Abstract
Background
The prediction of breast cancer intrinsic subtypes has been introduced as a valuable strategy to determine patient diagnosis and prognosis, and therapy response. The PAM50 method, based on the expression levels of 50 genes, uses a single sample predictor model to assign subtype labels to samples. Intrinsic errors reported within this assay demonstrate the challenge of identifying and understanding the breast cancer groups. In this study, we aim to: a) identify novel biomarkers for subtype individuation by exploring the competence of a newly proposed method named CM1 score, and b) apply an ensemble learning, as opposed to the use of a single classifier, for sample subtype assignment. The overarching objective is to improve class prediction.
Methods and Findings
The microarray transcriptome data sets used in this study are: the METABRIC breast cancer data recorded for over 2000 patients, and the public integrated source from ROCK database with 1570 samples. We first computed the CM1 score to identify the probes with highly discriminative patterns of expression across samples of each intrinsic subtype. We further assessed the ability of 42 selected probes on assigning correct subtype labels using 24 different classifiers from the Weka software suite. For comparison, the same method was applied on the list of 50 genes from the PAM50 method.
Conclusions
The CM1 score portrayed 30 novel biomarkers for predicting breast cancer subtypes, with the confirmation of the role of 12 well-established genes. Intrinsic subtypes assigned using the CM1 list and the ensemble of classifiers are more consistent and homogeneous than the original PAM50 labels. The new subtypes show accurate distributions of current clinical markers ER, PR and HER2, and survival curves in the METABRIC and ROCK data sets. Remarkably, the paradoxical attribution of the original labels reinforces the limitations of employing a single sample classifiers to predict breast cancer intrinsic subtypes.
Introduction
Breast cancer has been perceived as several distinct diseases characterised by intrinsic aberrations, heterogeneous behaviour and divergent clinical outcome [1]. The classification of breast cancer in discernible molecular subtypes has motivated translational researchers in the past decades towards the design of patient prognosis and the development of tailored treatments [2]. In this scenario, the analysis of breast tumours using microarray data has significantly improved the disease taxonomy and the discovery of new biomarkers for implementation in clinical practice [3–6]. In the early 2000s, five intrinsic subtypes were proposed: luminal A, luminal B, HER2-enriched, normal-like and basal-like breast tumours [7, 8]. Following this initial molecular taxonomy, further sub-classifications of breast cancer in distinct entities have been suggested [9–11].
The transcriptomic patterns observed across subtypes has given us insight into the molecular complexity and inherent alterations in tumour cells modelling the breast cancer heterogeneity and unpredicted outcome [12, 13]. Strikingly, intrinsic gene lists have been explored to reliably assign breast tumour samples into formal molecular subtypes, survival rate and treatment outline [3, 7, 8, 14–18]. Recently, Parker and colleagues [16] proposed a list of 50 genes that together with the Prediction Analysis for Microarrays (PAM) classification algorithm [19] aimed at identifying subtypes and enlarging the prognostic information with high potential for validation in clinical settings [16, 20, 21]. The resulting technique, called the PAM50 method, has been widely applied to categorize tumours into one of the five classical intrinsic subtypes.
Although independent cohorts attempted to identify molecular subtypes, the chosen microarray-based Single Sample Predictor (SSP) model revealed unreliable assignments and modest agreement between studies [21, 22]. In fact, the perceived inability of some analytical methods to deal with the challenges of processing high-dimensional data, in addition to the difficulties on validating independent/unpaired technologies may limit the precise characterisation of the subtypes [21, 23, 24]. Therefore, novel methods are urgently needed in order to provide better tumour stratification and accurate biomarkers identification [25, 26]. In this scenario, the high quality of the microarray gene expression data set processed by the Molecular Taxonomy of Breast Cancer International Consortium (METABRIC) [27], with over 2000 samples, offers a unique opportunity to refine and expand the list of transcripts that best discriminate intrinsic subtypes. A precise classification of breast tumours, consequently, would lead to improvements in the valuation of the disease, currently guided by oestrogen and progesterone receptor (ER and PR) status, and HER2 amplification [24, 28].
In this report, we focus on the use of a ranking feature method based on the newly proposed CM1 score [29] to identify probe sets that appear naturally from the METABRIC breast cancer data set. For doing so, we use the entire set of 48803 probes as an alternative to the selection from pre-existing literature as performed by other authors [15, 16]. Moreover, the quality of the probes for predicting subtypes is carefully appraised in the METABRIC data set (Illumina BeadArray) and further validated in different studies (Affymetrix GeneChip) accessed through the Research Online Cancer Knowledgebase (ROCK) interface [30]. However, instead of relying on a single method to assign sample subtype, as suggested by Parker et al. (2009) [16] with the PAM50 method, we explore an ensemble learning. Our analysis is based on the performance of a large set of classification models from the Weka software suite [31]; a technique previously recommended by Ravetti and Moscato [32]. The classifiers are used in combination with the list of probes selected using CM1 score and, alternatively, with the 50 genes from the PAM50 commercial assay [16]. We also compute several statistical measures to determine the power of both lists on predicting breast cancer subtypes. Ultimately, we correlate the study outcomes within current clinical information and survival analysis.
Materials and Methods
Data sets description
The METABRIC microarray data set used in this study is hosted by the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) and deposited in the European Genome-Phenome Archive (EGA) at http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ega/, under accession number EGAS00000000083. It consists of transcriptomic information (cDNA microarrays profiling) processed on the Illumina HT-12 v3 platform (Illumina_Human_WG-v3), as described in [27]. The log2-normalised gene expression values of primary tumours were divided into two subsets by METABRIC: discovery (997 samples) and validation (989 samples), which were respectively used as training and test sets in our experiments. The original study collected and analysed data under the approval of the ethics Institutional Review Board (details in [27]). The use of this data for research was also approved by the Human Ethics Research Committee (HREC) of The University of Newcastle, Australia, (approval number: H-2013–0277).
The second data set is publicly available in ROCK online portal [30] at http://rock.icr.ac.uk/, under data source access GSE47561. This source integrates ten data studies (GSE2034, GSE11121, GSE20194, GSE1456, GSE2603, GSE6532, GSE20437, E-TABM-185, GSE7390, GSE5847) performed on the Affymetrix Human Genome U133A Array (HG-U133A) platform. The matrix contains log2 RMA re-normalised gene expression data in a unique comprehensive report of 1570 samples. Thus, the GSE47561 data set was used as a second validation set to test our method.
In brief, both METABRIC and ROCK data sets have information on patients’ long-term clinical and pathological outcomes, including the sample assignment into intrinsic subtypes (luminal A, luminal B, HER2-enriched, normal-like, and basal-like) according to the PAM50 method [16]. The METABRIC data set has a more comprehensive description of patient clinical features, whereas the ROCK data set presents no standardized information across the ten different studies.
Study Design and Computing Resources
In this study, we propose a systematic approach that aims at improving breast cancer subtype prediction. The systematic approach is built based on feature selection and data mining concepts. We first compute the CM1 score—using the microarray mRNA expression values—to rank the whole set of probes based on their discriminative power across breast cancer subtypes. We then select the top 10 probes that best represent each intrinsic subtype. The quality of this selection is assessed using a set of classifiers from the Weka software suite with the METABRIC and ROCK data sets, followed by the statistical analysis. The process flow is depicted in Fig 1, and further explained in the remainder of this section.
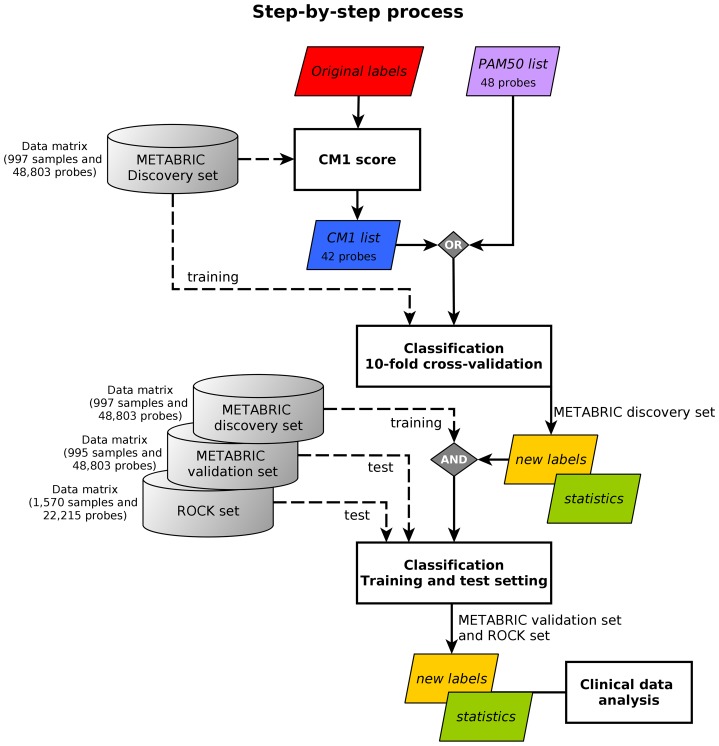
Fig 1. The step-by-step process.
The image shows the method steps based on CM1 score and ensemble learning. The METABRIC discovery set is used to compute the CM1 score, based on the original labels previously assigned with the PAM50 method. This step has an output of 42 discriminative probes selected, the CM1 list. The following step involve the sample subtype classification based on a 10-fold cross-validation. Samples in the METABRIC discovery set are considered to train 24 classifiers using the CM1 list and, alternatively, the PAM50 list. The samples are partitioned into ten folds; then a model is built using 90% of samples, which is used to predict the labels of the remaining 10%. After the ten turns are finished, the level of association between the predicted and original METABRIC labels is computed using several statistics. In the training-test setting, labels of samples in the METABRIC validation set and ROCK set are predicted with the models built in the discovery. Statistics measurements are again computed to assess the model performance on predicting breast cancer subtypes. In both classification steps, the new labels are attributed based on the consensus of the majority of the classifiers. Finally, the results or new labels are compared against the clinical data, the current markers ER, PR and HER2, and survival curves.
Selection of biomarkers using the CM1 score
The CM1 score is a supervised univariate method used to measure the difference in expression levels of samples in two different classes [29]. In this study, it is used as a ranking feature to select a subset of highly discriminative probes for each breast cancer intrinsic subtype. Let X and Y be a partition of a set of samples into two classes, with X the class of interest and Y the remaining classes. A sample either belongs to X or to Y. For each probe i we compute the CM1 score as:
| (1) |
where is the average expression value of the probe i for samples in class X, is the average expression value of the probe i for samples in class Y; max{y i} and min{y i} are the minimum and maximum expression values of the probe i for samples in the class Y. Eq 1 can be interpreted as the normalised difference between the averages of expression values in the class X and Y. The normalisation is proportional to the range of values in Y.
To define the most discriminative probes for each breast cancer subtype (luminal A, luminal B, HER2-enriched, normal-like and basal-like), we computed the CM1 score for each of 48803 probes taking the subtype of interest and the remaining ones. This results in 5 lists of 48803 CM1 scores.
Considering the fact that Parker et al. (2009) [16] were able to define the five breast cancer classes based on 50 genes, for each subtype we chose the 10 most important probes (5 with the greatest positive CM1 score values—indicating up-regulated probes relative to the other subtypes –, and 5 with the smallest negative values – representing down-regulation). This set is referred to as the balanced top ten in this paper. Collecting the balanced top ten lists of all subtypes leads to a new set of 42 unique Illumina probes, meaning that 8 probes appear in multiple subtypes. This list is hereafter called the CM1 list.
Assessment of the quality of the CM1 list based on ensemble learning
The quality of the CM1 list for distinguishing subtypes was assessed using a list of well-known classifiers available in the Weka data mining software suite [31]. It uses different types of classifiers such as bayesian, functions, lazy, meta, rule-based and decision trees. Each classifier was trained with a subset of the data comprising all samples in the METABRIC discovery set and the 42 probes in the CM1 list using both 10-fold cross-validation and training-test setting. In the 10-fold cross-validation, the samples are first partitioned into ten folds; then a model is built using 90% of samples, which is thereafter used to predict the labels of the remaining 10%. After the ten turns are finished, the level of association between the predicted and original METABRIC labels is computed using Cramer’s V [33]. In the training-test setting, labels of samples in the METABRIC validation set and ROCK data are predicted using models built with the samples in the discovery set. The new labels were attributed based on the consensus of the majority of the classifiers (i.e. more than 50% percent), and whenever such condition was not achieved samples were marked as inconsistent (INC).
A similar approach was performed with the PAM50 list to serve as baseline for comparing the results obtained with the 42 probes from the CM1 list. The 50 genes identified by Parker et al. (2009) [16] were mapped to Illumina probes by Curtis et al. (2012) [27], following strict criteria. Only genes and corresponding probe with perfect annotation [34] on the Illumina HT-12 v3 BeadChip were considered. Probes containing SNPs, multiple targets or mismatches, or lying in repeat-masked regions were discarded. Finally, a total of 48 probes corresponding to genes in the PAM50 list were selected to conduct the classification experiments as described for the CM1 list. For Affymetrics HG-U133A, the CM1 and PAM50 lists were mapped according to ‘genefu’ R package, using Entrez Gene ID as reference. For instance, the 42 probes from the CM1 list matched 33 probes, whereas the 48 from PAM50 list paired 43 probes in the Affymetrix platform. In case of multiple mappings the probe with the most variation was selected according to the ‘genefu’ instructions. Before testing the classifiers in ROCK data set, the Affymetrix and Illumina expression levels were min-max normalised.
The statistical analysis
Cramer’s V
Given a r × c contingency table describing the association between the original labels and those predicted by the majority of classifiers, Cramer’s V measures the level of association between those two nominal variables. The statistic ranges from 0, representing no association between the two variables, to 1, representing complete association. Cramer’s V is computed using Eq 2.
| (2) |
where N is the number of samples in the data set, and χ 2 is Pearson’s chi-squared value.
Average sensitivity (AS)
The average sensitivity (AS) [31] was also computed to assess the performance of classifiers with both lists. The AS is the average proportion of accurately classified samples of each subtype. Considering a r × c contingency table associating initial and predicted labels, the average sensitivity of a classifier is given by Eq 3.
| (3) |
where r is the number of classes (subtypes), n ii is the number of samples of class i correctly predicted as i, and n i• is the number of samples of class i (row marginals).
Fleiss’ kappa
The consensus of the different classification methods concerning the samples’ labels was measured by the popular interrater reliability metric Fleiss’ kappa [35, 36]. The statistic was used to gauge not only the agreement among classifiers trained with the different probe sets, but also between the labels assigned by the majority of classifiers and the original METABRIC labels. It also quantifies the agreement between predicted labels using the CM1 and PAM50 lists.
Assuming a s × c contingency table informing how many times each of the c classes were assigned to each of the s samples in the k different sample labellings, the Fleiss’ kappa statistic is computed as defined by Eq 4.
| (4) |
where n ij contains the number of times sample i was assigned label j, ∑j n ij = k, and p j = (∑i n ij)/sk is the probability with which the label j is assigned to a sample.
Kappa values range from to +1, which, according to Landis and Koch’s division [37], can be interpreted in the following manner: (1) values below zero are considered poor agreement; (2) values between zero and 0.2 are considered slight agreement; (3) 0.21 ≤ κ ≤ 0.40 is fair agreement; (4) 0.41 ≤ κ ≤ 0.60 moderate agreement; (5) 0.61 ≤ κ ≤ 0.80 substantial agreement; and (6) 0.81 ≤ κ ≤ 1 is regarded as an almost perfect agreement.
Adjusted Rand Index
The agreement between pairs of sample labellings was also quantified using this metric. It ranges between 0 to 1, where 1 indicates an almost perfect concordance between the two compared bipartitions, and 0 a complete discordance between them. The Adjusted Rand Index is a version of Rand index corrected for chance when the partitions are picked at random [38, 39]. Given a r × c contingency table between two labelling R and C, it can be measured by:
| (5) |
where 1 ≤ i ≤ r, 1 ≤ j ≤ c, and n ij is an entry of the contingency table representing the number of samples that are in class R i in the partition R and C j in the partition C, n i• and n •j are the table’s marginals.
