Abstract
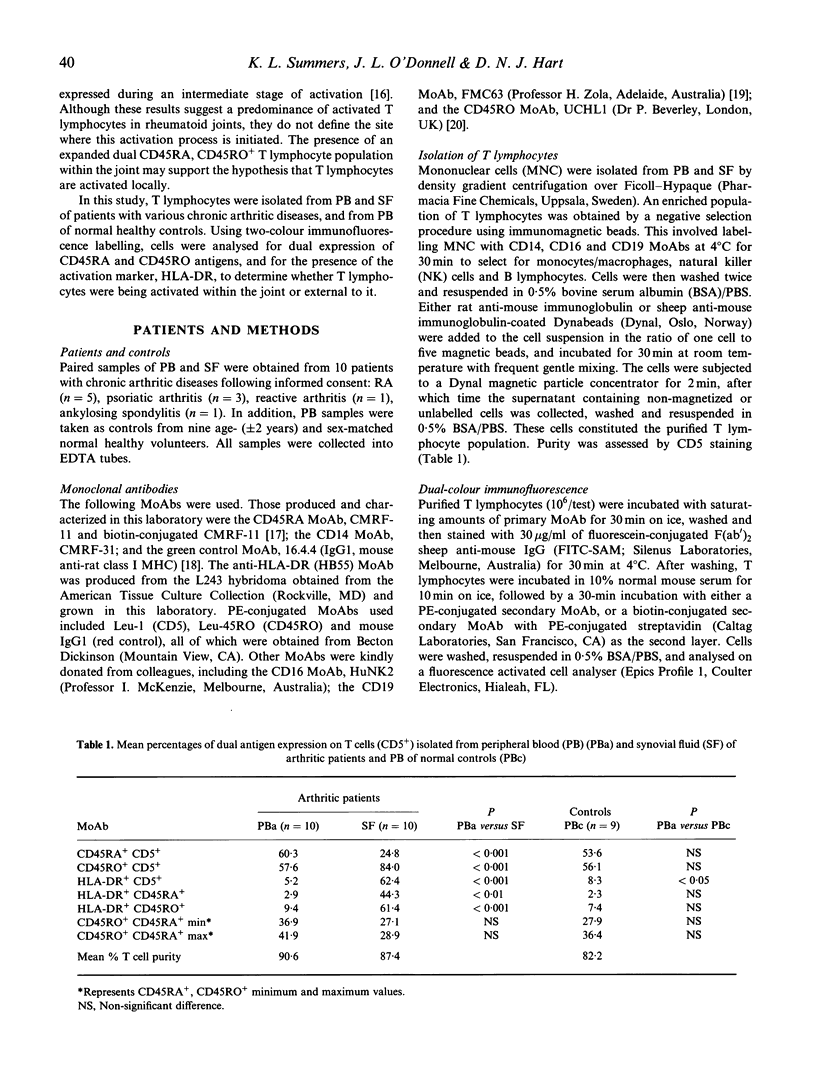
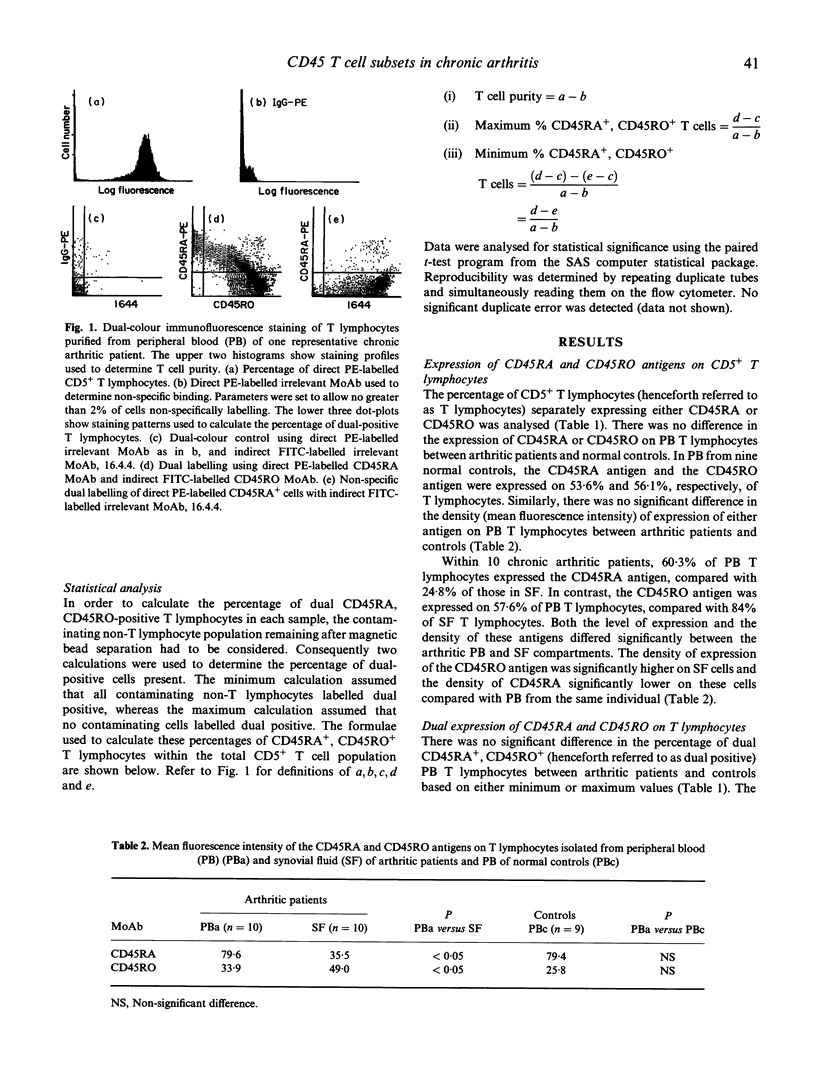
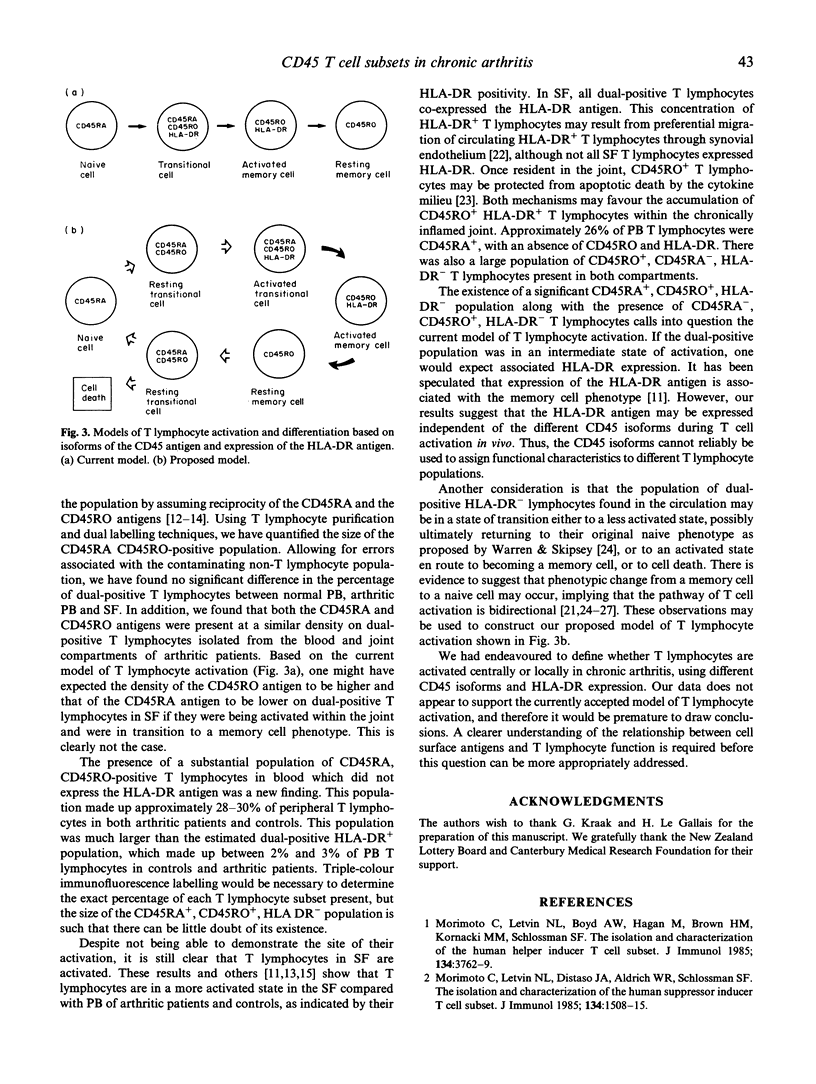
The site of T lymphocyte activation in chronic arthritis is unknown. Peripheral blood (PB) lymphocytes from chronic arthritis patients are in a 'naive' or non-activated state, as defined by expression of the CD45RA antigen and lack of HLA class II expression. In contrast, most synovial fluid (SF) T lymphocytes express a 'memory' or activated phenotype, as defined by the CD45RO antigen and high HLA class II expression. Following stimulation, naive cells lose CD45RA and gain CD45RO expression to become memory cells with a transitional stage of dual CD45RA, CD45RO antigen expression. To localize where this change in phenotype occurs we used dual colour immunofluorescence labelling to compare the percentage of dual CD45RA, CD45RO-positive T lymphocytes in PB and SF from chronic arthritic patients and from normal PB, assuming this population would be increased at the primary site of T lymphocyte activation. Expression of the intermediate and late activation marker, HLA-DR, was also analysed using dual colour immunofluorescence labelling. The percentage of dual positive T lymphocytes was similar between arthritic PB, SF, and normal PB, as was the density of both CD45RA and CD45RO antigens. Thus, CD45 isoform expression did not indicate where T lymphocytes were activated. However, we identified a previously unreported population of CD45RA+ CD45RO+ HLA-DR- T lymphocytes in arthritic and normal PB. In SF, this population was absent, but a substantial number of dual CD45RA, CD45RO-positive HLA-DR+ T lymphocytes were identified. This population would not be predicted by the current model of T lymphocyte activation. Division of T lymphocytes into functional groups on the basis of CD45 isoform expression is likely to be more complicated than previously thought. Based on our findings we propose an alternative model of T lymphocyte differentiation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akbar A. N., Terry L., Timms A., Beverley P. C., Janossy G. Loss of CD45R and gain of UCHL1 reactivity is a feature of primed T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2171–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akbar A. N., Timms A., Janossy G. Cellular events during memory T-cell activation in vitro: the UCHL1 (180,000 MW) determinant is newly synthesized after mitosis. Immunology. 