Abstract
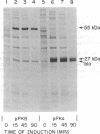
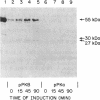
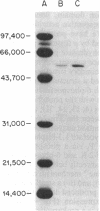
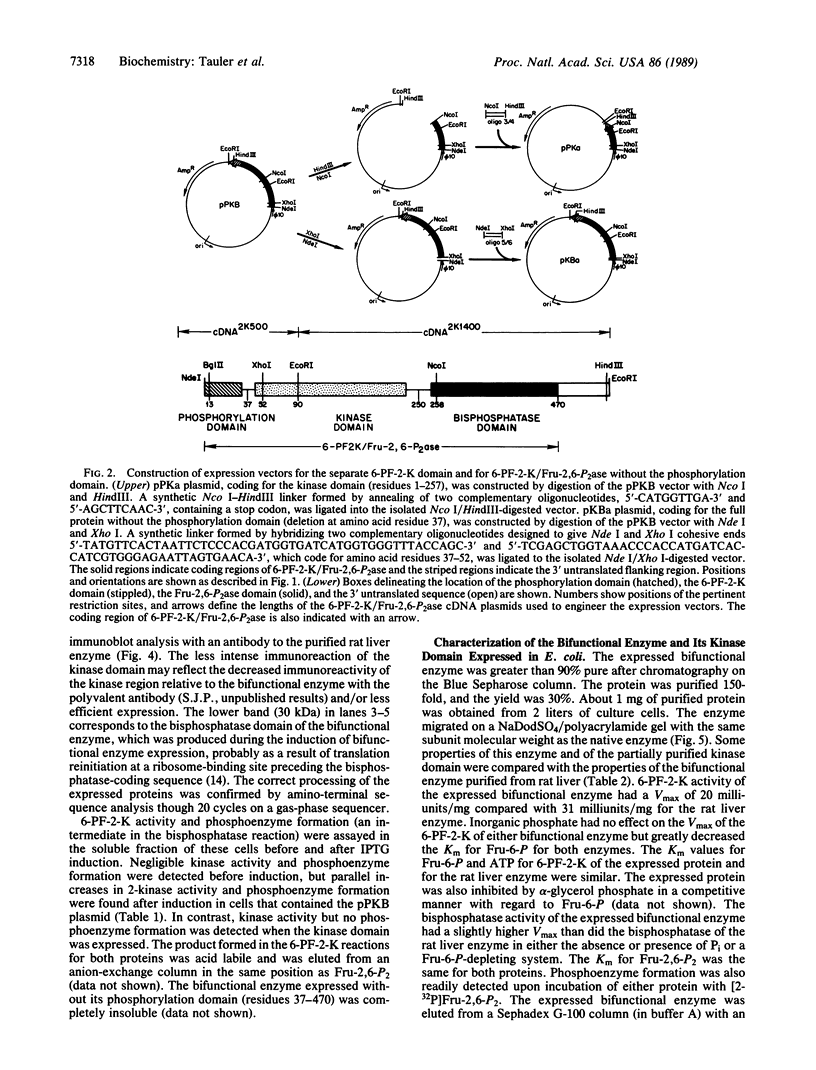
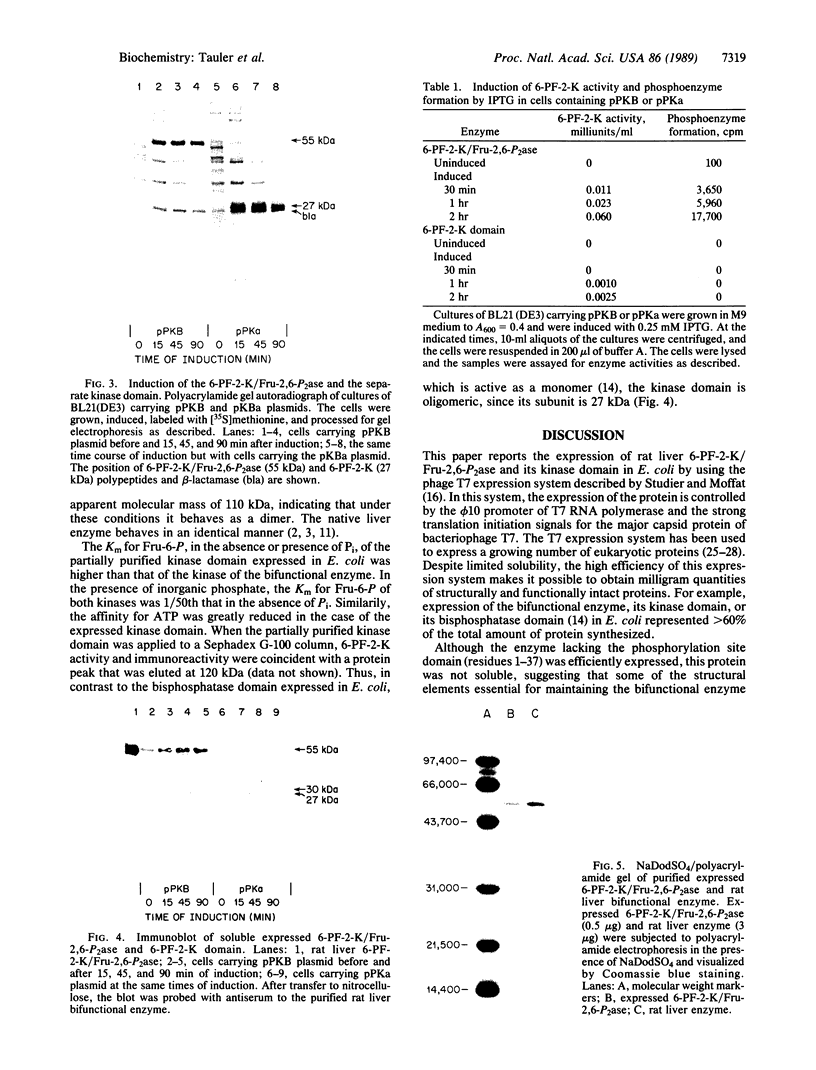
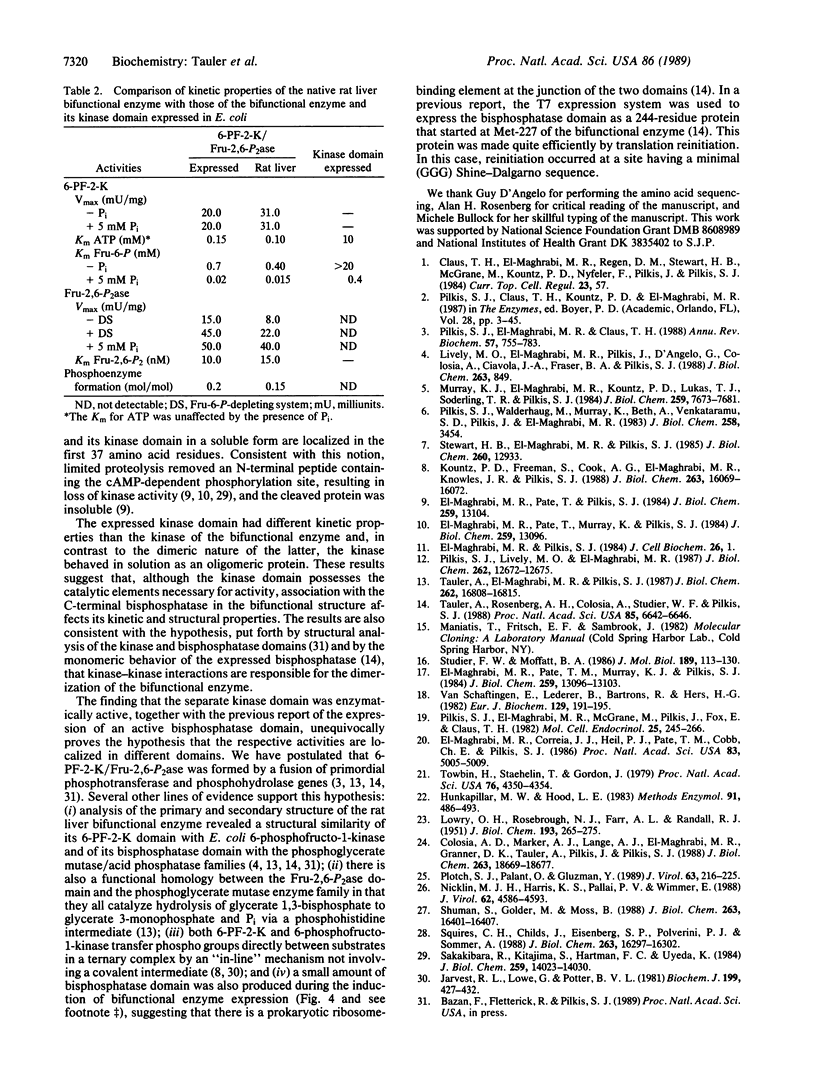
The rat liver bifunctional enzyme, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (ATP:D-fructose-6-phosphate 2-phosphotransferase/D-fructose-2,6-bisphosphate 2-phosphohydrolase, EC 2.7.1.105/EC 3.1.3.46) and its separate kinase domain were expressed in Escherichia coli by using an expression system based on bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. The bifunctional enzyme (470 residues per subunit) was efficiently expressed as a protein that starts with the initiator methionine residue and ends at the carboxyl-terminal tyrosine residue. The expressed protein was purified to homogeneity by anion exchange and Blue Sepharose chromatography and had kinetic and physical properties similar to the purified rat liver enzyme, including its behavior as a dimer during gel filtration, activation of the kinase by phosphate and inhibition by alpha-glycerol phosphate, and mediation of the bisphosphatase reaction by a phosphoenzyme intermediate. The expressed 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase also started with the initiator methionine but ended at residue 257. The partially purified kinase domain was catalytically active, had reduced affinities for ATP and fructose 6-phosphate compared with the kinase of the bifunctional enzyme, and had no fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase activity. The kinase domain also behaved as an oligomeric protein during gel filtration. The expression of an active kinase domain and the previous demonstration of an actively expressed bisphosphatase domain provide strong support for the hypothesis that the hepatic enzyme consists of two independent catalytic domains encoded by a fused gene.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Claus T. H., El-Maghrabi M. R., Regen D. M., Stewart H. B., McGrane M., Kountz P. D., Nyfeler F., Pilkis J., Pilkis S. J. The role of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1984;23:57–86. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152823-2.50006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colosia A. D., Marker A. J., Lange A. J., el-Maghrabi M. R., Granner D. K., Tauler A., Pilkis J., Pilkis S. J. Induction of rat liver 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase mRNA by refeeding and insulin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18669–18677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Maghrabi M. R., Pate T. M., Murray K. J., Pilkis S. J. Differential effects of proteolysis and protein modification on the activities of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13096–13103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Maghrabi