Survival analysis
The survival analysis for each breast cancer subtype is performed using Cox proportional hazards model from the package survival in the R software [40, 41]. Only patients who either died due to the disease or are still alive are considered for model estimation. The clinical parameters relevant for the survival study are chosen in correspondence with Curtis et al. (2012) [27]: age at the time of diagnosis, tumor size, tumor grade, the number of positive lymph nodes and ER status according to immunohistochemistry. Since the probability model based on the observations available at certain time points becomes less and less reliable with the increasing time, the median survival lines based on the last 10 observations are plotted in dash. Due to the compilation of ten different studies and the existence of significant gaps in patients’ clinical information, the survival curves in the ROCK data set are not representative across subtypes. In particular, the number of patients with information about overall survival and disease free survival is limited to only 405, with no specification on the cause of death (i.e. if due to disease or not).
Results
Section description and resources
To understand the results described in this section, we introduce the sequence of our approach which combines the CM1 score and ensemble learning. First, we detail the selection of discriminative probes ranked according to the CM1 score; calculated for each of the five breast cancer subtypes. Second, we show the quality of our probes by using 24 classification models based on a 10-fold cross-validation and training-test setting in the METABRIC and ROCK data sets. The same approach is also performed with the list of 50 genes used in the PAM50 method. In addition, statistical analysis are reported to determine the power of both lists on predicting breast cancer subtypes. Finally, we demonstrate the consistency between the new labels assigned with current clinical markers ER, PR and HER2, and survival curves. The step-by-step approach is detailed in the Materials and Methods section.
Using the CM1 list to differentiate the five intrinsic breast cancer subtypes
The CM1 score was applied to rank the set of 48803 probes for each of the five subtypes in the METABRIC discovery data set (Supporting Information S1 Table). It is important to remark that this method used the original PAM50 subtypes attributed to samples in the METABRIC discovery set. The purpose of doing so is to provide a better molecular characterisation of each class using the wealth of the METABRIC transcriptomic data, besides improving the breast cancer subtype prediction. The probes with the top five negative and top five positive CM1 scores were selected for each subtype. Here, we aimed at obtaining 50 probes that appear naturally from a rich and unique data set. We would then be able to compare such a list with the list of 50 genes embedded in the PAM50 method [16]—the PAM50 list. The final list comprising the union of the top ranked probes is displayed in Table 1, and their CM1 scores and ranks in each subtype in Table 2. Some of the 50 probes selected, however, discriminate more than one subtype and resulted in a list of 42 unique elements, the CM1 list. Our selection includes 30 novel biomarkers, while the remaining 12 genes are common with the PAM50 list.
Table 1. CM1 list.
| Probe ID | Gene name | Gene symbol and aliases | [Refs.] |
|---|---|---|---|
| ILMN_1684217 | Aurora kinase B | AURKB; AIK2, AIM1, ARK2, AurB, IPL1, STK5, AIM-1, STK12, PPP1R48, aurkb-sv1, aurkb-sv2 | [42–54] |
| ILMN_1683450 | Cell division cycle associated 5 | CDCA5; SORORIN | [55–58] |
| ILMN_1747016 | Centrosomal protein 55kDa | CEP55; CT111, URCC6, C10orf3 | [59–62] |
| ILMN_2212909 | Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase | MELK; HPK38 | [63–69] |
| ILMN_1714730 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2C | UBE2C; UBCH10, dJ447F3.2 | [70–74] |
| ILMN_1796059 | Ankyrin repeat domain 30A | ANKRD30A; NY-BR-1, RP11–20F24.1 | [75–82] |
| ILMN_1651329 | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 993 | LINC00993 | |
| ILMN_2310814 | Microtubule-associated protein tau | MAPT; TAU, MSTD, PPND, DDPAC, MAPTL, MTBT1, MTBT2, FTDP-17 | [83–89] |
| ILMN_1728787 | Anterior gradient 3 | AGR3; HAG3, hAG-3, BCMP11, PDIA18 | [90–92] |
| ILMN_1688071 | N-acetyltransferase 1 | NAT1; AAC1, MNAT, NATI, NAT-1 | [93–95] |
| ILMN_1729216 | Crystallin, alpha B | CRYAB; MFM2, CRYA2, CTPP2, HSPB5, CMD1II, CTRCT16 | [96–99] |
| ILMN_1666845 | Keratin 17 | KRT17; PC, K17, PC2, PCHC1 | [100, 101] |
| ILMN_1786720 | Prominin 1 | PROM1; RP41, AC133, CD133, MCDR2, STGD4, CORD12, PROML1, MSTP061 | [102–106] |
| ILMN_1753101 | V-set domain containing T cell activation inhibitor 1 | VTCN1; B7X, B7H4, B7S1, B7–H4, B7h.5, VCTN1, PRO1291, RP11–229A19.4 | [107–111] |
| ILMN_1798108 | Chromosome 6 open reading frame 211 | C6orf211 | |
| ILMN_1747911 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 | CDK1; CDC2, CDC28A, P34CDC2 | [112–116] |
| ILMN_1666305 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3 | CDKN3; KAP, CDI1, CIP2, KAP1 | [117] |
| ILMN_1678535 | Estrogen receptor 1 | ESR1; ER, ESR, Era, ESRA, ESTRR, NR3A1 | [118–121] |
| ILMN_2149164 | Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 | SFRP1; FRP, FRP1, FrzA, FRP-1, SARP2 | [122–139] |
| ILMN_1788874 | Serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 3 | SERPINA3; ACT, AACT, GIG24, GIG25 | [140–143] |
| ILMN_1785570 | Sushi domain containing 3 | SUSD3 | [141, 144] |
| ILMN_1803236 | Chloride channel accessory 2 | CLCA2; CACC, CACC3, CLCRG2, CaCC-3 | [145–148] |
| ILMN_2161820 | Glycine-N-acyltransferase-like 2 | GLYATL2; GATF-B, BXMAS2–10 | [149, 150] |
| ILMN_1810978 | Mucin-like 1 | MUCL1; SBEM | [151–156] |
| ILMN_1773459 | SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 11 | SOX11 | [157, 158] |
| ILMN_1674533 | Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 6 | TRPV6; CAT1, CATL, ZFAB, ECAC2, ABP/ZF, LP6728, HSA277909 | [159–164] |
| ILMN_1687235 ILMN_2358760 | Hepsin | HPN; TMPRSS1 | [165] |
| ILMN_1655915 | Matrix metallopeptidase 11 (stromelysin 3) | MMP11; ST3, SL-3, STMY3 | [166–176] |
| ILMN_1711470 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T (putative) | UBE2T; PIG50, HSPC150 | [177] |
| ILMN_1740609 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 15 | CCL15; LKN1, NCC3, SY15, HCC-2, LKN-1, MIP-5, NCC-3, SCYL3, MIP-1D, MRP-2B, SCYA15, HMRP-2B, MIP-1 delta | [178, 179] |
| ILMN_1789507 | Collagen, type XI, alpha 1 | COL11A1; STL2, COLL6, CO11A1 | [180, 181] |
| ILMN_1651282 | Collagen, type XVII, alpha 1 | COL17A1; BP180, BPA-2, BPAG2, LAD-1, BA16H23.2 | [182] |
| ILMN_1723684 | Duffy blood group, atypical chemokine receptor | DARC; FY, Dfy, GPD, GpFy, ACKR1, CCBP1, CD234, WBCQ1 | [183–186] |
| ILMN_1809099 | Interleukin 33 | IL33; DVS27, IL1F11, NF-HEV, NFEHEV, C9orf26, RP11–575C20.2 | [187] |
| ILMN_1766650 | Forkhead box A1 | FOXA1; HNF3A, TCF3A | [188–203] |
| ILMN_1811387 | Trefoil factor 3 (intestinal) | TFF3; ITF, P1B, TFI | [204–209] |
| ILMN_1738401 | Forkhead box C1 | FOXC1; ARA, IGDA, IHG1, FKHL7, IRID1, RIEG3, FREAC3, FREAC-3 | [210–212] |
| ILMN_1689146 | Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, pi | GABRP | [213, 214] |
| ILMN_1807423 | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3 | IGF2BP3; CT98, IMP3, KOC1, IMP-3, VICKZ3 | [215–221] |
| ILMN_1692938 | Phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 | PSAT1; PSA, EPIP, PSAT | [222, 223] |
| ILMN_1668766 | Rhophilin associated tail protein 1 | ROPN1; CT91, ODF6, ROPN1A, RHPNAP1, ropporin | [224] |
Table 2. Scores and ranks for the CM1 list.
| Luminal A | Luminal B | Her2 | Normal | Basal | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probe ID | score | rank | score | rank | score | rank | score | rank | score | rank | Symbol | PAM50 |
| ILMN_1728787 | 0.203 | 5 | 0.144 | 5 | -0.314 | 2 | 54 | -0.461 | 3 | AGR3 | ||
| ILMN_1796059 | 0.216 | 3 | 8730 | 1434 | 3666 | -0.390 | 5 | ANKRD30A | ||||
| ILMN_1684217 | -0.203 | 1 | 74 | 497 | 146 | 97 | AURKB | |||||
| ILMN_1798108 | 1980 | 0.155 | 2 | 68 | 405 | 179 | C6orf211 | |||||
| ILMN_1740609 | 476 | 43 | 970 | 0.252 | 3 | 2776 | CCL15 | |||||
| ILMN_1747911 | 80 | 0.144 | 4 | 2080 | 194 | 1496 | CDC2 | |||||
| ILMN_1683450 | -0.196 | 3 | 30 | 306 | 79 | 166 | CDCA5 | |||||
| ILMN_1666305 | 16 | 0.146 | 3 | 438 | 167 | 917 | CDKN3 | |||||
| ILMN_1747016 | -0.195 | 5 | 88 | 362 | 73 | 127 | CEP55 | x | ||||
| ILMN_1803236 | 1875 | 354 | 0.316 | 3 | 688 | 13483 | CLCA2 | |||||
| ILMN_1789507 | 12176 | 5363 | 1820 | -0.155 | 3 | 9245 | COL11A1 | |||||
| ILMN_1651282 | 915 | 16 | 4821 | 0.244 | 4 | 12205 | COL17A1 | |||||
| ILMN_1729216 | 6657 | -0.153 | 5 | 3008 | 52 | 45 | CRYAB | |||||
| ILMN_1723684 | 456 | 14 | 2830 | 0.255 | 2 | 4215 | DARC | |||||
| ILMN_1678535 | 8 | 0.181 | 1 | -0.360 | 1 | 7 | -0.440 | 4 | ESR1 | x | ||
| ILMN_1766650 | 70 | 85 | 12522 | 216 | -0.478 | 2 | FOXA1 | x | ||||
| ILMN_1738401 | 1047 | 10 | 2254 | 226 | 0.443 | 1 | FOXC1 | x | ||||
| ILMN_1689146 | 1177 | 13 | 1833 | 283 | 0.414 | 2 | GABRP | |||||
| ILMN_2161820 | 310 | 270 | 0.333 | 1 | 791 | 1479 | GLYATL2 | |||||
| ILMN_1687235 | 79 | 1942 | 58 | -0.157 | 2 | 211 | HPN | |||||
| ILMN_2358760 | 105 | 1941 | 73 | -0.152 | 4 | 284 | HPN | |||||
| ILMN_1807423 | 1269 | 2087 | 21820 | 11567 | 0.405 | 3 | IGF2BP3 | |||||
| ILMN_1809099 | 3400 | 141 | 6282 | 0.275 | 1 | 23413 | IL33 | |||||
| ILMN_1666845 | 8365 | -0.186 | 2 | 3879 | 35 | 29 | KRT17 | x | ||||
| ILMN_1651329 | 0.221 | 1 | 2481 | 1149 | 1159 | 20 | LOC646360 | |||||
| ILMN_2310814 | 0.221 | 2 | 8776 | 33 | 1131 | 23 | MAPT | x | ||||
| ILMN_2212909 | -0.196 | 4 | 137 | 501 | 92 | 65 | MELK | x | ||||
| ILMN_1655915 | 5274 | 3486 | 3832 | -0.166 | 1 | 4148 | MMP11 | x | ||||
| ILMN_1810978 | 20520 | 9 | 0.326 | 2 | 6 | 1495 | MUCL1 | |||||
| ILMN_1688071 | 0.215 | 4 | 902 | -0.256 | 5 | 24 | 19 | NAT1 | x | |||
| ILMN_1786720 | 988 | -0.174 | 3 | 273 | 465 | 20 | PROM1 | |||||
| ILMN_1692938 | 68 | 343 | 93 | 1864 | 0.391 | 5 | PSAT1 | |||||
| ILMN_1668766 | 721 | 62 | 1415 | 368 | 0.405 | 4 | ROPN1 | |||||
| ILMN_1788874 | 148 | 4633 | -0.259 | 4 | 1961 | 1462 | SERPINA3 | |||||
| ILMN_2149164 | 11497 | -0.203 | 1 | 1697 | 0.244 | 5 | 40 | SFRP1 | x | |||
| ILMN_1773459 | 185 | 621 | 0.293 | 5 | 10046 | 483 | SOX11 | |||||
| ILMN_1785570 | 11 | 2499 | -0.308 | 3 | 438 | 82 | SUSD3 | |||||
| ILMN_1811387 | 26 | 64 | 1263 | 661 | -0.521 | 1 | TFF3 | |||||
| ILMN_1674533 | 643 | 605 | 0.300 | 4 | 2756 | 1819 | TRPV6 | |||||
| ILMN_1714730 | -0.200 | 2 | 9 | 318 | 43 | 353 | UBE2C | x | ||||
| ILMN_1711470 | 56 | 7 | 1732 | -0.145 | 5 | 1113 | UBE2T | x | ||||
| ILMN_1753101 | 474 | -0.153 | 4 | 2424 | 3373 | 1522 | VTCN1 | |||||
The CM1 scores for the topmost 5 positive and negative probe IDs in each subtype are given. The ranks correspond to the position of the probe from the topmost positive or negative (with 1 being the top ranked score at either side). The rightmost two columns indicate the gene symbol the probe maps to, and which genes appear also in the PAM50 list.
The effectiveness of the CM1 list for segregating the five subtypes is depicted in Fig 2. The figure shows the expression values of the top five negative and top five positive ranked probes for each subtype across 997 samples in the METABRIC discovery set. For instance, the ten probes selected for the basal-like subtype—the most representative class—expose a consistent separation between samples from this class and the remaining ones. The second heat map in Fig 3 illustrates the expression levels of unique probes from the CM1 list in the Illumina platform, in which rows represent probes and columns represent samples. Rows and columns were ordered according to gene expression similarity using a memetic algorithm [27]. This image also exposes the overall discriminative power of our list for distinguishing samples of the five subtypes.
