Abstract
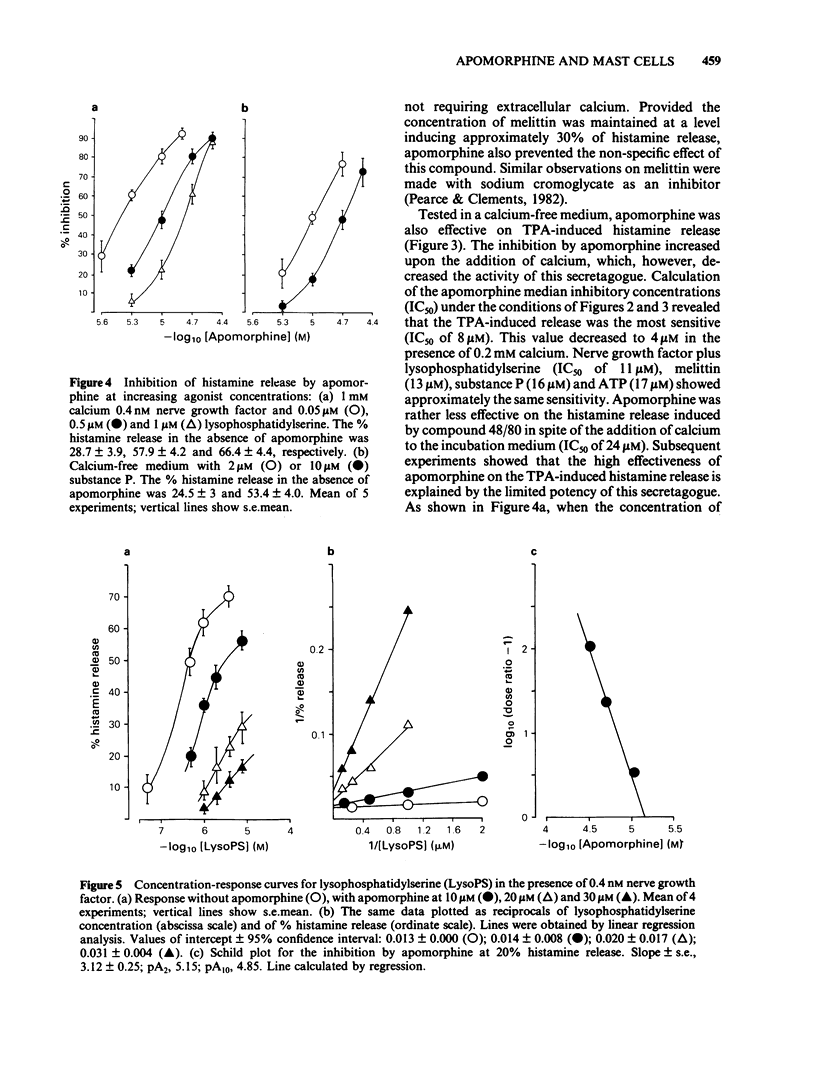
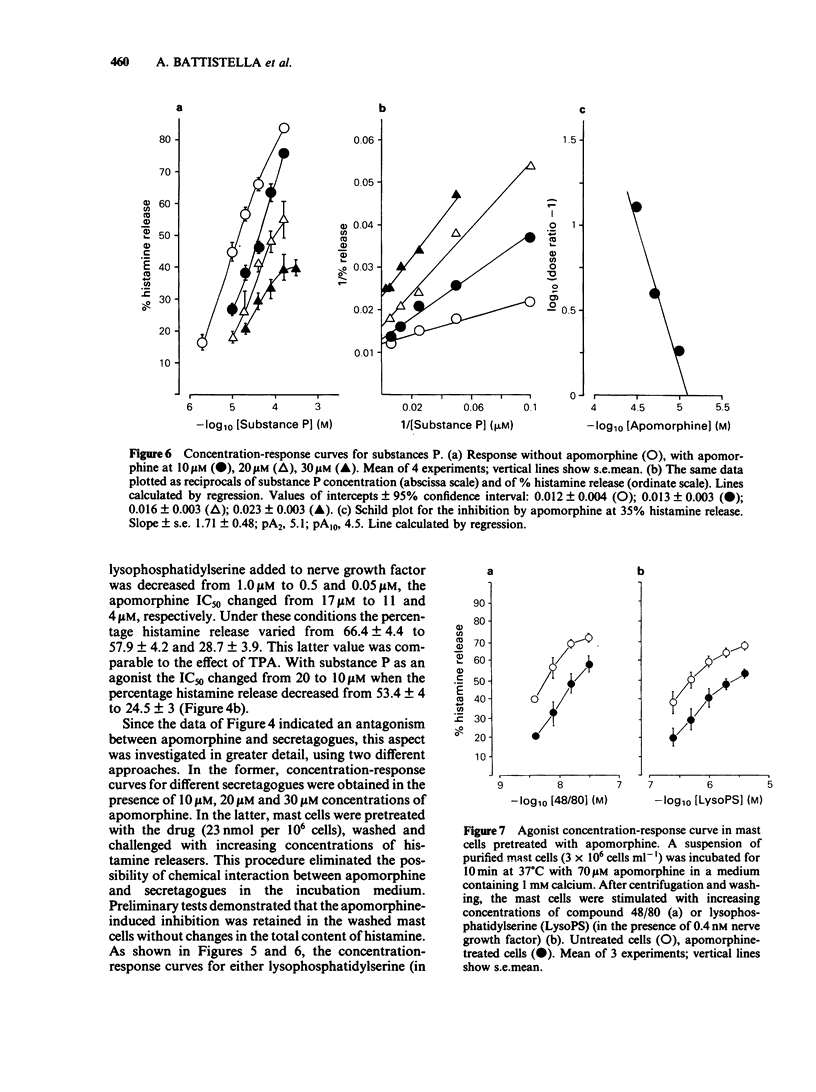
The apomorphine-induced inhibition of histamine release in rat peritoneal mast cells was studied by means of secretagogues stimulating different pathways of mast cell activation. Apomorphine inhibited the mast cell response to all releasing agents (lysophosphatidylserine plus nerve growth factor, compound 48/80, substance P, ATP, tetradecanoylphorbolacetate, melittin). The IC50 ranged from 4 microM to 24 microM at concentrations of secretagogues releasing 30-50% of mast cell histamine. However, the potency of the drug decreased at higher secretagogue concentrations. Mast cells, pretreated with apomorphine and washed, released little histamine upon stimulation. The secretory response could be partially restored on increasing the concentration of secretagogues. The results suggest that apomorphine affects a regulatory step controlling the terminal sequence of mast cell secretory activity. As indicated by the reduced potency of the drug, the control by the apomorphine-sensitive reaction loses efficiency under conditions of massive histamine release.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battistella A., Mietto L., Toffano G., Palatini P., Bigon E., Bruni A. Synergism between lysophosphatidylserine and the phorbol ester tetradecanoylphorbolacetate in rat mast cells. Life Sci. 1985 Apr 22;36(16):1581–1587. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigon E., Boarato E., Bruni A., Leon A., Toffano G. Pharmacological effects of phosphatidylserine liposomes: the role of lysophosphatidylserine. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;67(4):611–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boarato E., Mietto L., Toffano G., Bigon E., Bruni A. Different responses of rodent mast cells to lysophosphatidylserine. Agents Actions. 1984 Jun;14(5-6):613–618. doi: 10.1007/BF01978895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruni A., Bigon E., Boarato E., Mietto L., Leon A., Toffano G. Interaction between nerve growth factor and lysophosphatidylserine on rat peritoneal mast cells. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 22;138(2):190–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80438-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Activation and inhibition of calcium-dependent histamine secretion by ATP ions applied to rat mast cells. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:229–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Evidence for a role of phosphatidylinositol turnover in stimulus-secretion coupling. Studies with rat peritoneal mast cells. Biochem J. 1979 Mar 15;178(3):681–687. doi: 10.1042/bj1780681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant B., Krüger P. G. Histamine release from isolated rat peritoneal mast cells induced by adenosine-5'-triphosphate. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Dec;71(4):291–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fewtrell C. M., Foreman J. C., Jordan C. C., Oehme P., Renner H., Stewart J. M. The effects of substance P on histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine release in the rat. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:393–411. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katakami Y., Kaibuchi K., Sawamura M., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic action of protein kinase C and calcium for histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):573–578. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennerly D. A., Sullivan T. J., Parker C. W. Activation of phospholipid metabolism during mediator release from stimulated rat mast cells. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):152–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietto L., Battistella A., Toffano G., Bruni A. Modulation of lysophosphatidylserine-dependent histamine release. Agents Actions. 1984 Apr;14(3-4):376–378. doi: 10.1007/BF01973832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L. Calcium and histamine secretion from mast cells. Prog Med Chem. 1982;19:59–109. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70328-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L., Clements J. Effect of disodium cromoglycate and cyclic AMP-active drugs on cytotoxic histamine release from rat mast cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 1;31(13):2247–2250. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. W., Lenney J. F. Molecular weight studies on the active constituents of compound 48-80. J Med Chem. 1972 Mar;15(3):320–323. doi: 10.1021/jm00273a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. R., Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Sha'afi R. Direct demonstration of increased intracellular concentration of free calcium as measured by quin-2 in stimulated rat peritoneal mast cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow C. M., Austen K. F. Role of cyclic nucleotides in the activation-secretion response. Prog Allergy. 1984;34:236–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