M. R., Pate T. M., Murray K. J., Pilkis S. J. Differential effects of proteolysis and protein modification on the activities of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13096–13103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Maghrabi M. R., Pate T. M., Pilkis J., Pilkis S. J. Effect of sulfhydryl modification on the activities of rat liver 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13104–13110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis S. J. Rat liver 6-phosphofructo 2-kinase/fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase: a review of relationships between the two activities of the enzyme. J Cell Biochem. 1984;26(1):1–17. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240260102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Analysis of phenylthiohydantoins by ultrasensitive gradient high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:486–493. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvest R. L., Lowe G., Potter B. V. The stereochemical course of phosphoryl transfer catalysed by Bacillus stearothermophilus and rabbit skeletal-muscle phosphofructokinase with a chiral [16O,17O,18O]phosphate ester. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 1;199(2):427–432. doi: 10.1042/bj1990427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kountz P. D., Freeman S., Cook A. G., el-Maghrabi M. R., Knowles J. R., Pilkis S. J. The stereochemical course of phospho group transfer catalyzed by rat liver 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16069–16072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lively M. O., el-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis J., D'Angelo G., Colosia A. D., Ciavola J. A., Fraser B. A., Pilkis S. J. Complete amino acid sequence of rat liver 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):839–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K. J., El-Maghrabi M. R., Kountz P. D., Lukas T. J., Soderling T. R., Pilkis S. J. Amino acid sequence of the phosphorylation site of rat liver 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7673–7681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklin M. J., Harris K. S., Pallai P. V., Wimmer E. Poliovirus proteinase 3C: large-scale expression, purification, and specific cleavage activity on natural and synthetic substrates in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4586–4593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4586-4593.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., El-Maghrabi M. R., McGrane M., Pilkis J., Fox E., Claus T. H. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate: a mediator of hormone action at the fructose 6-phosphate/fructose 1,6-bisphosphate substrate cycle. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Mar;25(3):245–266. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., Lively M. O., el-Maghrabi M. R. Active site sequence of hepatic fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Homology in primary structure with phosphoglycerate mutase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12672–12675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., el-Maghrabi M. R., Claus T. H. Hormonal regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycolysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:755–783. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotch S. J., Palant O., Gluzman Y. Purification and properties of poliovirus RNA polymerase expressed in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):216–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.216-225.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara R., Kitajima S., Hartman F. C., Uyeda K. Hexose phosphate binding sites of fructose-6-phosphate,2-kinase:fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Interaction with N-bromoacetylethanolamine phosphate and 3-bromo-1,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 1,4-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14023–14028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Golder M., Moss B. Characterization of vaccinia virus DNA topoisomerase I expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16401–16407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires C. H., Childs J., Eisenberg S. P., Polverini P. J., Sommer A. Production and characterization of human basic fibroblast growth factor from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16297–16302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauler A., Rosenberg A. H., Colosia A., Studier F. W., Pilkis S. J. Expression of the bisphosphatase domain of rat liver 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6642–6646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauler A., el-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis S. J. Functional homology of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase, phosphoglycerate mutase, and 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate mutase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16808–16815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Lederer B., Bartrons R., Hers H. G. A kinetic study of pyrophosphate: fructose-6-phosphate phosphotransferase from potato tubers. Application to a microassay of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):191–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Maghrabi M. R., Correia J. J., Heil P. J., Pate T. M., Cobb C. E., Pilkis S. J. Tissue distribution, immunoreactivity, and physical properties of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5005–5009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]