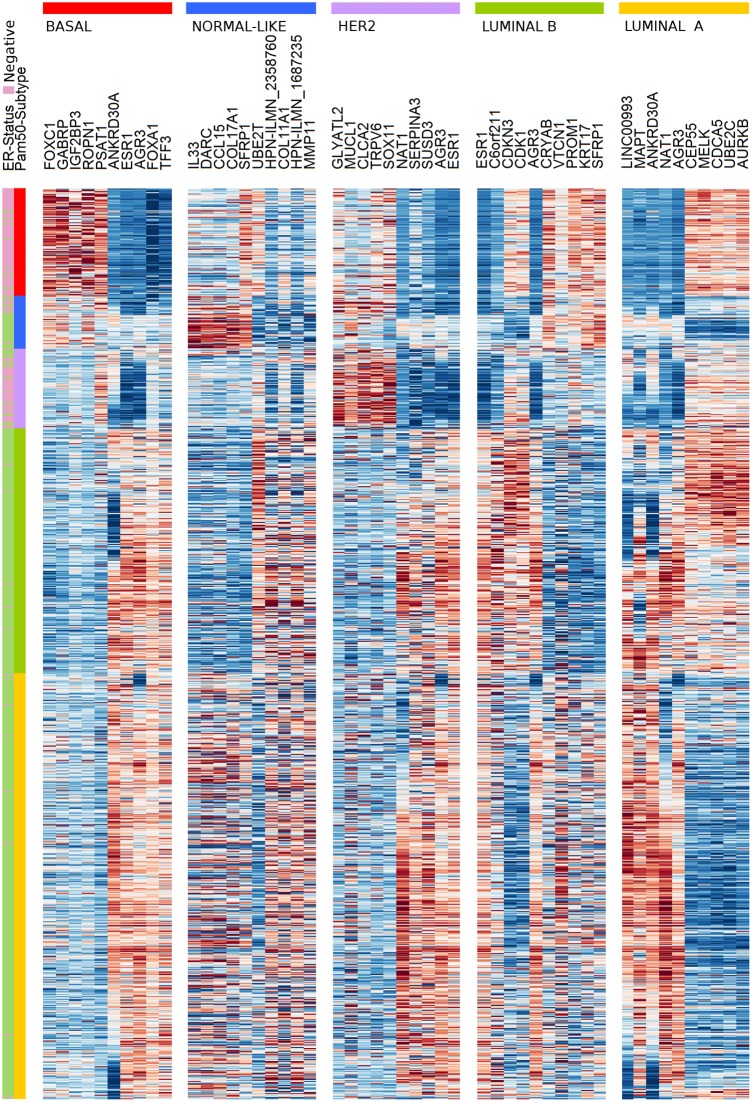
Fig 2. The gene expression profile of the balanced top ten probes selected for each of the five breast cancer intrinsic subtypes across 997 samples from the discovery set.
The annotated genes are defined for each subtype as an intrinsic, highly discriminative, signature. Samples were ordered according to the gene expression similarities in each breast cancer subtype. Colours represent the selected genes and sample subtypes: luminal A (yellow), luminal B (green), HER2-enriched (purple), normal-like (blue), and basal-like (red).
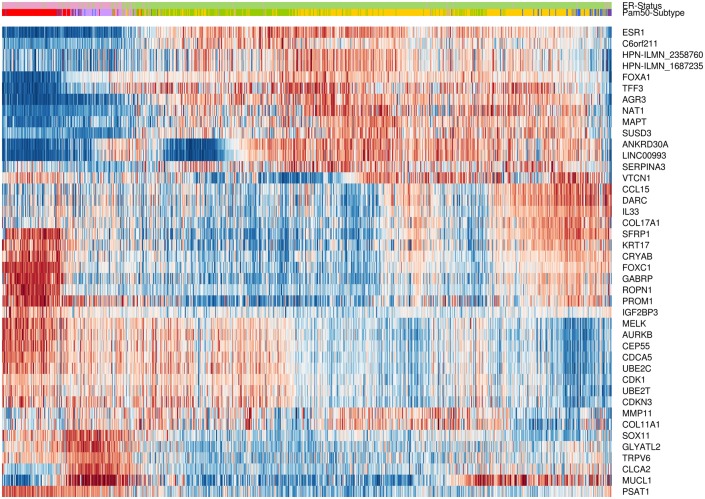
Fig 3. Gene expression patterns of the 42 probes selected using the CM1 score.
The heat map diagram exhibit 42 probes (rows) and 997 samples (columns) from the discovery set ordered according to gene expression similarity, based on a memetic algorithm [27]. The labels highlighted on top show the sample distribution according to the ER positive and negative status. It also illustrates the original PAM50 subtypes luminal A (yellow), luminal B (green), HER2-enriched (purple), normal-like (blue), and basal-like (red) in the METABRIC discovery set. Two probes in the CM1 list refer to the same gene, HPN, which was then appended with the corresponding Illumina probe ID.
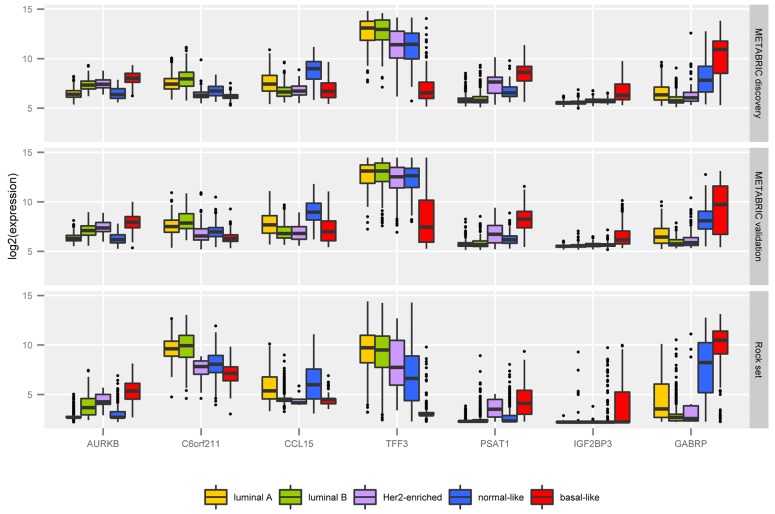
A detailed description of our 42 probes in the context of the literature can be found in Supporting Information S1 Text. Among them we highlight seven, targeting the following transcripts: AURKB, CCL15, C6orf211, GABRP, IGF2BP3, PSAT1, and TFF3. Fig 4 shows the box plot of their expression levels across intrinsic subtypes in the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and the ROCK set. We emphasized these transcripts due to the remarkable differential expression behaviour across the five classes. Besides, they are novel potential markers for breast cancer subtyping, not considered by Parker et al [16]. Box plots of expression levels for all transcripts in the CM1 list in the METABRIC discovery and validation and ROCK data sets are provided in Supporting Information S1 Fig. Even though those probes were selected from the METABRIC discovery set only, their variation across subtypes in the validation set and ROCK test set are also impressive.
Fig 4. The mRNA log2 normalised expression values of 7 novel highly discriminative biomarkers across the five intrinsic subtypes in the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK set.
The box plot uncover the values of 997 samples in the METABRIC discovery set, 989 in the validation set, and 1570 in the ROCK test set.
The ensemble of classifiers reveal high levels of agreement between CM1 and PAM50 lists
After applying the ensemble learning, several statistical measures were computed as referred in Materials and Methods. The main purpose of the statistics is to determine the performance of the 24 classification methods from the Weka software suite. In other words, we investigate the consistency of intrinsic subtype labels attributed by the majority of classifiers having as input either the CM1 or PAM50 lists. The quality of both lists was estimated according to the Cramer’s V statistic and the Average Sensitivity. Additionally, we computed the popular interrater reliability metric Fleiss’ kappa to establish the consensus of sample labelling across different classifiers. This metric was used to gauge the agreement among classifiers trained with CM1 and PAM50 lists against the original labels in the data sets, and between the labels assigned by the majority of classifiers using both lists. Ultimately, we applied the Adjusted Rand Index to quantify the agreement between pairs of samples that are either in the same class or in different classes according to both lists.
Average Cramer’s V statistic and Average Sensitivity to measure the performance of individual classifiers
We determined the performance of the ensemble learning (Supporting Information S2 Table, and S3 Table) with two measures: Cramer’s V statistic and Average Sensitivity (Table 3). Cramer’s V is used to measure the strength of association among variables in the row and column, given a contingency table (Tables 4, 5 and 6). The rows represent the original PAM50 labels and the columns the subtypes assigned by the majority of the classifiers in the ensemble. For instance, Cramer’s V statistic showed an average association between original and predicted subtypes of 0.73±0.06 and 0.63±0.04 in the METABRIC discovery and validation sets respectively with the CM1 list; and 0.75±0.06 and 0.64±0.04 with PAM50 list. Expanding the validation process using the ROCK test set, Cramer’s V ranged from 0.57±0.06 with the CM1, and 0.58±0.05 using PAM50 list.
Table 3. The ensemble learning overall performance on assigning labels to samples in the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK test set.
| CM1 list | PAM50 list | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | CV | AS | CV | AS |
| METABRIC discovery | 0.731 ± 0.057 | 0.763 ± 0.060 | 0.752 ± 0.064 | 0.781 ± 0.070 |
| METABRIC validation | 0.632 ± 0.036 | 0.641 ± 0.039 | 0.643 ± 0.041 | 0.650 ± 0.047 |
| ROCK test set | 0.571 ± 0.060 | 0.673 ± 0.077 | 0.578 ± 0.054 | 0.687 ± 0.081 |
Values are given as average ± std. deviation. CV- Cramer’s V; AS- Average Sensitivity
Table 4. Contingency tables for predicted labels using the 24 classifiers trained with the CM1 list.
| METABRIC discovery | METABRIC validation | ROCK test set | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA | LB | H | N | B | I | LA | LB | H | N | B | I | LA | LB | H | N | B | I | |
| LA | 435 | 19 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 8 | 252 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 452 | 122 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 17 |
| LB | 24 | 234 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 62 | 156 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 18 | 371 | 42 | 0 | 2 | 14 |
| H | 4 | 4 | 67 | 0 | 2 | 10 | 23 | 45 | 71 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| N | 13 | 0 | 8 | 31 | 0 | 6 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 59 | 0 | 5 | 115 | 8 | 36 | 74 | 56 | 50 |
| B | 0 | 0 | 10 | 2 | 103 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 22 | 19 | 142 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 166 | 4 |
Rows contain labels assigned by the majority of classifiers trained with the CM1 list, while columns contain the the original METABRIC labels assigned using the PAM50 method. In this table, LA corresponds to luminal A, LB corresponds to luminal B, H to HER2-enriched, N to normal-like, and B to basal-like. Labels marked as I refer to inconsistent assignments; situations where the classifiers did not achieve the majority on attributing a subtype label.
Table 5. Contingency tables for predicted labels using the 24 classifiers trained with the PAM50 list.
| METABRIC discovery | METABRIC validation | ROCK test set | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA | LB | H | N | B | I | LA | LB | H | N | B | I | LA | LB | H | N | B | I | |
| LA | 440 | 17 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 254 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 530 | 46 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| LB | 25 | 239 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 56 | 162 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 53 | 327 | 34 | 0 | 3 | 30 |
| H | 0 | 5 | 72 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 21 | 39 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| N | 9 | 0 | 2 | 34 | 1 | 12 | 82 | 0 | 0 | 55 | 0 | 7 | 105 | 4 | 18 | 92 | 67 | 53 |
| B | 0 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 103 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 20 | 14 | 145 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 172 | 2 |
Rows contain labels assigned by the majority of classifiers trained with the PAM50 list, while columns contain the the original METABRIC labels assigned using the PAM50 method. In this table, LA corresponds to luminal A, LB corresponds to luminal B, H to HER2-enriched, N to normal-like, and B to basal-like. Labels marked as I refer to inconsistent assignments; situations where the classifiers did not achieve the majority on attributing a subtype label.
Table 6. Contingency tables for predicted labels using the 24 classifiers trained with CM1 and PAM50 lists.
| METABRIC discovery | METABRIC validation | ROCK Set | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA | LB | H | N | B | I | LA | LB | H | N | B | I | LA | LB | H | N | B | I | |
| LA | 450 | 15 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 7 | 390 | 14 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 14 | 550 | 8 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 17 |
| LB | 20 | 235 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 12 | 185 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 112 | 361 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 |
| H | 0 | 0 | 75 | 2 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 83 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 4 | 67 | 0 | 8 | 21 |
| N | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 61 | 1 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 0 | 7 |
| B | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 101 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 140 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 219 | 3 |
| I | 4 | 11 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 12 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 26 | 4 | 2 | 13 | 15 | 25 |
Rows contain the labels assigned by the majority of classifiers trained with the CM1 list, while columns contain labels assigned by the majority of classifiers trained with PAM50 list. In this table, LA corresponds to luminal A, LB corresponds to luminal B, H to HER2-enriched, N to normal-like, and B to basal-like. Labels marked as I refer to inconsistent assignments; situations where the classifiers did not achieve the majority on attributing a subtype label.
The Average Sensitivity statistic was used to characterize the average proportion of accurately labelled samples in each subtype. Considering the analysis with CM1 list, the measure was 0.76±0.06 in the METABRIC discovery set and 0.64±0.04 in the validation set; and with PAM50 list was 0.78±0.07 and 0.65±0.05, respectively. Likewise, the average sensitivity calculated for the ROCK test set was 0.67±0.07 using the CM1 and 0.69±0.08 with PAM50 list. A complete table containing the performance of all individual classification methods is available in the (Supporting Information S2 Table and S3 Table).
The levels of agreement explained by interrater reliability metric Fleiss’ kappa
Fleiss’ kappa was computed to assess the reliability of agreement between two raters, as displayed in Table 7. We initially compared the agreement Among classifiers which indicates the overall performance of classifiers alone. We then compared Predicted vs Original, that is, the agreement between subtypes assigned by the majority of classifiers using CM1 and PAM50 lists compared to the original PAM50 labels in the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK test set. We also calculated the kappa between labels attributed by the majority of classifiers using both lists, CM1 vs PAM50. We refer to the Materials and Methods section for an interpretation of κ values. For instance, the high levels of agreement between two raters reflect more than what would be expected by chance.
Table 7. Agreement of the 24 classifiers on assigning labels to samples in the data sets measured by Fleiss’ kappa statistic.
| METABRIC | ROCK | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| discovery | validation | test set | ||
| Among classifiers | CM1 | 0.73 | 0.753 | 0.626 |
| PAM50 | 0.724 | 0.729 | 0.59 | |
| Predicted vs. Original | CM1 | 0.814 | 0.596 | 0.591 |
| PAM50 | 0.84 | 0.618 | 0.641 | |
| CM1 vs PAM50 | 0.859 | 0.832 | 0.804 | |
Rows entitled Among classifiers indicate agreement of classifiers alone, not considering the labels. Predicted vs Original show the agreement between the mostly predicted and initial labels of samples (PAM50 method). Finally, rows entitled CM1 vs PAM50 contain the agreement between the mostly predicted labels using the CM1 and PAM50 lists with the ensemble learning.
Considering the agreement of the ensemble of classifiers, there was a substantial agreement in both METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK test set (Table 7). Fleiss’ kappa was 0.73, 0.75 and 0.63 with the CM1 list for METABRIC discovery, validation and ROCK data sets, respectively. Values obtained with the PAM50 list were 0.72, 0.73 and 0.6, respectively. By comparing the subtypes predicted by the majority of classifiers and original PAM50 labels, there was an almost perfect agreement with CM1 (κ = 0.81) and PAM50 (κ = 0.84) lists in the discovery set. In the validation and ROCK sets, on the other hand, labels showed only a moderate agreement for both lists (κ ≃ 0.6). Strikingly, the Fleiss’ kappa between subtypes predicted using the CM1 and PAM50 lists (κ = 0.86, 0.83, and 0.8 in the METABRIC discovery, validation, and ROCK sets, respectively) revealed an almost perfect agreement. This statistical measure confirm our visual analysis of the contingency tables as they find strong relationship across the subtype labels in each data set. A detail of the agreement among classifiers by intrinsic subtype is shown in (Supporting Information S4 Table).
The agreement according to the Adjusted Rand Index
The agreement between the different sample labellings was also scrutinized using the Adjusted Rand Index measure (Table 8). The values obtained with the CM1 list were 0.757 in the METABRIC discovery and 0.426 in the validation sets, and 0.453 in the ROCK test set. For PAM50 list, the values were 0.792, 0.457 and 0.507, respectively. Similar to Fleiss’ kappa, the agreement between labels predicted with CM1 and PAM50 lists is higher than the agreement with the original labels. The Adjusted Rand Index values were 0.822, 0.788 and 0.642 for the three data sets, respectively. The numbers obtained with this measure also revealed remarkable concordance of CM1 and PAM50 lists assigned labels.
