Abstract
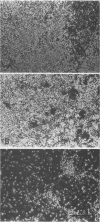
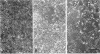
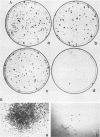
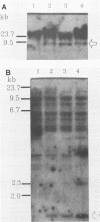
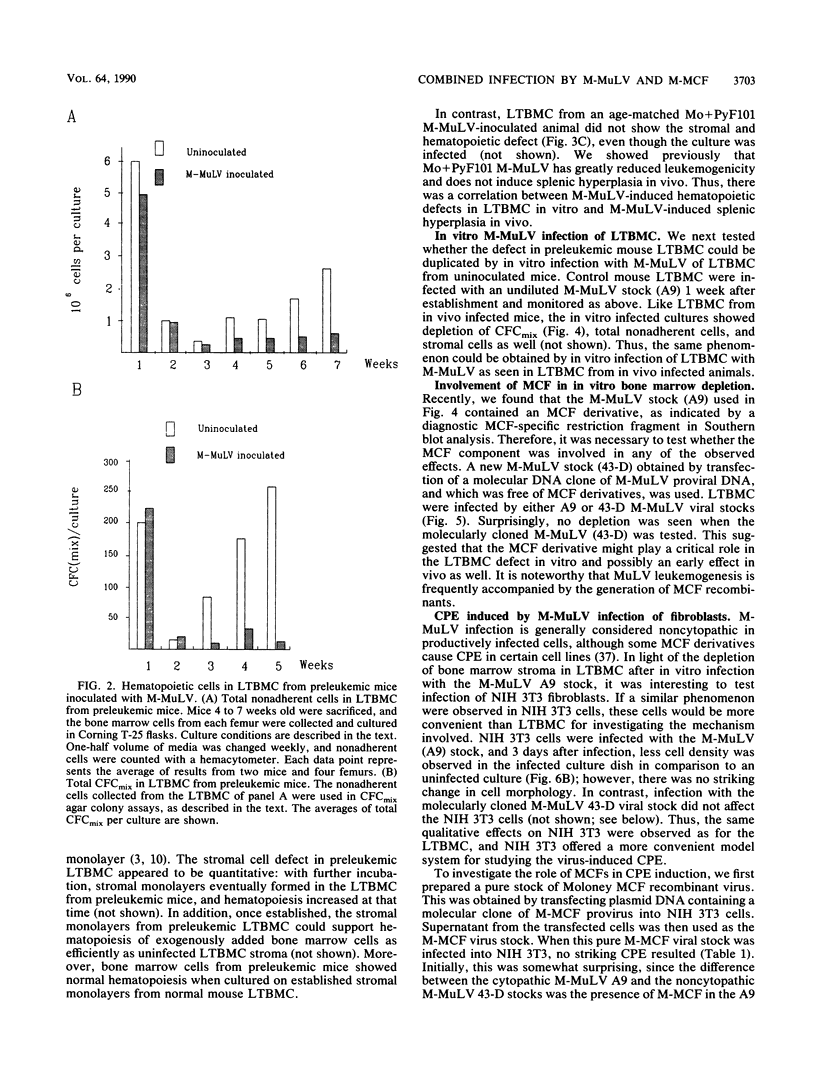
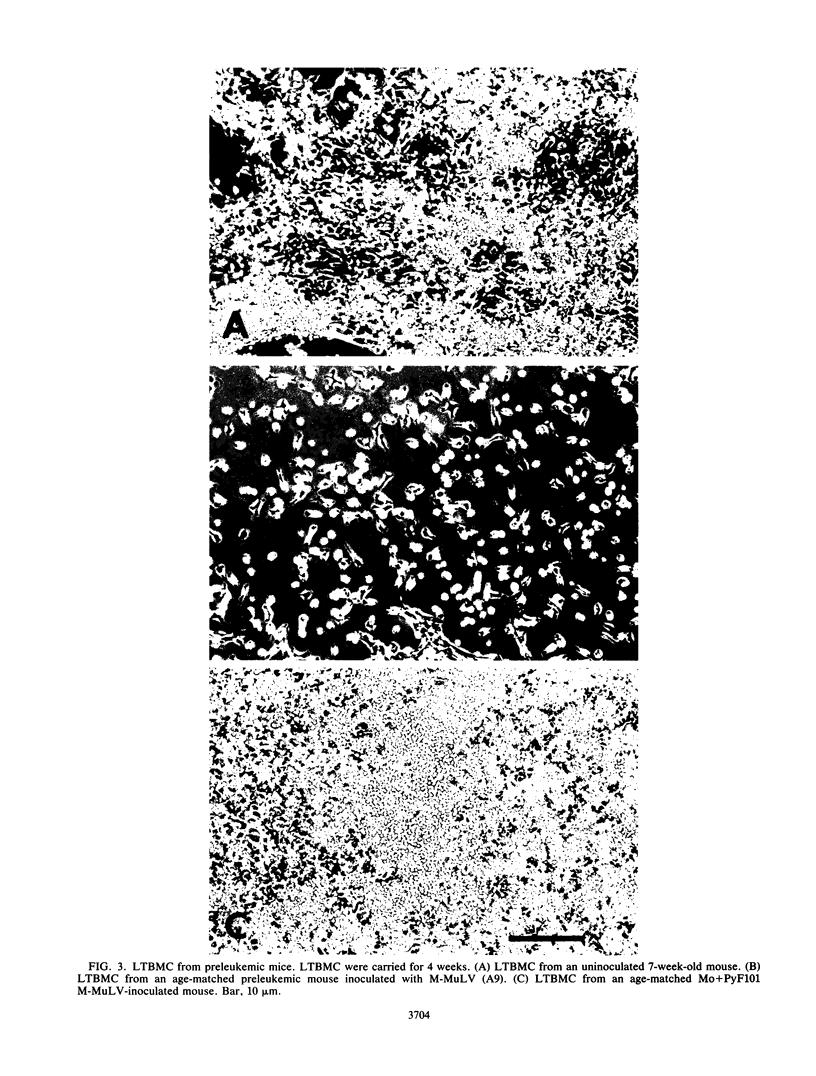