1989 Feb;66(2):213–218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cush J. J., Pietschmann P., Oppenheimer-Marks N., Lipsky P. E. The intrinsic migratory capacity of memory T cells contributes to their accumulation in rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Dec;35(12):1434–1444. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii Y., Okumura M., Inada K., Nakahara K. Reversal of CD45R isoform switching in CD8+ T cells. Cell Immunol. 1992 Jan;139(1):176–184. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90110-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanly J. G., Pledger D., Parkhill W., Roberts M., Gross M. Phenotypic characteristics of dissociated mononuclear cells from rheumatoid synovial membrane. J Rheumatol. 1990 Oct;17(10):1274–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoy M. D., O'Donnell J. L., Hart D. N. Dual CD45RA, CD45RO positive T-lymphocytes within rheumatoid arthritic joints. Pathology. 1993 Apr;25(2):167–173. doi: 10.3109/00313029309084793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y., Shimizu H., Yoshida M., Takaya M., Arimori S. Accessory molecules expressed on the peripheral blood or synovial fluid T lymphocytes from patients with Sjögren's syndrome or rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992 Sep-Oct;10(5):447–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko H. S., Fu S. M., Winchester R. J., Yu D. T., Kunkel H. G. Ia determinants on stimulated human T lymphocytes. Occurrence on mitogen- and antigen-activated T cells. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):246–255. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensson K., Borrebaeck C. A., Carlsson R. Human CD4+ T cells expressing CD45RA acquire the lymphokine gene expression of CD45RO+ T-helper cells after activation in vitro. Immunology. 1992 May;76(1):103–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensson K., Dohlsten M., Fischer H., Ericsson P. O., Hedlund G., Sjögren H. O., Carlsson R. Phenotypical and functional differentiation of CD4+ CD45RA+ human T cells following polyclonal activation. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Sep;32(3):243–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaSalle J. M., Hafler D. A. The coexpression of CD45RA and CD45RO isoforms on T cells during the S/G2/M stages of cell cycle. Cell Immunol. 1991 Nov;138(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90144-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky H. P., Bauer K., Pope R. M. Increased helper inducer and decreased suppressor inducer phenotypes in the rheumatoid joint. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jan;31(1):52–59. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie C. A., McLean A., Alcock C., Beverley P. C. Lifespan of human lymphocyte subsets defined by CD45 isoforms. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):264–265. doi: 10.1038/360264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Boyd A. W., Hagan M., Brown H. M., Kornacki M. M., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human helper inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3762–3769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Distaso J. A., Aldrich W. R., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human suppressor inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao H., Eguchi K., Kawakami A., Migita K., Otsubo T., Ueki Y., Shimomura C., Tezuka H., Matsunaga M., Maeda K. Phenotypic characterization of lymphocytes infiltrating synovial tissue from patients with rheumatoid arthritis: analysis of lymphocytes isolated from minced synovial tissue by dual immunofluorescent staining. J Rheumatol. 1990 Feb;17(2):142–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Treer J. R., Ferguson-Darnell B., Collins P. A., Buck D., Terstappen L. W. Control of lymphocyte recirculation in man. I. Differential regulation of the peripheral lymph node homing receptor L-selectin on T cells during the virgin to memory cell transition. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):1105–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitzalis C., Kingsley G., Murphy J., Panayi G. Abnormal distribution of the helper-inducer and suppressor-inducer T-lymphocyte subsets in the rheumatoid joint. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Nov;45(2):252–258. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein D. M., Sohen S., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. CD4+CD45RA+ and CD4+CD45RA- T cell subsets in man maintain distinct function and CD45RA expression persists on a subpopulation of CD45RA+ cells after activation with Con A. Cell Immunol. 1990 Sep;129(2):449–467. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90220-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein D. M., Yamada A., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Cyclic regulation of CD45 isoform expression in a long term human CD4+CD45RA+ T cell line. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1175–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., Roberts-Thomson P. J. Lymphocyte surface marker expression in rheumatic diseases: evidence for prior activation of lymphocytes in vivo. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Feb;49(2):81–87. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.2.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. H., Brown M. H., Rowe D., Callard R. E., Beverley P. C. Functional subsets of human helper-inducer cells defined by a new monoclonal antibody, UCHL1. Immunology. 1986 May;58(1):63–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starling G. C., Davidson S. E., McKenzie J. L., Hart D. N. Inhibition of natural killer-cell mediated cytolysis with monoclonal antibodies to restricted and non-restricted epitopes of the leucocyte common antigen. Immunology. 1987 Jul;61(3):351–356. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara T., Miyawaki T., Ohta K., Tamaru Y., Yokoi T., Nakamura S., Taniguchi N. Apoptotic cell death of primed CD45RO+ T lymphocytes in Epstein-Barr virus-induced infectious mononucleosis. Blood. 1992 Jul 15;80(2):452–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren H. S., Skipsey L. J. Loss of activation-induced CD45RO with maintenance of CD45RA expression during prolonged culture of T cells and NK cells. Immunology. 1991 Sep;74(1):78–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zola H., MacArdle P. J., Bradford T., Weedon H., Yasui H., Kurosawa Y. Preparation and characterization of a chimeric CD19 monoclonal antibody. Immunol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;69(Pt 6):411–422. doi: 10.1038/icb.1991.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