Table 8. Agreement measured by the Adjusted Rand Index between different samples’ labellings.
| METABRIC | ROCK | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| discovery | validation | test set | |
| CM1 | 0.757 | 0.426 | 0.453 |
| PAM50 | 0.792 | 0.457 | 0.507 |
| CM1-PAM50 | 0.822 | 0.788 | 0.642 |
This contains the agreement between the original and predicted labels of samples in the discovery and validation sets. CM1-METABRIC refers to agreement between the labels predicted by the majority of classifiers trained with the CM1 list and the original METABRIC labels; PAM50-METABRIC is the agreement between labels predicted by the majority of classifiers trained with the PAM50 list and original METABRIC labels; and CM1-PAM50 is the agreement between predicted labels using both lists.
The use of an ensemble learning with the CM1 list improves the subtype distribution in the METABRIC and ROCK data sets
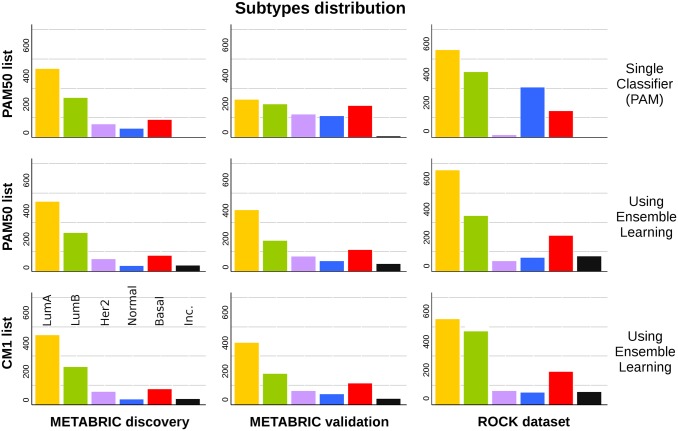
The number of samples in each original PAM50 subtype is markedly different across the METABRIC sets (Fig 5). In the discovery set, there is a clear abundance of luminal A and B subtypes, precisely 73.62% of all samples. In contrast, the proportion of luminals in the validation set is only 48.14%. The ratio of luminal A to luminal B samples changed from 1.74 in the discovery to 1.14 in the validation set. However, when the CM1 or PAM50 lists are used in conjunction with the ensemble of classifiers, samples in the discovery and validation sets are more homogeneously distributed. The percentage of samples in the discovery set labelled as luminal A and B using CM1 and PAM50 lists are 73.53% and 73.72%, respectively. These proportions match the original number (73.62%). On the other hand, in the validation set the CM1 and PAM50 lists assigned a total of 64% and 63.19% luminal samples, against the 48.14% previously mentioned. The distribution of subtypes also become more similar to the discovery set. Likewise, ROCK test set also changed the pattern of class distribution after the performance of the ensemble of classifiers. The differences in class distributions might not be attributed to the randomisation procedure used by the studies as the performance of the ensemble of classifiers with both lists reconcile the distribution of subtypes.
Fig 5. Class distribution in the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and in the ROCK set.
The bars represent the number of samples in each breast cancer subtype. In the first row, the labels refer to the original assignment using the PAM50 method. The following rows show the new labels attributed using an ensemble of 24 classifiers with PAM50 and CM1 lists, respectively. Samples were classified as inconsistent if there was no consensus between the majority of classifiers as to what should be the correct subtype.
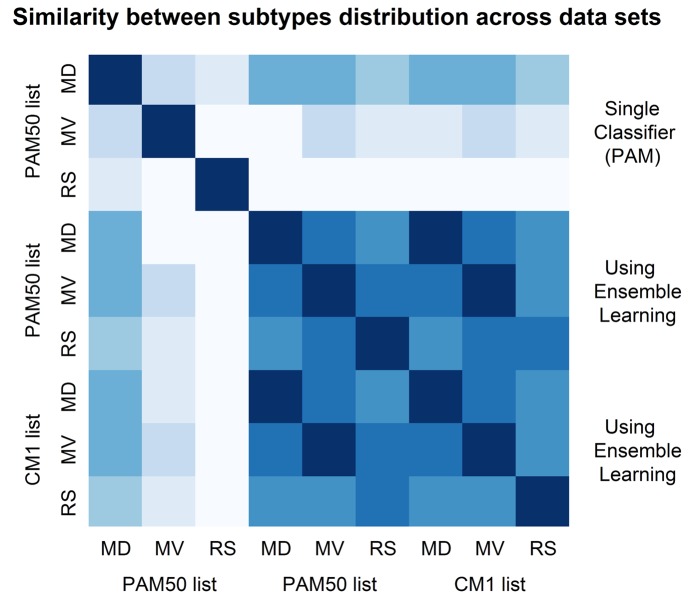
We summarize the similarities and differences in subtypes distribution (graphically displayed in Fig 5) by computing the square root of the Jensen-Shannon divergence [225]. This is a true metric of distance between probability distributions. Its plot in Fig 6 shows the similarity between all possible pairs of data sets based on their distribution of subtype labels (Supporting Information S4 Table). It can be observed that the original labels are the most divergent ones, especially in the METABRIC validation and ROCK test sets. The high similarity of samples distribution among subtypes based on the assignments with CM1 or PAM50 lists is evident. Such similarity was not expected for the ROCK set as the ensemble of classifiers was trained with METABRIC discovery (Illumina platform data) and tested in the ROCK set (Affymetrix platform data). The limited number of probes matching Illumina and Affymetrix in both lists (as described in Materials and Methods) seems not to affect the performance of the ensemble learning. Yet the divergences in the original class distributions might not be attributed to the randomisation procedure used by the consortium. These results point out to the relative strength and robustness of a set of classifiers compared to single methods to predict breast cancer subtype labels. They also indicate that there is an issue to be considered by researchers when using the original PAM50 labels from the METABRIC study for analysing data and building predictive models.
Fig 6. Similarity between subtypes distribution in the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and in the ROCK set.
The image shows the similarity between the subtypes distribution for METABRIC discovery (MD) and validation (MD) sets, and ROCK test set (RS). The labels were assigned in the original data sets using the PAM50 method, and relabelled in this study with an ensemble learning using PAM50 and CM1 lists. The similarity is measured using the square root of the Jensen-Shannon divergence. Darker shades represent more similar distributions, while lighter shades refer to divergent patterns. The diagonal shows the darkest color as each data set is the closest to itself. According to this image, labels assigned using an ensemble learning with CM1 and PAM50 lists are highly similar, and both exhibit lower levels of agreement with the original labels assigned using a single classifier (PAM), or PAM50 method.
Breast cancer intrinsic subtypes show different clinical markers distribution and survival curves
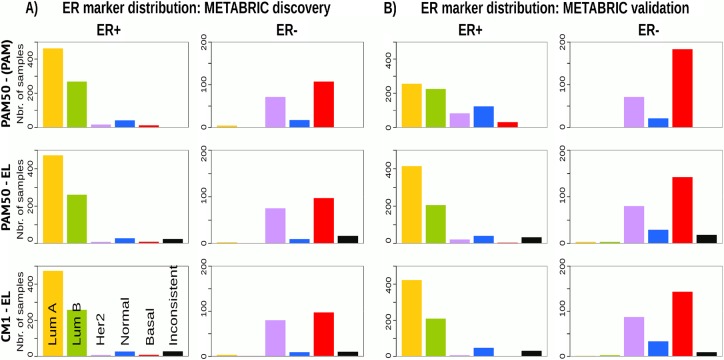
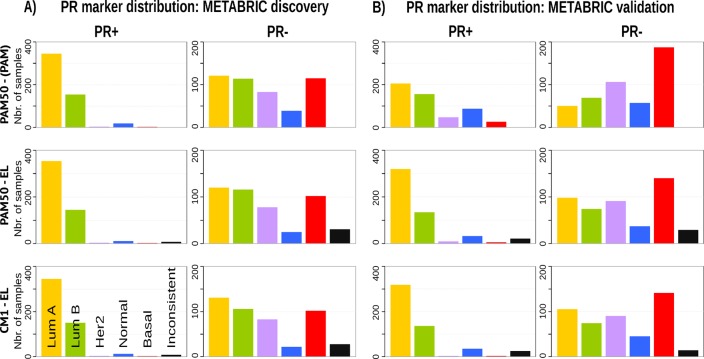
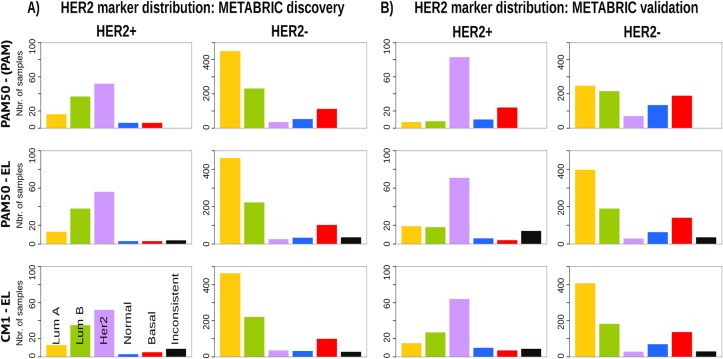
Given the heterogeneity among breast cancer patients and the intricate assignment of PAM50 labels in the original METABRIC data set, we further investigated whether significant differences exist in the analysis of current clinical markers (ER, PR and HER2). Figs 7, 8 and 9 show, respectively, the distribution of the ER, PR and HER2 across intrinsic subtypes in the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, considering the original PAM50 labels and the labels assigned by ensemble of classifiers using CM1 and PAM50 lists. The new subtype labelling markedly improves the status of the clinical markers in the METABRIC data set. For instance, the ER marker distribution across subtypes shows an important decrease in the number of HER2-enriched and basal-like samples that are ER-positive according to the original PAM50 labels. The PR marker, likewise, varies the distribution when predicted labels based on the ensemble of classifiers using either CM1 and PAM50 list are compared with the original labels. HER2 amplification has a particular behaviour across all subtypes. Under the new subtype labels, the distribution of the three clinical markers becomes more consistent with what is expected according to the literature for each class: luminal A (ER+ and/or PR+, HER2−); luminal B (ER+ and/or PR+, HER2±); HER2-enriched (ER−, PR− and HER2+); and basal-like (ER−, PR−, HER2−) [226].
Fig 7. ER marker distribution across subtypes in the METABRIC data sets.
(A) Discovery and (B) Validation. The bars represent the number of samples with ER positive and negative in the five intrinsic subtypes, based on the patients’ clinical information. The top row is based on the original subtype labels obtained with the PAM50 list and a single classifier (PAM). Middle and bottom rows are based on the labels obtained by Ensemble Learning using the PAM50 and CM1 lists, respectively.
Fig 8. PR marker distribution across subtypes in the METABRIC data set.
(A) Discovery and (B) Validation. The bars represent the number of samples with PR positive and negative distributed in the five intrinsic subtypes, based on the patients’ clinical information. The top row is based on the original subtype labels obtained with the PAM50 list and a single classifier (PAM). Middle and bottom rows are based on the labels obtained by Ensemble Learning using the PAM50 and CM1 lists, respectively.
Fig 9. HER2 distribution across subtypes in the METABRIC data sets.
(A) Discovery and (B) Validation. The bars represent the number of samples with HER2 amplification (positive or negative) for each intrinsic subtype based on the patients’ clinical information. The top row is based on the original subtype labels obtained with the PAM50 list and a single classifier (PAM). Middle and bottom rows are based on the labels obtained by Ensemble Learning using the PAM50 and CM1 lists, respectively.
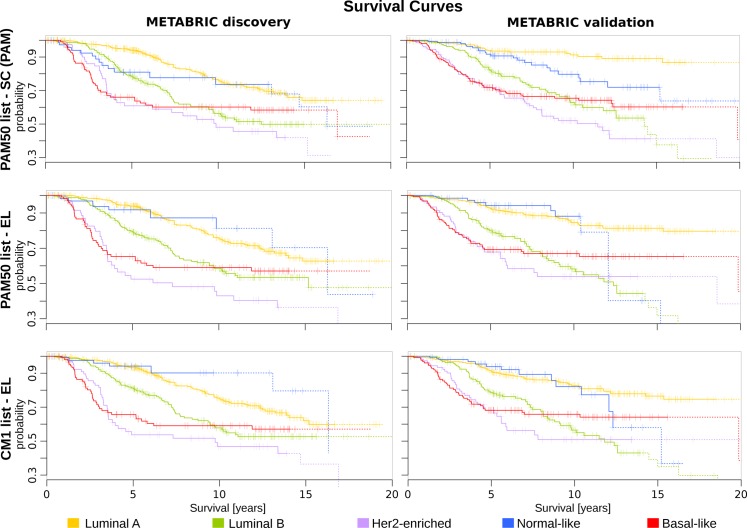
Subsequently, we illustrate the survival curves for all breast cancer subtypes using Cox proportional hazards model, as described in Materials and Methods. The curves were plotted based on the original PAM50 labels and those assigned by the majority of classifiers. For generating the survival curves, we included the most relevant clinical variables as covariates: grade, size, age at diagnosis, number of lymph nodes positive, and ER status (immunohistochemistry) [27]. This analysis revealed different curves in the METABRIC discovery and validation sets (Fig 10). For instance, luminal B and basal-like subtypes show a similar pattern across data sets. Luminal A, HER2-enriched and normal-like, on the other hand, have a more consistent survival pattern when the CM1 and PAM50 lists are used in conjunction with the ensemble learning. Taken as a whole, the results of this section support the increased robustness of labels assigned by the ensemble of classifiers with the CM1 or PAM50 lists, and point out to inconsistencies in the original subtype assignment in the METABRIC study.
Fig 10. The survival curves for METABRIC discovery and validation sets.
The survival curves for each breast cancer subtype are generated using Cox proportional hazards model based on the grade and size of the tumour, patient’s age, number of lymph nodes positive and ER status. Each curve represents the survival probability at a certain time after the diagnosis. Ticks on the curve correspond to the observations of patients who are still alive, while drops indicate the death. The probability curves based on the last 10 observations are plotted in dash. The top row is based on the original subtype labels obtained with the PAM50 list and a single classifier (PAM). Middle and bottom rows are based on the labels obtained by Ensemble Learning using the PAM50 and CM1 lists, respectively.
Discussion
In this study, we exposed the power of the CM1 list for improving the breast cancer subtype prediction in the METABRIC and ROCK data sets. The CM1 score portrayed 30 novel genes as potential biomarkers, along with 12 well-established markers shared between CM1 and PAM50 lists. The 42 biomarkers have a great potential to differentiate breast cancer intrinsic subtypes. Among them, AGR3, HPN, ANKRD30A, AURKB, PROM1, VTCN1, CRYAB, CDK1, CDKN3, SERPINA3, SOX11, TRPV6, CLCA2, MUCL1, COL11A1, DARC, TFF3, IGF2BP3, IL33, SUSD3, PSAT1, and GABRP are reported in different studies associated with breast cancer; however not in the context of subtype differentiation. Noteworthy, the CM1 list revealed a set of probes for which little literature exists in relation to breast cancer subtypes: CDCA5, CCL15, COL17A1, GLYATL2, ROPN1, LINC00993 and C6orf211. Their expression levels vary across different subtypes, and are yet a new avenue to be explored. We also emphasize the 12 common genes (CEP55, ESR1, FOXA1, FOXC1, KRT17, MAPT, MELK, MMP11, NAT1, SFRP1, UBE2C, and UBE2T) due to their important role for breast cancer disease and intrinsic subtyping.
Within the application of an ensemble of classifiers, CM1 and PAM50 lists showed concordant predictive power for disease subtyping. In fact, there was an almost perfect agreement between the labellings obtained with the majority of classifiers using both lists; however different from the original labels. In this study, we want to highlight the weakness of relying in a single method to assign subtypes labels, as opposed to the power and robustness of an ensemble learning. We therefore discourage label assignments based on a single classifier and also suggests a thorough review of those intrinsic subtypes given the importance of such data sets to breast cancer research. The results indicate that there is an issue to be considered by researchers when using the original PAM50 labels for analysing data. The use of incorrect labels would lead to a plethora of misguided and misleading results by other investigators that use METABRIC or ROCK data sets.
