Abstract
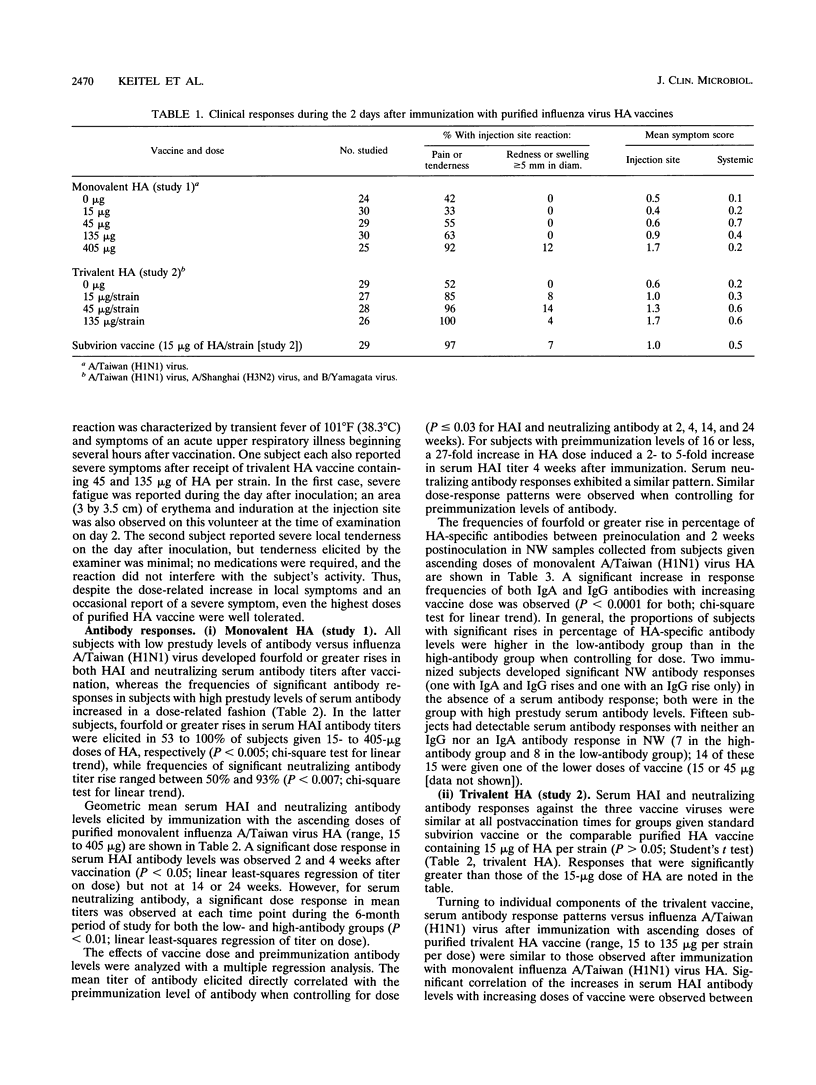
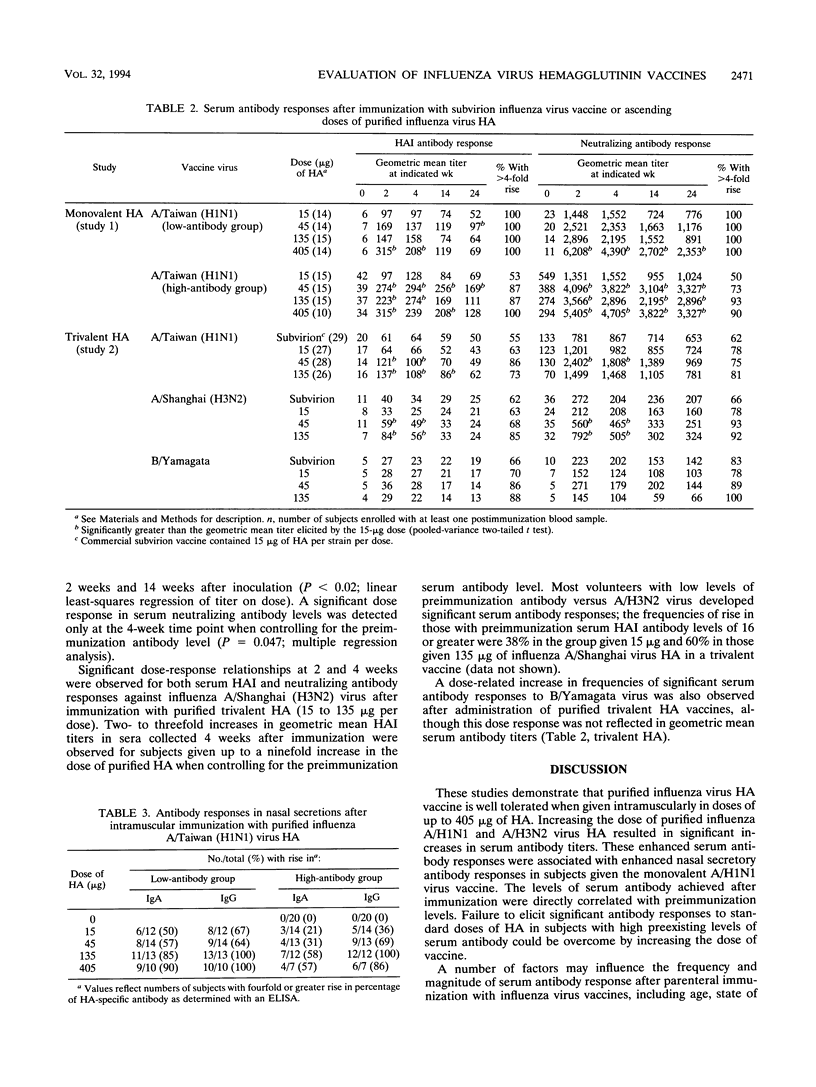
The reactogenicity and immunogenicity of purified influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA) vaccines administered intramuscularly were evaluated in two placebo-controlled clinical trials. A total of 139 healthy young adults were randomized to receive increasing doses of monovalent influenza A/Taiwan/1/86 (H1N1) virus HA (range, 0 to 405 micrograms per dose [study 1]). An additional 139 subjects were given increasing doses of a trivalent HA vaccine containing equal amounts of A/H1N1 virus, A/Shanghai/16/89 (H3N2) virus, and influenza B/Yamagata/16/88 virus HA (range, 0 to 135 micrograms of HA per strain, 0 to 405 micrograms per dose) or a standard dose of commercial influenza vaccine (study 2). Increasing doses of HA were associated with increasing frequencies of symptoms at the vaccination site early after vaccination, but all doses were well tolerated. Occurrence of systemic symptoms was unrelated to dose. Increasing the dose of HA resulted in increasingly higher postimmunization levels of serum hemagglutination inhibiting and neutralizing antibody levels versus influenza A/H1N1 virus in study 1 (P < 0.05); these enhanced responses persisted for up to 6 months. Nasal secretory immunoglobulin A and G antibody responses were assessed 2 weeks after immunization with monovalent H1N1 virus HA; the frequencies of significant responses also increased in a dose-related fashion. Similar increases in serum antibody levels were noted for both A/H1N1 and A/H3N2 viruses in study 2. These data provide a basis for proceeding with the evaluation of high doses of purified HA in the elderly.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caplan E. S., Hughes T. P., O'Donnel S., Levine M. M., Hornick R. B. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity of parenteral monovalent influenza A/Victoria/3/75 (H3N2) virus vaccine in healthy adults. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136 (Suppl):S484–S490. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_3.s484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cate T. R., Couch R. B., Parker D., Baxter B. Reactogenicity, immunogenicity, and antibody persistence in adults given inactivated influenza virus vaccines - 1978. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):737–747. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements M. L., Murphy B. R. Development and persistence of local and systemic antibody responses in adults given live attenuated or inactivated influenza A virus vaccine. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):66–72. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.66-72.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch R. B., Webster R. G., Kasel J. A., Cate T. R. Efficacy of purified influenza subunit vaccines and relation to the major antigenic determinants on the hemagglutinin molecule. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):553–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdle W. R., Coleman M. T., Mostow S. R., Kaye H. S., Schoenbaum S. C. Inactivated influenza vaccines. 2. Laboratory indices of protection. Postgrad Med J. 1973 Mar;49(569):159–163. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.49.569.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feery B. J., Hampson A. W., Forsyth J. R., Evered M. G. Effect of dose on antibody response to subunit influenza vaccine. Med J Aust. 1977 Sep 3;2(10):324–327. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1977.tb99166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank A. L., Puck J., Hughes B. J., Cate T. R. Microneutralization test for influenza A and B and parainfluenza 1 and 2 viruses that uses continuous cell lines and fresh serum enhancement. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):426–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.426-432.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorse G. J., Belshe R. B., Munn N. J. Local and systemic antibody responses in high-risk adults given live-attenuated and inactivated influenza A virus vaccines. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):911–918. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.911-918.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorse G. J., Belshe R. B., Munn N. J. Superiority of live attenuated compared with inactivated influenza A virus vaccines in older, chronically ill adults. Chest. 1991 Oct;100(4):977–984. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.4.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gremillion D. H., Meiklejohn G., Graves P., I J. Efficacy of single-dose influenza in Air Force recruits. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;147(6):1099–1099. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.6.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. A., Quinnan G. V., Jr, Weksler M. E., Gaerlan P. F., Denning C. R. Immunization of elderly people with high doses of influenza vaccine. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1988 Mar;36(3):209–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1988.tb01802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasel J. A., Fulk R. V., Togo Y., Hornick R. B., Heiner G. G., Dawkins A. T., Jr, Mann J. J. Influenza antibody in human respiratory secretions after subcutaneous or respiratory immunization with inactivated virus. Nature. 1968 May 11;218(5141):594–595. doi: 10.1038/218594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keitel W. A., Couch R. B., Cate T. R., Six H. R., Baxter B. D. Cold recombinant influenza B/Texas/1/84 vaccine virus (CRB 87): attenuation, immunogenicity, and efficacy against homotypic challenge. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):22–26. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight V., Couch R. B., Douglas R. G., Tauraso N. M. Serological responses and results of natural infectious challenge of recipients of zonal ultracentrifuged influenza A2-Aichi-2-68 vaccine. Bull World Health Organ. 1971;45(6):767–771. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Montagne J. R., Noble G. R., Quinnan G. V., Curlin G. T., Blackwelder W. C., Smith J. I., Ennis F. A., Bozeman F. M. Summary of clinical trials of inactivated influenza vaccine - 1978. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):723–736. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J. J., Waldman R. H., Togo Y., Heiner G. G., Dawkins A. T., Kasel J. A. Antibody response in respiratory secretions of volunteers given live and dead influenza virus. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):726–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzkin H., Nili E. Accidental tenfold overdose of influenza vaccine: a clinical and serological study. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 May;20(5):411–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palache A. M., Beyer W. E., Lüchters G., Völker R., Sprenger M. J., Masurel N. Influenza vaccines: the effect of vaccine dose on antibody response in primed populations during the ongoing interpandemic period. A review of the literature. Vaccine. 1993;11(9):892–908. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palache A. M., Beyer W. E., Sprenger M. J., Masurel N., de Jonge S., Vardy A., Charpentier B., Noury J., van Beek W. C., Borst R. J. Antibody response after influenza immunization with various vaccine doses: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-centre, dose-response study in elderly nursing-home residents and young volunteers. Vaccine. 1993;11(1):3–9. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90333-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers D. C., Sears S. D., Murphy B. R., Thumar B., Clements M. L. Systemic and local antibody responses in elderly subjects given live or inactivated influenza A virus vaccines. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2666–2671. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2666-2671.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben F. L., Jackson G. G. A new subunit influenza vaccine: acceptability compared with standard vaccines and effect of dose on antigenicity. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):656–664. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben F. L., Potter C. W., Stuart-Harris C. H. Humoral and secretory antibody responses to immunization with low and high dosage split influenza virus vaccine. Arch Virol. 1975;47(2):157–166. doi: 10.1007/BF01320555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbaum S. C., Mostow S. R., Dowdle W. R., Coleman M. T., Kaye H. S. Studies with inactivated influenza vaccines purified by zonal centrifugation. 2. Efficacy. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;41(3):531–535. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears S. D., Clements M. L., Betts R. F., Maassab H. F., Murphy B. R., Snyder M. H. Comparison of live, attenuated H1N1 and H3N2 cold-adapted and avian-human influenza A reassortant viruses and inactivated virus vaccine in adults. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1209–1219. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. M., Monto A. S., Foster D. A. Antibody response to inactivated influenza vaccines of various antigenic concentrations. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):333–335. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treanor J. J., Mattison H. R., Dumyati G., Yinnon A., Erb S., O'Brien D., Dolin R., Betts R. F. Protective efficacy of combined live intranasal and inactivated influenza A virus vaccines in the elderly. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Oct 15;117(8):625–633. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-8-625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahradnik J. M., Kasel J. A., Martin R. R., Six H. R., Cate T. R. Immune responses in serum and respiratory secretions following vaccination with a live cold-recombinant (CR35) and inactivated A/USSR/77 (H1N1) influenza virus vaccine. J Med Virol. 1983;11(4):277–285. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890110403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


