transmembrane protein tyrosine kinase, is a receptor for macrophage-stimulating protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3933–3937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. H., Ronsin C., Gesnel M. C., Coupey L., Skeel A., Leonard E. J., Breathnach R. Identification of the ron gene product as the receptor for the human macrophage stimulating protein. Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):117–119. doi: 10.1126/science.7939629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner K. M., Behrens J., Vandekerckhove J., Birchmeier W. Scatter factor: molecular characteristics and effect on the invasiveness of epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):2097–2108. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner K. M., Sachs M., Birchmeier W. The Met receptor tyrosine kinase transduces motility, proliferation, and morphogenic signals of scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor in epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):145–154. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Yuhki N., Wang M. H., Skeel A., Leonard E. J. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of human macrophage stimulating protein (MSP, MST1) confirms MSP as a member of the family of kringle proteins and locates the MSP gene on chromosome 3. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15461–15468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G. Purification and biological characterization of human hepatopoietin A, a polypeptide growth factor for hepatocytes. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 15;49(12):3314–3320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]