In spite of luminals sharing the same origin and large molecular commonalities [227, 228], the ensemble of classifiers accurately predicted luminal samples in the METABRIC data set, and showed some ambiguity on assigning the subtype A or B for a small number of samples, specially in the ROCK data set. This may be a consequence of the reduced number of probes matching across Illumina and Affymetrix platforms. HER2-enriched notably improved label consistency in the ROCK data. Furthermore, the normal-like tumours received more often contradictory and inaccurate subtype labelling among both data sets. The poor overall outcome for this subtype is supported by the discussion that normal-like is an artefact of sample processing with high contamination of normal breast tissue [13, 16, 229]; however, still crucial to be elucidated. Ultimately, the basal-like subtype maintained the classification with a unique profile, markedly divergent from other subtypes [21, 22, 230]; even though this group has recently been partitioned into new fundamental classes [9, 10].
Overall, the new intrinsic subtype labels based on the CM1 list and ensemble learning revealed more accurate distributions of clinical markers (ER, PR and HER2) and survival curves, when compared to the original PAM50 labels in the METABRIC cohort and ROCK test set. Interestingly, the CM1 list shows ESR1 (ER) among the 42 probes, but brings other independent genes that are also relevant for overall predictions. Robust data sets like METABRIC have contributed to the understanding of breast cancer disease in terms of its molecular complexity and intrinsic alterations. The main limitations of the research in the field, nevertheless, is the uncertainty in the exact classification of intrinsic subtypes; over and above the discovery of molecular signatures and standard clinical biomarkers. Under consideration, a consistent taxonomy needs yet to be established prior to implementation in clinical practice. Additional research involving the genome, transcriptome, proteome, and epigenome, will lastly portray a true landscape of subtypes and contribute to breast cancer management.
Supporting Information
The document shows the CM1 probe list along with an extensive literature review. The 42 CM1 biomarkers revealed a great potential to differentiate breast cancer intrinsic subtypes in the METABRIC and ROCK data sets. The 30 novel markers and 12 well-established genes vary the expression levels across different subtypes. The vast majority has been associated with breast cancer disease, either included or not in the subtyping context.
(PDF)
Box plots illustrating the expression levels for all selected transcripts in the CM1 list in the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK test set. The figure shows the probes differential behaviour across breast cancer intrinsic subtypes.
(TIFF)
Table listing the CM1 score used to rank the set of 48803 probes for each of the five breast cancer subtypes in the METABRIC discovery data set. In each case, we selected the top 10 highly discriminative probes (5 with the greatest positive CM1 score values—indicating up-regulated probes relative to the other subtypes, and 5 with the smallest negative values—representing down-regulation).
(XLSX)
Table describing the performance of each classifier on the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK test set using the CM1 list. It shows the percentage of correctly, incorrectly and not classified samples, Fleiss Kappa index, Cramer’s V, Average Sensitivity, and other values for classification. The 24 classifiers from the Weka software suite are also listed. The labels predicted by each classifier for all samples using CM1 list are defined as: 1—luminal A, 2—luminal B, 3—HER2-enriched, 4—normal-like, 5—basal-like. Count of predicted labels was obtained with the consensus of the majority of classifiers.
(XLSX)
Table describing the performance of each classifier on the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK test set using the PAM50 list. It shows the percentage of correctly, incorrectly and not classified samples, Fleiss Kappa index, Cramer’s V, Average Sensitivity, and other values for classification. The 24 classifiers from the Weka software suite are also listed. The labels predicted by each classifier for all samples using CM1 list are defined as: 1—luminal A, 2—luminal B, 3—HER2-enriched, 4—normal-like, 5—basal-like. Count of predicted labels was obtained with the consensus of the majority of classifiers.
(XLSX)
Table containing the Fleiss’ Kappa agreement of labels for the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK test set. It shows the overall agreement Among classifiers using CM1 and PAM50 lists, as well as the agreement for each subtype. The predicted—original are described in the table and contain the agreement between the mostly predicted and initial labels of samples; whereas the CM1—PAM50 show agreement between labels assigned by the majority of classifiers using CM1 and PAM50 lists. The file also has the Jensen-Shannon divergence between two probability distributions. Numbers represent the similarity between subtypes distribution for METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK test set. The similarity is measured using the square root of the Jensen-Shannon divergence.
(XLSX)
Acknowledgments
This study makes use of data generated by the Molecular Taxonomy of Breast Cancer International Consortium. Funding for the project was provided by Cancer Research UK and the British Columbia Cancer Agency Branch.
PM is supported by Australian Research Council (ARC, http://www.arc.gov.au/) Future Fellowship FT120100060. This project is partially funded by ARC Discovery Project DP120102576, Australia.
PM and RB also acknowledge the support of Cancer Institute of New South Wales (http://www.cancerinstitute.org.au/), Big Data Big Impact Grant 13/DATA/1–03 “The integration of bioinformatics, chemoinformatics, and toxicogenomics methods: a new approach for the identification of combination tailored therapies and novel drug targets in breast cancer.”
Data Availability
The METABRIC microarray data set is available at the European Genome-Phenome Archive (EGA) at http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ega/, under accession number EGAS00000000083. The ROCK microarray dataset is available at the ROCK online portal at http://rock.icr.ac.uk/, under data source access GSE47561, and also in GEO at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/ under the same accession number, GSE47561.
Funding Statement
PM is supported by Australian Research Council (ARC) Future Fellowship FT120100060 (http://arc.gov.au/). This project is partially funded by Australian Research Council Discovery Project DP120102576 (http://arc.gov.au/) and Cancer Institute of New South Wales, Australia, Grant 13/DATA/1-03 (http://www.cancerinstitute.org.au/). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Reis-Filho JS, Pusztai L. Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: classification, prognostication, and prediction. The Lancet. 2011;378(9805):1812–1823. 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61539-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Portier BP, Gruver AM, Huba MA, Minca EC, Cheah AL, Wang Z, et al. From morphologic to molecular: established and emerging molecular diagnostics for breast carcinoma. N Biotechnol. 2012;29(6):665–81. 10.1016/j.nbt.2012.03.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. van’t Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, He YD, Hart AAM, Mao M, et al. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature. 2002;415:530–536. 10.1038/415530a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Prat A, Ellis MJ, Perou CM. Practical implications of gene-expression-based assays for breast oncologists. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2012;9(1):48–57. 10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.178 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Kelly CM, Bernard PS, Krishnamurthy S, Wang B, Ebbert MT, Bastien RR, et al. Agreement in risk prediction between the 21-gene recurrence score assay (Oncotype DX(R)) and the PAM50 breast cancer intrinsic Classifier in early-stage estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Oncologist. 2012;17(4):492–498. 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Dowsett M, Sestak I, Lopez-Knowles E, Sidhu K, Dunbier AK, Cowens JW, et al. Comparison of PAM50 risk of recurrence score with oncotype DX and IHC4 for predicting risk of distant recurrence after endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(22):2783–2790. 10.1200/JCO.2012.46.1558 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406(6797):747–752. 10.1038/35021093 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(19):10869–10874. 10.1073/pnas.191367098 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Herschkowitz JI, Simin K, Weigman VJ, Mikaelian I, Usary J, Hu Z, et al. Identification of conserved gene expression features between murine mammary carcinoma models and human breast tumors. Genome Biol. 2007;8(5):R76 10.1186/gb-2007-8-5-r76 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Prat A, Parker JS, Karginova O, Fan C, Livasy C, Herschkowitz JI, et al. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12(5):R68 10.1186/bcr2635 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME, Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y, et al. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(7):2750–2767. 10.1172/JCI45014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Nielsen TO, Parker JS, Leung S, Voduc D, Ebbert M, Vickery T, et al. A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(21):5222–5232. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Weigelt B, Baehner FL, Reis-Filho JS. The contribution of gene expression profiling to breast cancer classification, prognostication and prediction: a retrospective of the last decade. J Pathol. 2010;220(2):263–280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van’t Veer LJ, Dai H, Hart AAM, Voskuil DW, et al. A Gene-expression Signature as a Predictor of Survival in Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(25):1999–2009. 10.1056/NEJMoa021967 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Hu Z, Fan C, Oh DS, Marron JS, He X, Qaqish BF, et al. The molecular portraits of breast tumors are conserved across microarray platforms. BMC Genomics. 2006;7(96). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Parker JS, Mullins M, Cheang MC, Leung S, Voduc D, Vickery T, et al. Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(8):1160–1167. 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.1370 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Bastien RR, Rodríguez-Lescure A, Ebbert MT, Prat A, Munárriz B, Rowe L, et al. PAM50 Breast Cancer Subtyping by RT-qPCR and Concordance with Standard Clinical Molecular Markers. BMC Med Genomics. 2012;5(44):1–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Sørlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie T, Marron JS, Nobel A, et al. Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(14):8418–8423. Available from: http://www.pnas.org/content/100/14/8418.abstract. 10.1073/pnas.0932692100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Tibshirani R, Hastie T, Narasimhan B, Chu G. Diagnosis of multiple cancer types by shrunken centroids of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(10):6567–6572. 10.1073/pnas.082099299 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Perou CM, Parker JS, Prat A, Ellis MJ, Bernard PS. Clinical implementation of the intrinsic subtypes of breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(8):718–719. 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70176-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Weigelt B, Mackay A, A’hern R, Natrajan R, Tan DS, Dowsett M, et al. Breast cancer molecular profiling with single sample predictors: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(4):339–349. 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70008-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Haibe-Kains B, Desmedt C, Loi S, Culhane AC, Bontempi G, Quackenbush J, et al. A three-gene model to robustly identify breast cancer molecular subtypes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104(4):311–325. 10.1093/jnci/djr545 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Sotiriou C, Pusztai L. Gene-Expression Signatures in Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:790–800. 10.1056/NEJMra0801289 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Weigelt B, Reis-Filho JS. Histological and molecular types of breast cancer: is there a unifying taxonomy? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6(12):718–730. 10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.166 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Colombo PE, Milanezi F, Weigelt B, Reis-Filho J. Microarrays in the 2010s: the contribution of microarray-based gene expression profiling to breast cancer classification, prognostication and prediction. Breast Cancer Res. 2010;13(212):1–15. Available from: 10.1186/bcr2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Weigelt B, Pusztai L, Ashworth A, Reis-Filho JS. Challenges translating breast cancer gene signatures into the clinic. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2012;9(1):58–64. 10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.125 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin SF, Turashvili G, Rueda OM, Dunning MJ, et al. The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature. 2012;486(7403):346–352. 10.1038/nature10983 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Ambs S. Prognostic Significance of Subtype Classification for Short- and Long-Term Survival in Breast Cancer: Survival Time Holds the Key. Plo Med. 2010;7:e1000281 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000281 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Marsden J, Budden D, Craig H, Moscato P. Language Individuation and Marker Words: Shakespeare and His Maxwell’s Demon. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(6):e66813 10.1371/journal.pone.0066813 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Ur-Rehman S, Gao Q, Mitsopoulos C, Zvelebil M. ROCK: a resource for integrative breast cancer data analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;139(3):907–921. 10.1007/s10549-013-2593-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Witten IH, Frank E. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques. 2nd ed. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann; 2005.
- 32. Gómez Ravetti M, Moscato P. Identification of a 5-Protein Biomarker Molecular Signature for Predicting Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE. 2008. 09;3(9):e3111 10.1371/journal.pone.0003111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Liebetrau AM. Measures of association. 32. Sage; 1983.
- 34. Dunning MJ, Curtis C, Barbosa-Morais NL, Caldas C, Tavare S, Lynch AG. The importance of platform annotation in interpreting microarray data. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(8):717 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70115-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Fleiss JL. Measuring nominal scale agreement among many raters. Psychol Bull. 1971;76(5):378–382. 10.1037/h0031619 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fleiss JL, Levin B, Paik MC. 18. In: The Measurement of Interrater Agreement. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2004. p. 598–626.
- 37. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1):159–174. 10.2307/2529310 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Hubert L, Arabie P. Comparing partitions. Journal of Classification. 1985;2(1):193–218. 10.1007/BF01908075 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Vinh NX, Epps J, Bailey J. Information Theoretic Measures for Clusterings Comparison: Is a Correction for Chance Necessary? In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning; 2009. p. 1073–1080.
- 40. Therneau TM. Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model. Springer Science & Business Media; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 41. Kalbfleisch JD, Prentice RL. The Statistical Analysis of Failure Time Data. John Wiley & Sons; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 42. Ciriello G, Sinha R, Hoadley K, Jacobsen A, Reva B, Perou C, et al. The molecular diversity of Luminal A breast tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;141(3):409–420. 10.1007/s10549-013-2699-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Hegyi K, Egervari K, Sandor Z, Mehes G. Aurora kinase B expression in breast carcinoma: cell kinetic and genetic aspects. Pathobiology. 2012;79(6):314–322. 10.1159/000338082 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Ahn SG, Lee HM, Lee HW, Lee SA, Lee SR, Leem SH, et al. Prognostic Discrimination Using a 70-Gene Signature among Patients with Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer and an Intermediate 21-Gene Recurrence Score. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(12):23685–23699. 10.3390/ijms141223685 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Fiskus W, Hembruff S, Rao R, Sharma P, Balusu R, Venkannagari S, et al. Co-treatment with vorinostat synergistically enhances activity of Aurora kinase inhibitor against human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;135(2):433–444. 10.1007/s10549-012-2171-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Gully C, Zhang F, Chen J, Yeung J, Velazquez-Torres G, Wang E, et al. Antineoplastic effects of an Aurora B kinase inhibitor in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2010;9(1):42 10.1186/1476-4598-9-42 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Arbitrario J, Belmont B, Evanchik M, Flanagan WM, Fucini R, Hansen S, et al. SNS-314, a pan-Aurora kinase inhibitor, shows potent anti-tumor activity and dosing flexibility in vivo. Cancer Chem Pharmacol. 2010;65(4):707–717. 10.1007/s00280-009-1076-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Hardwicke MA, Oleykowski CA, Plant R, Wang J, Liao Q, Moss K, et al. GSK1070916, a potent Aurora B/C kinase inhibitor with broad antitumor activity in tissue culture cells and human tumor xenograft models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8(7):1808–1817. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0041 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Ueki T, Nishidate T, Park JH, Lin ML, Shimo A, Hirata K, et al. Involvement of elevated expression of multiple cell-cycle regulator, DTL/RAMP (denticleless/RA-regulated nuclear matrix associated protein), in the growth of breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2008;27(43):5672–5683. 10.1038/onc.2008.186 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Kalous O, Conklin D, Desai A, Dering J, Goldstein J, Ginther C, et al. AMG 900, pan-Aurora kinase inhibitor, preferentially inhibits the proliferation of breast cancer cell lines with dysfunctional p53. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;141(3):397–408. 10.1007/s10549-013-2702-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Bush TL, Payton M, Heller S, Chung G, Hanestad K, Rottman JB, et al. AMG 900, a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Aurora Kinases, Potentiates the Activity of Microtubule-Targeting Agents in Human Metastatic Breast Cancer Models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12(11):2356–2366. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-1178 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Romanelli A, Clark A, Assayag F, Chateau-Joubert S, Poupon MF, Servely JL, et al. Inhibiting Aurora Kinases Reduces Tumor Growth and Suppresses Tumor Recurrence after Chemotherapy in Patient-Derived Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(12):2693–2703. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0441-T [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Sanchez-Bailon MP, Calcabrini A, Gomez-Dominguez D, Morte B, Martin-Forero E, Gomez-Lopez G, et al. Src kinases catalytic activity regulates proliferation, migration and invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cell Signal. 2012;24(6):1276–1286. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22570868. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.02.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Soncini C, Carpinelli P, Gianellini L, Fancelli D, Vianello P, Rusconi L, et al. PHA-680632, a novel Aurora kinase inhibitor with potent antitumoral activity. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(13):4080–4089. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16818708. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1964 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Mertsch S, Schmitz N, Jeibmann A, Geng JG, Paulus W, Senner V. Slit2 involvement in glioma cell migration is mediated by Robo1 receptor. J Neurooncol. 2008;87(1):1–7. 10.1007/s11060-007-9484-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Zhang W, Kawanishi M, Miyake K, Kagawa M, Kawai N, Murao K, et al. Association between YKL-40 and adult primary astrocytoma. Cancer. 2010;116(11):2688–2697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Carretero M, Ruiz-Torres M, Rodriguez-Corsino M, Barthelemy I, Losada A. Pds5B is required for cohesion establishment and Aurora B accumulation at centromeres. EMBO J. 2013;32(22):2938–2949. 10.1038/emboj.2013.230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Nguyen MH, Koinuma J, Ueda K, Ito T, Tsuchiya E, Nakamura Y, et al. Phosphorylation and Activation of Cell Division Cycle Associated 5 by Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Play a Crucial Role in Human Lung Carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2010;70(13):5337–5347. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4372 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Murphy KJ, Ter Horst JP, Cassidy AW, DeSouza IE, Morgunova M, Li C, et al. Temporal dysregulation of cortical gene expression in the isolation reared Wistar rat. J Neurochem. 2010;113(3):601–614. 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06617.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Inoda S, Hirohashi Y, Torigoe T, Nakatsugawa M, Kiriyama K, Nakazawa E, et al. Cep55/c10orf3, a tumor antigen derived from a centrosome residing protein in breast carcinoma. J Immunother. 2009;32(5):474–485. 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181a1d109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Colak D, Nofal A, Albakheet A, Nirmal M, Jeprel H, Eldali A, et al. Age-specific gene expression signatures for breast tumors and cross-species conserved potential cancer progression markers in young women. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(5):e63204 10.1371/journal.pone.0063204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Martin KJ, Patrick DR, Bissell MJ, Fournier MV. Prognostic breast cancer signature identified from 3D culture model accurately predicts clinical outcome across independent datasets. PLoS ONE. 2008;3(8):e2994 10.1371/journal.pone.0002994 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Lin ML, Park JH, Nishidate T, Nakamura Y, Katagiri T. Involvement of maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (MELK) in mammary carcinogenesis through interaction with Bcl-G, a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family. Breast Cancer Res. 2007;9(1):R17 10.1186/bcr1650 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Agnati LF, Genedani S, Leo G, Forni A, Woods AS, Filaferro M, et al. Abeta peptides as one of the crucial volume transmission signals in the trophic units and their interactions with homocysteine. Physiological implications and relevance for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm. 2007;114(1):21–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Canevari G, Re Depaolini S, Cucchi U, Bertrand JA, Casale E, Perrera C, et al. Structural insight into maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (MELK) conformation and inhibition toward structure-based drug design. Biochem. 2013;52(37):6380–6387. 10.1021/bi4005864 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Mahasenan KV, Li C. Novel inhibitor discovery through virtual screening against multiple protein conformations generated via ligand-directed modeling: a maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase example. J Chem Inf Model. 2012;52(5):1345–1355. 10.1021/ci300040c [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Hebbard LW, Maurer J, Miller A, Lesperance J, Hassell J, Oshima RG, et al. Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase is upregulated and required in mammary tumor-initiating cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 2010;70(21):8863–8873. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1295 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Pickard MR, Green AR, Ellis IO, Caldas C, Hedge VL, Mourtada-Maarabouni M, et al. Dysregulated expression of Fau and MELK is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(4):R60 10.1186/bcr2350 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Warsow G, Struckmann S, Kerkhoff C, Reimer T, Engel N, Fuellen G. Differential network analysis applied to preoperative breast cancer chemotherapy response. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(12):e81784 10.1371/journal.pone.0081784 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Loussouarn D, Campion L, Leclair F, Campone M, Charbonnel C, Ricolleau G, et al. Validation of UBE2C protein as a prognostic marker in node-positive breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2009;101(1):166–173. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Rawat A, Gopal G, Selvaluxmy G, Rajkumar T. Inhibition of ubiquitin conjugating enzyme UBE2C reduces proliferation and sensitizes breast cancer cells to radiation, doxorubicin, tamoxifen and letrozole. Cell Oncol. 2013;36(6):459–467. 10.1007/s13402-013-0150-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Psyrri A, Kalogeras KT, Kronenwett R, Wirtz RM, Batistatou A, Bournakis E, et al. Prognostic significance of UBE2C mRNA expression in high-risk early breast cancer. A Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group (HeCOG) Study. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(6):1422–1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Taylor KJ, Sims AH, Liang L, Faratian D, Muir M, Walker G, et al. Dynamic changes in gene expression in vivo predict prognosis of tamoxifen-treated patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12(3):R39 10.1186/bcr2593 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Parris TZ, Kovacs A, Aziz L, Hajizadeh S, Nemes S, Semaan M, et al. Additive effect of the AZGP1, PIP, S100A8 and UBE2C molecular biomarkers improves outcome prediction in breast carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2014;134(7):1617–1629. 10.1002/ijc.28497 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Jäger D, Filonenko V, Gout I, Frosina D, Eastlake-Wade S, Castelli S, et al. NY-BR-1 is a Differentiation Antigen of the Mammary Gland. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2007;15(1):77–83. 10.1097/01.pai.0000213111.05108.a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Woodard AH, Yu J, Dabbs DJ, Beriwal S, Florea AV, Elishaev E, et al. NY-BR-1 and PAX8 immunoreactivity in breast, gynecologic tract, and other CK7+ carcinomas: potential use for determining site of origin. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011;136(3):428–435. 10.1309/AJCPUFNMEZ3MK1BK [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Varga Z, Theurillat JP, Filonenko V, Sasse B, Odermatt B, Jungbluth AA, et al. Preferential nuclear and cytoplasmic NY-BR-1 protein expression in primary breast cancer and lymph node metastases. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(9):2745–2751. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2192 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Seil I, Frei C, Sültmann H, Knauer SK, Engels K, Jäger E, et al. The differentiation antigen NY-BR-1 is a potential target for antibody-based therapies in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;120(12):2635–2642. 10.1002/ijc.22620 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Balafoutas D, zur Hausen A, Mayer S, Hirschfeld M, Jaeger M, Denschlag D, et al. Cancer testis antigens and NY-BR-1 expression in primary breast cancer: prognostic and therapeutic implications. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:271 10.1186/1471-2407-13-271 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Giger O, Caduff R, O’Meara A, Diener PA, Knuth A, Jager D, et al. Frequent expression of the breast differentiation antigen NY-BR-1 in mammary and extramammary Paget’s disease. Pathol Int. 2010;60(11):726–734. 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2010.02591.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Theurillat JP, Zurrer-Hardi U, Varga Z, Storz M, Probst-Hensch NM, Seifert B, et al. NY-BR-1 protein expression in breast carcinoma: a mammary gland differentiation antigen as target for cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2007;56(11):1723–1731. 10.1007/s00262-007-0316-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Theurillat JP, Zurrer-Hardi U, Varga Z, Barghorn A, Saller E, Frei C, et al. Distinct expression patterns of the immunogenic differentiation antigen NY-BR-1 in normal breast, testis and their malignant counterparts. Int J Cancer. 2008;122(7):1585–1591. 10.1002/ijc.23241 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Ikeda H, Taira N, Hara F, Fujita T, Yamamoto H, Soh J, et al. The estrogen receptor influences microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) expression and the selective estrogen receptor inhibitor fulvestrant downregulates MAPT and increases the sensitivity to taxane in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12(3):R43 10.1186/bcr2598 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Valet F, de Cremoux P, Spyratos F, Servant N, Dujaric ME, Gentien D, et al. Challenging single- and multi-probesets gene expression signatures of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: experience of the REMAGUS 02 phase II trial. Breast. 2013;22(6):1052–1059. 10.1016/j.breast.2013.08.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Kotoula V, Kalogeras KT, Kouvatseas G, Televantou D, Kronenwett R, Wirtz RM, et al. Sample parameters affecting the clinical relevance of RNA biomarkers in translational breast cancer research. Virchows Arch. 2013;462(2):141–154. 10.1007/s00428-012-1357-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Spicakova T, O’Brien MM, Duran GE, Sweet-Cordero A, Sikic BI. Expression and silencing of the microtubule-associated protein Tau in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9(11):2970–2981. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0780 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Tanaka S, Nohara T, Iwamoto M, Sumiyoshi K, Kimura K, Takahashi Y, et al. Tau expression and efficacy of paclitaxel treatment in metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009;64(2):341–346. 10.1007/s00280-008-0877-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Fountzilas G, Kotoula V, Pectasides D, Kouvatseas G, Timotheadou E, Bobos M, et al. Ixabepilone administered weekly or every three weeks in HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer patients; a randomized non-comparative phase II trial. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(7):e69256 10.1371/journal.pone.0069256 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Mihaly Z, Kormos M, Lanczky A, Dank M, Budczies J, Szasz MA, et al. A meta-analysis of gene expression-based biomarkers predicting outcome after tamoxifen treatment in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;140(2):219–232. 10.1007/s10549-013-2622-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Fletcher GC, Patel S, Tyson K, Adam PJ, Schenker M, Loader JA, et al. hAG-2 and hAG-3, human homologues of genes involved in differentiation, are associated with oestrogen receptor-positive breast tumours and interact with metastasis gene C4.4a and dystroglycan. Br J Cancer. 2003;88(4):579–585. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600740 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Persson S, Rosenquist M, Knoblach B, Khosravi-Far R, Sommarin M, Michalak M. Diversity of the protein disulfide isomerase family: identification of breast tumor induced Hag2 and Hag3 as novel members of the protein family. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2005;36(3):734–740. 10.1016/j.ympev.2005.04.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Wang K, Deng QT, Liao N, Zhang GC, Liu YH, Xu FP, et al. Tau expression correlated with breast cancer sensitivity to taxanes-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Tumour Biol. 2013;34(1):33–38. 10.1007/s13277-012-0507-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Kim SJ, Kang H, Chang HL, Jung YC, Sim H, Lee KS, et al. Promoter hypomethylation of the N-acetyltransferase 1 gene in breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 2008;19:663–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Sim E, Lack N, Wang CJ, Long H, Westwood I, Fullam E, et al. Arylamine N-acetyltransferases: structural and functional implications of polymorphisms. Toxicology. 2008;254(3):170–183. 10.1016/j.tox.2008.08.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Sim E, Walters K, Boukouvala S. Arylamine N-acetyltransferases: from structure to function. Drug Metab Rev. 2008;40(3):479–510. 10.1080/03602530802186603 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Kabbage M, Trimeche M, Nasr H, Hammann P, Kuhn L, Hamrita B, et al. Expression of the molecular chaperone aB-crystallin in infiltrating ductal breast carcinomas and the significance thereof: an immunohistochemical and proteomics-based strategy. Tumour Biol. 2012;33(6):2279–2288. 10.1007/s13277-012-0490-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Ruan Q, Han S, Jiang WG, Boulton ME, Chen ZJ, Law BK, et al. AlphaB-crystallin, an effector of unfolded protein response, confers anti-VEGF resistance to breast cancer via maintenance of intracrine VEGF in endothelial cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2011;9(12):1632–1643. 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 98. Campbell-Lloyd AJ, Mundy J, Deva R, Lampe G, Hawley C, Boyle G, et al. Is alpha-B crystallin an independent marker for prognosis in lung cancer? Heart Lung Circ. 2013;22(9):759–766. 10.1016/j.hlc.2013.01.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Cortesi L, Barchetti A, De Matteis E, Rossi E, Della Casa L, Marcheselli L, et al. Identification of protein clusters predictive of response to chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. J Proteome Res. 2009;8(11):4916–4933. 10.1021/pr900239h [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. van de Rijn M, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Haas P, Kallioniemi O, Kononen J, et al. Expression of Cytokeratins 17 and 5 Identifies a Group of Breast Carcinomas with Poor Clinical Outcome. Am J Pathol. 2002;161(6):1991–1996. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1850928/. 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64476-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Gorski JJ, James CR, Quinn JE, Stewart GE, Staunton KC, Buckley NE, et al. BRCA1 transcriptionally regulates genes associated with the basal-like phenotype in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;122(3):721–731. 10.1007/s10549-009-0565-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Liu Q, Li JG, Zheng XY, Jin F, Dong HT. Expression of CD133, PAX2, ESA, and GPR30 in invasive ductal breast carcinomas. Chin Med J. 2009;122(22):2763–2769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Coradini D, Fornili M, Ambrogi F, Boracchi P, Biganzoli E. TP53 mutation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and stemlike features in breast cancer subtypes. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:254085 10.1155/2012/254085 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Bertheau P, Turpin E, Rickman DS, Espie M, de Reynies A, Feugeas J, et al. Exquisite Sensitivity of TP53 Mutant and Basal Breast Cancers to a Dose-Dense Epirubicin-Cyclophosphamide Regimen. PLoS Med. 2007;4(3):585–594. 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040090 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Liu N, Yu Q, Liu TJ, Gebreamlak EP, Wang SL, Zhang RJ, et al. P-cadherin expression and basal-like subtype in breast cancers. Med Oncol. 2012;29(4):2606–2612. 10.1007/s12032-012-0218-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106. Nadal R, Ortega FG, Salido M, Lorente JA, Rodriguez-Rivera M, Delgado-Rodriguez M, et al. CD133 expression in circulating tumor cells from breast cancer patients: potential role in resistance to chemotherapy. Int J Cancer. 2013;133(10):2398–2407. 10.1002/ijc.28263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Qian Y, Shen L, Cheng L, Wu Z, Yao H. B7–H4 expression in various tumors determined using a novel developed monoclonal antibody. Clin Exp Med. 2011;11(3):163–170. 10.1007/s10238-010-0125-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Suh WK, Wang S, Duncan GS, Miyazaki Y, Cates E, Walker T, et al. Generation and characterization of B7–H4/B7S1/B7x-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26(17):6403–6411. 10.1128/MCB.00755-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109. Salceda S, Tang T, Kmet M, Munteanu A, Ghosh M, Macina R, et al. The immunomodulatory protein B7–H4 is overexpressed in breast and ovarian cancers and promotes epithelial cell transformation. Exp Cell Res. 2005;306(1):128–141. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.01.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Heinonen H, Nieminen A, Saarela M, Kallioniemi A, Klefstrom J, Hautaniemi S, et al. Deciphering downstream gene targets of PI3K/mTOR/p70S6K pathway in breast cancer. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:348 10.1186/1471-2164-9-348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Tringler B, Zhuo S, Pilkington G, Torkko KC, Singh M, Lucia MS, et al. B7–h4 is highly expressed in ductal and lobular breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(5):1842–1848. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1658 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Zhang W, Peng G, Lin SY, Zhang P. DNA damage response is suppressed by the high cyclin-dependent kinase 1 activity in mitotic mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(41):35899–35905. 10.1074/jbc.M111.267690 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113. Kim SJ, Nakayama S, Miyoshi Y, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Matsushima T, et al. Determination of the specific activity of CDK1 and CDK2 as a novel prognostic indicator for early breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2008;19(1):68–72. 10.1093/annonc/mdm358 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114. Kim SJ, Nakayama S, Shimazu K, Tamaki Y, Akazawa K, Tsukamoto F, et al. Recurrence risk score based on the specific activity of CDK1 and CDK2 predicts response to neoadjuvant paclitaxel followed by 5-fluorouracil, epirubicin and cyclophosphamide in breast cancers. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(4):891–897. 10.1093/annonc/mdr340 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115. Torikoshi Y, Gohda K, Davis ML, Symmans WF, Pusztai L, Kazansky A, et al. Novel functional assay for spindle-assembly checkpoint by cyclin-dependent kinase activity to predict taxane chemosensitivity in breast tumor patient. J Cancer. 2013;4(9):697–702. 10.7150/jca.6248 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116. Xia Q, Cai Y, Peng R, Wu G, Shi Y, Jiang W. The CDK1 inhibitor RO3306 improves the response of BRCA-pro fi cient breast cancer cells to PARP inhibition. Int J Oncol. 2014;44(3):735–744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117. Yu YN, Yip GW, Tan PH, Thike AA, Matsumoto K, Tsujimoto M, et al. Y-box binding protein 1 is up-regulated in proliferative breast cancer and its inhibition deregulates the cell cycle. Int J Oncol. 2010;37(2):483–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118. Kim C, Tang G, Pogue-Geile KL, Costantino JP, Baehner FL, Baker J, et al. Estrogen receptor (ESR1) mRNA expression and benefit from tamoxifen in the treatment and prevention of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(31):4160–4167. 10.1200/JCO.2010.32.9615 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119. Stossi F, Madak-Erdogan Z, Katzenellenbogen BS. Macrophage-elicited loss of estrogen receptor-alpha in breast cancer cells via involvement of MAPK and c-Jun at the ESR1 genomic locus. Oncogene. 2012;31(14):1825–1834. 10.1038/onc.2011.370 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120. Aguilar H, Sole X, Bonifaci N, Serra-Musach J, Islam A, Lopez-Bigas N, et al. Biological reprogramming in acquired resistance to endocrine therapy of breast cancer. Oncogene. 2010;29(45):6071–6083. 10.1038/onc.2010.333 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121. Dunbier AK, Anderson H, Ghazoui Z, Lopez-Knowles E, Pancholi S, Ribas R, et al. ESR1 is co-expressed with closely adjacent uncharacterised genes spanning a breast cancer susceptibility locus at 6q25.1. PLoS Genet. 2011;7(4):e1001382 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001382 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122. Vargas AC, McCart Reed AE, Waddell N, Lane A, Reid LE, Smart CE, et al. Gene expression profiling of tumour epithelial and stromal compartments during breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;135(1):153–165. 10.1007/s10549-012-2123-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123. Gauger KJ, Chenausky KL, Murray ME, Schneider SS. SFRP1 reduction results in an increased sensitivity to TGF-beta signaling. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:59 10.1186/1471-2407-11-59 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124. Mukherjee N, Bhattacharya N, Alam N, Roy A, Roychoudhury S, Panda CK. Subtype-specific alterations of the Wnt signaling pathway in breast cancer: clinical and prognostic significance. Cancer Sci. 2012;103(2):210–220. 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.02131.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125. Gostner JM, Fong D, Wrulich OA, Lehne F, Zitt M, Hermann M, et al. Effects of EpCAM overexpression on human breast cancer cell lines. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:45 10.1186/1471-2407-11-45 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126. Matsuda Y, Schlange T, Oakeley EJ, Boulay A, Hynes NE. WNT signaling enhances breast cancer cell motility and blockade of the WNT pathway by sFRP1 suppresses MDA-MB-231 xenograft growth. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(3):R32 10.1186/bcr2317 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127. Suzuki H, Toyota M, Carraway H, Gabrielson E, Ohmura T, Fujikane T, et al. Frequent epigenetic inactivation of Wnt antagonist genes in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008;98(6):1147–1156. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604259 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128. Dahl E, Wiesmann F, Woenckhaus M, Stoehr R, Wild PJ, Veeck J, et al. Frequent loss of SFRP1 expression in multiple human solid tumours: association with aberrant promoter methylation in renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2007;26(38):5680–5691. 10.1038/sj.onc.1210345 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129. Shulewitz M, Soloviev I, Wu T, Koeppen H, Polakis P, Sakanaka C. Repressor roles for TCF-4 and Sfrp1 in Wnt signaling in breast cancer. Oncogene. 2006;25(31):4361–4369. 10.1038/sj.onc.1209470 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130. Ugolini F, Charafe-Jauffret E, Bardou VJ, Geneix J, Adelaide J, Labat-Moleur F, et al. WNT pathway and mammary carcinogenesis: loss of expression of candidate tumor suppressor gene SFRP1 in most invasive carcinomas except of the medullary type. Oncogene. 2001;20(41):5810–5817. 10.1038/sj.onc.1204706 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131. Dumont N, Crawford YG, Sigaroudinia M, Nagrani SS, Wilson MB, Buehring GC, et al. Human mammary cancer progression model recapitulates methylation events associated with breast premalignancy. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(6):R87 10.1186/bcr2457 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132. Park SY, Kwon HJ, Choi Y, Lee HE, Kim SW, Kim JH, et al. Distinct patterns of promoter CpG island methylation of breast cancer subtypes are associated with stem cell phenotypes. Mod Pathol. 2012;25(2):185–196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133. Cooper SJ, von Roemeling CA, Kang KH, Marlow LA, Grebe SK, Menefee ME, et al. Reexpression of tumor suppressor, sFRP1, leads to antitumor synergy of combined HDAC and methyltransferase inhibitors in chemoresistant cancers. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(10):2105–2115. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0873 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134. Browne EP, Punska EC, Lenington S, Otis CN, Anderton DL, Arcaro KF. Increased promoter methylation in exfoliated breast epithelial cells in women with a previous breast biopsy. Epigenetics. 2011;6(12):1425–1435. 10.4161/epi.6.12.18280 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135. Yang ZQ, Liu G, Bollig-Fischer A, Haddad R, Tarca AL, Ethier SP. Methylation-associated silencing of SFRP1 with an 8p11–12 amplification inhibits canonical and non-canonical WNT pathways in breast cancers. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(7):1613–1621. 10.1002/ijc.24518 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136. Martin-Manso G, Calzada MJ, Chuman Y, Sipes JM, Xavier CP, Wolf V, et al. sFRP-1 binds via its netrin-related motif to the N-module of thrombospondin-1 and blocks thrombospondin-1 stimulation of MDA-MB-231 breast carcinoma cell adhesion and migration. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2011;509(2):147–156. 10.1016/j.abb.2011.03.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137. Veeck J, Niederacher D, An H, Klopocki E, Wiesmann F, Betz B, et al. Aberrant methylation of the Wnt antagonist SFRP1 in breast cancer is associated with unfavourable prognosis. Oncogene. 2006;25(24):3479–3488. 10.1038/sj.onc.1209386 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138. Gauger KJ, Schneider SS. Tumour supressor secreted frizzled related protein 1 regulates p53-mediated apoptosis. Cell Biol Int. 2014;38(1):124–130. 10.1002/cbin.10176 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139. Klopocki E, Kristiansen G, Wild PJ, Klaman I, Castanos-Velez E, Singer G, et al. Loss of SFRP1 is associated with breast cancer progression and poor prognosis in early stage tumors. Int J Oncol. 2004;25(3):641–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140. Sano H, Wada S, Eguchi H, Osaki A, Saeki T, Nishiyama M. Quantitative prediction of tumor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: novel marker genes and prediction model using the expression levels. Breast Cancer. 2012;19(1):37–45. 10.1007/s12282-011-0263-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141. Cimino D, Fuso L, Sfiligoi C, Biglia N, Ponzone R, Maggiorotto F, et al. Identification of new genes associated with breast cancer progression by gene expression analysis of predefined sets of neoplastic tissues. Int J Cancer. 2008;123(6):1327–1338. 10.1002/ijc.23660 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142. Yamamura J, Miyoshi Y, Tamaki Y, Taguchi T, Iwao K, Monden M, et al. mRNA expression level of estrogen-inducible gene, alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, is a predictor of early tumor recurrence in patients with invasive breast cancers. Cancer Sci. 2004;95(11):887–892. 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2004.tb02198.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143. Miller WR, Larionov A. Changes in expression of oestrogen regulated and proliferation genes with neoadjuvant treatment highlight heterogeneity of clinical resistance to the aromatase inhibitor, letrozole. Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12(4):R52 10.1186/bcr2611 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144. Moy I, Todorovic V, Dubash AD, Coon JS, Parker JB, Buranapramest M, et al. Estrogen-dependent sushi domain containing 3 regulates cytoskeleton organization and migration in breast cancer cells Oncogene. 2014;. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145. Sasaki Y, Koyama R, Maruyama R, Hirano T, Tamura M, Sugisaka J, et al. CLCA2, a target of the p53 family, negatively regulates cancer cell migration and invasion. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012;13(14):1512–1521. 10.4161/cbt.22280 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146. Walia V, Ding M, Kumar S, Nie D, Premkumar LS, Elble RC. hCLCA2 Is a p53-Inducible Inhibitor of Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation. Cancer Res. 2009;69(16):6624–6632. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147. Walia V, Yu Y, Cao D, Sun M, McLean JR, Hollier BG, et al. Loss of breast epithelial marker hCLCA2 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and indicates higher risk of metastasis. Oncogene. 2012;31(17):2237–2246. 10.1038/onc.2011.392 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148. Li X, Cowell JK, Sossey-Alaoui K. CLCA2 tumour suppressor gene in 1p31 is epigenetically regulated in breast cancer. Oncogene. 2004;23(7):1474–1480. 10.1038/sj.onc.1207249 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149. Waluk DP, Schultz N, Hunt MC. Identification of glycine N-acyltransferase-like 2 (GLYATL2) as a transferase that produces N-acyl glycines in humans. FASEB J. 2010;24(8):2795–2803. 10.1096/fj.09-148551 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150. Waluk DP, Sucharski F, Sipos L, Silberring J, Hunt MC. Reversible lysine acetylation regulates activity of human glycine N-acyltransferase-like 2 (hGLYATL2): implications for production of glycine-conjugated signaling molecules. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(20):16158–16167. 10.1074/jbc.M112.347260 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151. Liu L, Liu Z, Qu S, Zheng Z, Liu Y, Xie X, et al. Small breast epithelial mucin tumor tissue expression is associated with increased risk of recurrence and death in triple-negative breast cancer patients. Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:71 10.1186/1746-1596-8-71 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152. Liu ZZ, Xie XD, Qu SX, Zheng ZD, Wang YK. Small breast epithelial mucin (SBEM) has the potential to be a marker for predicting hematogenous micrometastasis and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Clin Experim Metast. 2010;27(4):251–259. 10.1007/s10585-010-9323-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153. Valladares-Ayerbes M, Iglesias-Diaz P, Diaz-Prado S, Ayude D, Medina V, Haz M, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of small breast epithelial mucin mRNA as a marker for bone marrow micrometastasis in breast cancer: a pilot study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009;135(9):1185–1195. 10.1007/s00432-009-0559-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154. Weigelt B, Verduijn P, Bosma AJ, Rutgers EJ, Peterse HL, van’t Veer LJ. Detection of metastases in sentinel lymph nodes of breast cancer patients by multiple mRNA markers. Br J Cancer. 2004;90(8):1531–1537. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601659 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155. Skliris GP, Hube F, Gheorghiu I, Mutawe MM, Penner C, Watson PH, et al. Expression of small breast epithelial mucin (SBEM) protein in tissue microarrays (TMAs) of primary invasive breast cancers. Histopathology. 2008;52(3):355–369. 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02955.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156. Miksicek RJ, Myal Y, Watson PH, Walker C, Murphy LC, Leygue E. Identification of a Novel Breast- and Salivary Gland-specific, Mucin-like Gene Strongly Expressed in Normal and Tumor Human Mammary Epithelium. Cancer Res. 2002;62:2736–2740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157. Lopez FJ, Cuadros M, Cano C, Concha A, Blanco A. Biomedical application of fuzzy association rules for identifying breast cancer biomarkers. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2012;50(9):981–990. 10.1007/s11517-012-0914-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158. Zvelebil M, Oliemuller E, Gao Q, Wansbury O, Mackay A, Kendrick H, et al. Embryonic mammary signature subsets are activated in Brca1-/- and basal-like breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(2):R25 10.1186/bcr3403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159. Bolanz KA, Hediger MA, Landowski CP. The role of TRPV6 in breast carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7(2):271–279. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0478 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160. Bowen CV, DeBay D, Ewart HS, Gallant P, Gormley S, Ilenchuk TT, et al. In vivo detection of human TRPV6-rich tumors with anti-cancer peptides derived from soricidin. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(3):e58866 10.1371/journal.pone.0058866 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161. Peters AA, Simpson PT, Bassett JJ, Lee JM, Da Silva L, Reid LE, et al. Calcium channel TRPV6 as a potential therapeutic target in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(10):2158–2168. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0965 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162. Kim SY, Yang D, Myeong J, Ha K, Kim SH, Park EJ, et al. Regulation of calcium influx and signaling pathway in cancer cells via TRPV6-Numb1 interaction. Cell Calcium. 2013;53(2):102–111. 10.1016/j.ceca.2012.10.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163. Landowski CP, Bolanz KA, Suzuki Y, Hediger MA. Chemical inhibitors of the calcium entry channel TRPV6. Pharm Res. 2011;28(2):322–330. 10.1007/s11095-010-0249-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164. Dhennin-Duthille I, Gautier M, Faouzi M, Guilbert A, Brevet M, Vaudry D, et al. High expression of transient receptor potential channels in human breast cancer epithelial cells and tissues: correlation with pathological parameters. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;28(5):813–822. 10.1159/000335795 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165. Xing P, Li Jg, Jin F, Zhao Tt, Liu Q, Dong Ht, et al. Clinical and Biological Significance of Hepsin Overexpression in Breast Cancer. J Investig Med. 2011;59(5):803–810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166. Delassus GS, Cho H, Park J, Eliceiri GL. New pathway links from cancer-progression determinants to gene expression of matrix metalloproteinases in breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 2008;217(3):739–744. 10.1002/jcp.21548 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167. Delassus GS, Cho H, Eliceiri GL. New signaling pathways from cancer progression modulators to mRNA expression of matrix metalloproteinases in breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226(12):3378–3384. 10.1002/jcp.22694 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168. Kwon YJ, Hurst DR, Steg AD, Yuan K, Vaidya KS, Welch DR, et al. Gli1 enhances migration and invasion via up-regulation of MMP-11 and promotes metastasis in ERalpha negative breast cancer cell lines. Clin Experim Metast. 2011;28(5):437–449. 10.1007/s10585-011-9382-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169. Min KW, Kim DH, Do SI, Pyo JS, Kim K, Chae S, et al. Diagnostic and Prognostic Relevance of MMP-11 Expression in the Stromal Fibroblast-Like Cells Adjacent to Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(3):433–442. 10.1245/s10434-012-2734-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170. Kasper G, Reule M, Tschirschmann M, Dankert N, Stout-Weider K, Lauster R, et al. Stromelysin-3 over-expression enhances tumourigenesis in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines: involvement of the IGF-1 signalling pathway. BMC Cancer. 2007;7:12 10.1186/1471-2407-7-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171. Cheng CW, Yu JC, Wang HW, Huang CS, Shieh JC, Fu YP, et al. The clinical implications of MMP-11 and CK-20 expression in human breast cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2010;411(3–4):234–241. 10.1016/j.cca.2009.11.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172. Eiseler T, Doppler H, Yan IK, Goodison S, Storz P. Protein kinase D1 regulates matrix metalloproteinase expression and inhibits breast cancer cell invasion. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(1):R13 10.1186/bcr2232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173. Garcia MF, Gonzalez-Reyes S, Gonzalez LO, Junquera S, Berdize N, Del Casar JM, et al. Comparative study of the expression of metalloproteases and their inhibitors in different localizations within primary tumours and in metastatic lymph nodes of breast cancer. Int J Exp Pathol. 2010;91(4):324–334. 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2010.00709.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174. Eiro N, Fernandez-Garcia B, Gonzalez LO, Vizoso FJ. Cytokines related to MMP-11 expression by inflammatory cells and breast cancer metastasis. Oncoimmunology. 2013;2(5):e24010 10.4161/onci.24010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175. Tan J, Buache E, Alpy F, Daguenet E, Tomasetto CL, Ren GS, et al. Stromal matrix metalloproteinase-11 is involved in the mammary gland postnatal development Oncogene. 2013;. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176. Hegedus L, Cho H, Xie X, Eliceiri GL. Additional MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell matrix metalloproteinases promote invasiveness. J Cell Physiol. 2008;216(2):480–485. 10.1002/jcp.21417 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177. Ueki T, Park JH, Nishidate T, Kijima K, Hirata K, Nakamura Y, et al. Ubiquitination and downregulation of BRCA1 by ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T overexpression in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009;69(22):8752–8760. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1809 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178. Li Y, Wu J, Zhang W, Zhang N, Guo H. Identification of serum CCL15 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2013;108(1):99–106. 10.1038/bjc.2012.494 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179. Itatani Y, Kawada K, Fujishita T, Kakizaki F, Hirai H, Matsumoto T, et al. Loss of SMAD4 From Colorectal Cancer Cells Promotes CCL15 Expression to Recruit CCR1+ Myeloid Cells and Facilitate Liver Metastasis. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(5):1064–1075.e11. 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.07.033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180. Ellsworth RE, Seebach J, Field LA, Heckman C, Kane J, Hooke JA, et al. A gene expression signature that defines breast cancer metastases. Clin Experim Metast. 2009;26(3):205–213. 10.1007/s10585-008-9232-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181. Kim H, Watkinson J, Varadan V, Anastassiou D. Multi-cancer computational analysis reveals invasion-associated variant of desmoplastic reaction involving INHBA, THBS2 and COL11A1. BMC Med Genomics. 2010;3:51 10.1186/1755-8794-3-51 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182. van Zalen S, Nijenhuis M, Jonkman MF, Pas HH. Two major 5’-untranslated regions for type XVII collagen mRNA. J Dermatol Sci. 2006;43(1):11–19. 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2006.02.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183. Wang J, He Q, Shao YG, Ji M. Chemokines fluctuate in the progression of primary breast cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17:596–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184. Bandyopadhyay S, Zhan R, Chaudhuri A, Watabe M, Pai SK, Hirota S, et al. Interaction of KAI1 on tumor cells with DARC on vascular endothelium leads to metastasis suppression. Nat Med. 2006;12(8):933–938. 10.1038/nm1444 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185. Zeng XH, Ou ZL, Yu KD, Feng LY, Yin WJ, Li J, et al. Coexpression of atypical chemokine binders (ACBs) in breast cancer predicts better outcomes. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;125(3):715–727. 10.1007/s10549-010-0875-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186. Liu XF, Li LF, Ou ZL, Shen R, Shao ZM. Correlation between Duffy blood group phenotype and breast cancer incidence. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:374 10.1186/1471-2407-12-374 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187. Wu J, Liu S, Liu G, Dombkowski A, Abrams J, Martin-Trevino R, et al. Identification and functional analysis of 9p24 amplified genes in human breast cancer. Oncogene. 2012;31(3):333–341. 10.1038/onc.2011.227 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188. Ni M, Chen Y, Lim E, Wimberly H, Bailey ST, Imai Y, et al. Targeting androgen receptor in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2011;20(1):119–131. 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.05.026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189. Augello MA, Hickey TE, Knudsen KE. FOXA1: master of steroid receptor function in cancer. EMBO J. 2011;30(19):3885–3894. 10.1038/emboj.2011.340 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190. Robinson JL, Macarthur S, Ross-Innes CS, Tilley WD, Neal DE, Mills IG, et al. Androgen receptor driven transcription in molecular apocrine breast cancer is mediated by FoxA1. EMBO J. 2011;30(15):3019–3027. 10.1038/emboj.2011.216 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191. Bernardo GM, Keri RA. FOXA1: a transcription factor with parallel functions in development and cancer. Biosci Rep. 2012;32(2):113–130. 10.1042/BSR20110046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192. Fu X, Huang C, Schiff R. More on FOX News: FOXA1 on the horizon of estrogen receptor function and endocrine response. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(2):307 10.1186/bcr2849 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193. Meyer KB, Carroll JS. FOXA1 and breast cancer risk. Nat Genet. 2012;44(11):1176–1177. 10.1038/ng.2449 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194. Cowper-Sal lari R, Zhang X, Wright JB, Bailey SD, Cole MD, Eeckhoute J, et al. Breast cancer risk-associated SNPs modulate the affinity of chromatin for FOXA1 and alter gene expression. Nat Genet. 2012;44(11):1191–1198. 10.1038/ng.2416 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195. Katika MR, Hurtado A. A functional link between FOXA1 and breast cancer SNPs. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(1):303 10.1186/bcr3360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196. Badve S, Turbin D, Thorat MA, Morimiya A, Nielsen TO, Perou CM, et al. FOXA1 expression in breast cancer–correlation with luminal subtype A and survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(15 Pt 1):4415–4421. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197. Mehta RJ, Jain RK, Leung S, Choo J, Nielsen T, Huntsman D, et al. FOXA1 is an independent prognostic marker for ER-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;131(3):881–890. 10.1007/s10549-011-1482-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198. Habashy HO, Powe DG, Rakha EA, Ball G, Paish C, Gee J, et al. Forkhead-box A1 (FOXA1) expression in breast cancer and its prognostic significance. Europ J Cancer. 2008;44(11):1541–1551. 10.1016/j.ejca.2008.04.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199. Albergaria A, Paredes J, Sousa B, Milanezi F, Carneiro V, Bastos J, et al. Expression of FOXA1 and GATA-3 in breast cancer: the prognostic significance in hormone receptor-negative tumours. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(3):R40 10.1186/bcr2327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200. Hurtado A, Holmes KA, Ross-Innes CS, Schmidt D, Carroll JS. FOXA1 is a key determinant of estrogen receptor function and endocrine response. Nat Genet. 2011;43(1):27–33. 10.1038/ng.730 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201. Naderi A, Meyer M, Dowhan DH. Cross-regulation between FOXA1 and ErbB2 signaling in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Neoplasia. 2012;14(4):283–296. 10.1593/neo.12294 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202. Kong SL, Li G, Loh SL, Sung WK, Liu ET. Cellular reprogramming by the conjoint action of ERalpha, FOXA1, and GATA3 to a ligand-inducible growth state. Mol Syst Biol. 2011;7:526 10.1038/msb.2011.59 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203. Magnani L, Lupien M. Chromatin and epigenetic determinants of estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) signaling. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014;382(1):633–641. 10.1016/j.mce.2013.04.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204. Lasa A, Garcia A, Alonso C, Millet P, Cornet M, Ramon y Cajal T, et al. Molecular detection of peripheral blood breast cancer mRNA transcripts as a surrogate biomarker for circulating tumor cells. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(9):e74079 10.1371/journal.pone.0074079 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205. Lacroix M. Significance, detection and markers of disseminated breast cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006;13:1033–1067. 10.1677/ERC-06-0001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206. Ahmed AR, Griffiths AB, Tilby MT, Westley BR, May FE. TFF3 is a normal breast epithelial protein and is associated with differentiated phenotype in early breast cancer but predisposes to invasion and metastasis in advanced disease. Am J Pathol. 2012;180(3):904–916. 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.11.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207. Fenne IS, Helland T, Flageng MH, Dankel SN, Mellgren G, Sagen JV. Downregulation of steroid receptor coactivator-2 modulates estrogen-responsive genes and stimulates proliferation of mcf-7 breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(7):e70096 10.1371/journal.pone.0070096 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208. Roll JD, Rivenbark AG, Sandhu R, Parker JS, Jones WD, Carey LA, et al. Dysregulation of the epigenome in triple-negative breast cancers: basal-like and claudin-low breast cancers express aberrant DNA hypermethylation. Exp Mol Pathol. 2013;95(3):276–287. 10.1016/j.yexmp.2013.09.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209. Sandhu R, Rivenbark AG, Mackler RM, Livasy CA, Coleman WB. Dysregulation of microRNA expression drives aberrant DNA hypermethylation in basal-like breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2014;44(2):563–572. 10.3892/ijo.2013.2197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210. Wang J, Ray PS, Sim MS, Zhou XZ, Lu KP, Lee AV, et al. FOXC1 regulates the functions of human basal-like breast cancer cells by activating NF-kappaB signaling. Oncogene. 2012;31(45):4798–4802. 10.1038/onc.2011.635 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211. Sizemore ST, Keri RA. The forkhead box transcription factor FOXC1 promotes breast cancer invasion by inducing matrix metalloprotease 7 (MMP7) expression. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(29):24631–24640. 10.1074/jbc.M112.375865 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212. Tkocz D, Crawford NT, Buckley NE, Berry FB, Kennedy RD, Gorski JJ, et al. BRCA1 and GATA3 corepress FOXC1 to inhibit the pathogenesis of basal-like breast cancers. Oncogene. 2012;31(32):3667–3678. 10.1038/onc.2011.531 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213. Andres SA, Brock GN, Wittliff JL. Interrogating differences in expression of targeted gene sets to predict breast cancer outcome. BMC Cancer. 2013;13(326):1–18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214. Symmans WF, Fiterman DJ, Anderson SK, Ayers M, Rouzier R, Dunmire V, et al. A single-gene biomarker identifies breast cancers associated with immature cell type and short duration of prior breastfeeding. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12(4):1059–1069. 10.1677/erc.1.01051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215. Bell JL, Wachter K, Muhleck B, Pazaitis N, Kohn M, Lederer M, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs): post-transcriptional drivers of cancer progression? Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(15):2657–2675. 10.1007/s00018-012-1186-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216. Fadare O, Liang SX, Crispens MA, Jones HW, Khabele D, Gwin K, et al. Expression of the oncofetal protein IGF2BP3 in endometrial clear cell carcinoma: assessment of frequency and significance. Hum Pathol. 2013;44(8):1508–1515. 10.1016/j.humpath.2012.12.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217. Lochhead P, Imamura Y, Morikawa T, Kuchiba A, Yamauchi M, Liao X, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 2 messenger RNA binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) is a marker of unfavourable prognosis in colorectal cancer. Europ J Cancer. 2012;48(18):3405–3413. 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.06.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218. Samanta S, Pursell B, Mercurio AM. IMP3 protein promotes chemoresistance in breast cancer cells by regulating breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) expression. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(18):12569–12573. 10.1074/jbc.C112.442319 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219. Samanta S, Sharma VM, Khan A, Mercurio AM. Regulation of IMP3 by EGFR signaling and repression by ERbeta: implications for triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene. 2012;31(44):4689–4697. 10.1038/onc.2011.620 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220. Won JR, Gao D, Chow C, Cheng J, Lau SY, Ellis MJ, et al. A survey of immunohistochemical biomarkers for basal-like breast cancer against a gene expression profile gold standard. Mod Pathol. 2013;26(11):1438–1450. 10.1038/modpathol.2013.97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221. Walter O, Prasad M, Lu S, Quinlan RM, Edmiston KL, Khan A. IMP3 is a novel biomarker for triple negative invasive mammary carcinoma associated with a more aggressive phenotype. Hum Pathol. 2009;40(11):1528–1533. 10.1016/j.humpath.2009.05.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222. Bu D, Lewis CM, Sarode V, Chen M, Ma X, Lazorwitz AM, et al. Identification of Breast Cancer DNA Methylation Markers Optimized for Fine-Needle Aspiration Samples. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2013;22(12):2212–2221. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-13-0208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223. Martens JW, Nimmrich I, Koenig T, Look MP, Harbeck N, Model F, et al. Association of DNA methylation of phosphoserine aminotransferase with response to endocrine therapy in patients with recurrent breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65(10):4101–4117. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0064 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224. Lan J, Zhao J, Liu Y. Molecular cloning, sequence characterization, polymorphism and association analysis of porcine ROPN1 gene. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(3):2739–2743. 10.1007/s11033-011-1029-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225. Berretta R, Moscato P. Cancer Biomarker Discovery: The Entropic Hallmark. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(8):e12262 10.1371/journal.pone.0012262 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226. de Kruijf EM, Bastiaannet E, Rubertá F, de Craen AJM, Kuppen PJK, Smit VTHBM, et al. Comparison of frequencies and prognostic effect of molecular subtypes between young and elderly breast cancer patients. Molecular Oncology. 2014;8(5):1014–1025. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1574789114000775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227. Nguyen PL, Taghian AG, Katz MS, Niemierko A, Abi Raad RF, Boon WL, et al. Breast cancer subtype approximated by estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER-2 is associated with local and distant recurrence after breast-conserving therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(14):2373–2378. 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.4287 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228. Polyak K. Heterogeneity in breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(10):3786–3788. 10.1172/JCI60534 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229. Peppercorn J, Perou CM, Carey LA. Molecular subtypes in breast cancer evaluation and management: divide and conquer. Cancer Invest. 2008;26(1):1–10. 10.1080/07357900701784238 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230. Mackay A, Weigelt B, Grigoriadis A, Kreike B, Natrajan R, A’Hern R, et al. Microarray-based class discovery for molecular classification of breast cancer: analysis of interobserver agreement. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103(8):662–673. 10.1093/jnci/djr071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The document shows the CM1 probe list along with an extensive literature review. The 42 CM1 biomarkers revealed a great potential to differentiate breast cancer intrinsic subtypes in the METABRIC and ROCK data sets. The 30 novel markers and 12 well-established genes vary the expression levels across different subtypes. The vast majority has been associated with breast cancer disease, either included or not in the subtyping context.
(PDF)
Box plots illustrating the expression levels for all selected transcripts in the CM1 list in the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK test set. The figure shows the probes differential behaviour across breast cancer intrinsic subtypes.
(TIFF)
Table listing the CM1 score used to rank the set of 48803 probes for each of the five breast cancer subtypes in the METABRIC discovery data set. In each case, we selected the top 10 highly discriminative probes (5 with the greatest positive CM1 score values—indicating up-regulated probes relative to the other subtypes, and 5 with the smallest negative values—representing down-regulation).
(XLSX)
Table describing the performance of each classifier on the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK test set using the CM1 list. It shows the percentage of correctly, incorrectly and not classified samples, Fleiss Kappa index, Cramer’s V, Average Sensitivity, and other values for classification. The 24 classifiers from the Weka software suite are also listed. The labels predicted by each classifier for all samples using CM1 list are defined as: 1—luminal A, 2—luminal B, 3—HER2-enriched, 4—normal-like, 5—basal-like. Count of predicted labels was obtained with the consensus of the majority of classifiers.
(XLSX)
Table describing the performance of each classifier on the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK test set using the PAM50 list. It shows the percentage of correctly, incorrectly and not classified samples, Fleiss Kappa index, Cramer’s V, Average Sensitivity, and other values for classification. The 24 classifiers from the Weka software suite are also listed. The labels predicted by each classifier for all samples using CM1 list are defined as: 1—luminal A, 2—luminal B, 3—HER2-enriched, 4—normal-like, 5—basal-like. Count of predicted labels was obtained with the consensus of the majority of classifiers.
(XLSX)
Table containing the Fleiss’ Kappa agreement of labels for the METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK test set. It shows the overall agreement Among classifiers using CM1 and PAM50 lists, as well as the agreement for each subtype. The predicted—original are described in the table and contain the agreement between the mostly predicted and initial labels of samples; whereas the CM1—PAM50 show agreement between labels assigned by the majority of classifiers using CM1 and PAM50 lists. The file also has the Jensen-Shannon divergence between two probability distributions. Numbers represent the similarity between subtypes distribution for METABRIC discovery and validation sets, and ROCK test set. The similarity is measured using the square root of the Jensen-Shannon divergence.
(XLSX)
Data Availability Statement
The METABRIC microarray data set is available at the European Genome-Phenome Archive (EGA) at http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ega/, under accession number EGAS00000000083. The ROCK microarray dataset is available at the ROCK online portal at http://rock.icr.ac.uk/, under data source access GSE47561, and also in GEO at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/ under the same accession number, GSE47561.