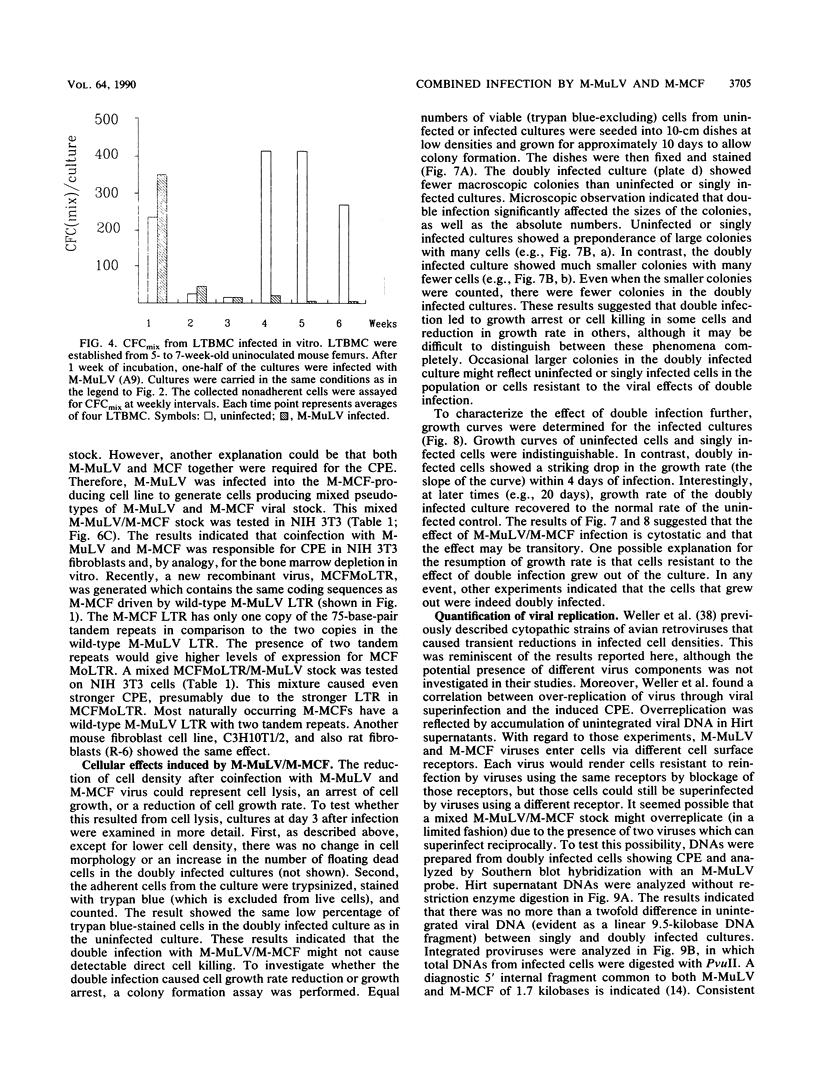
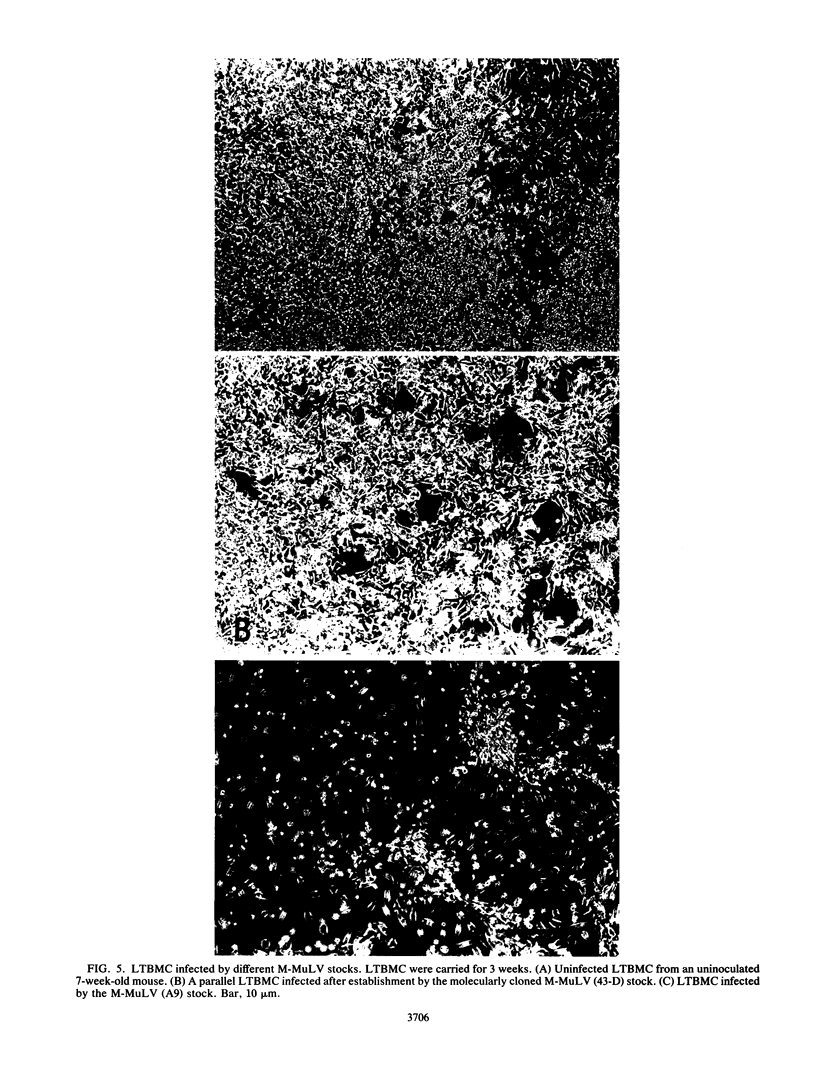
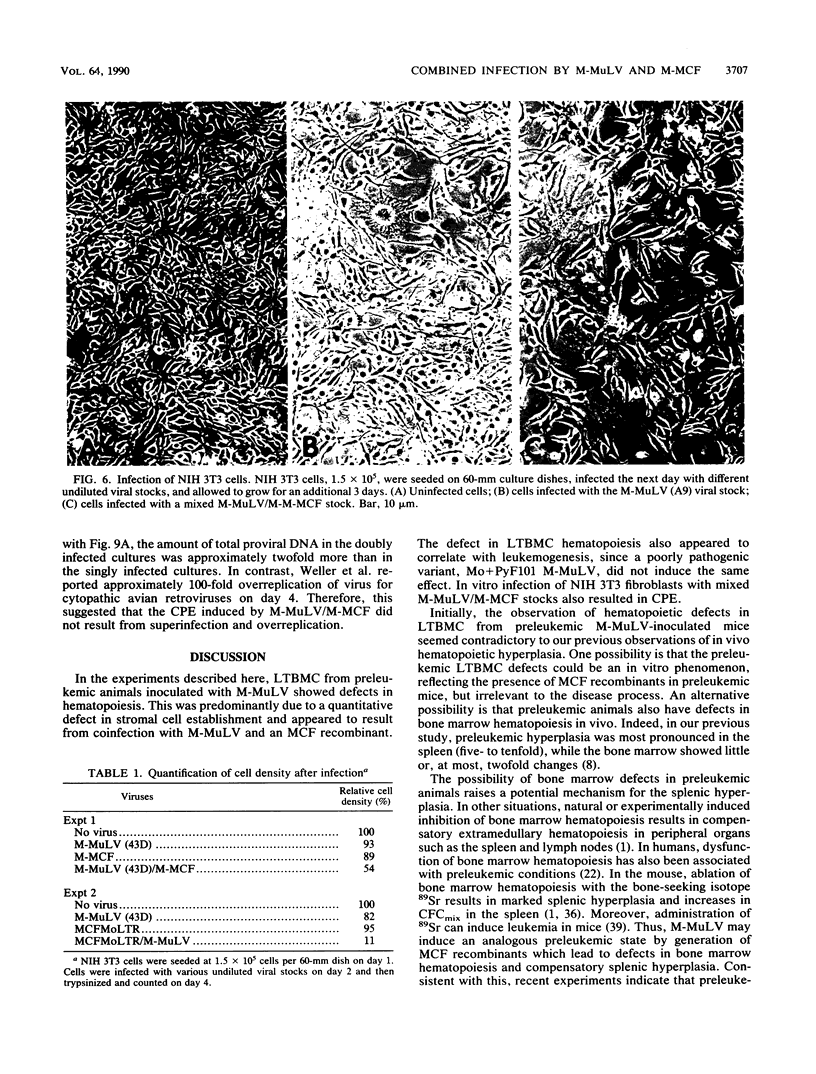
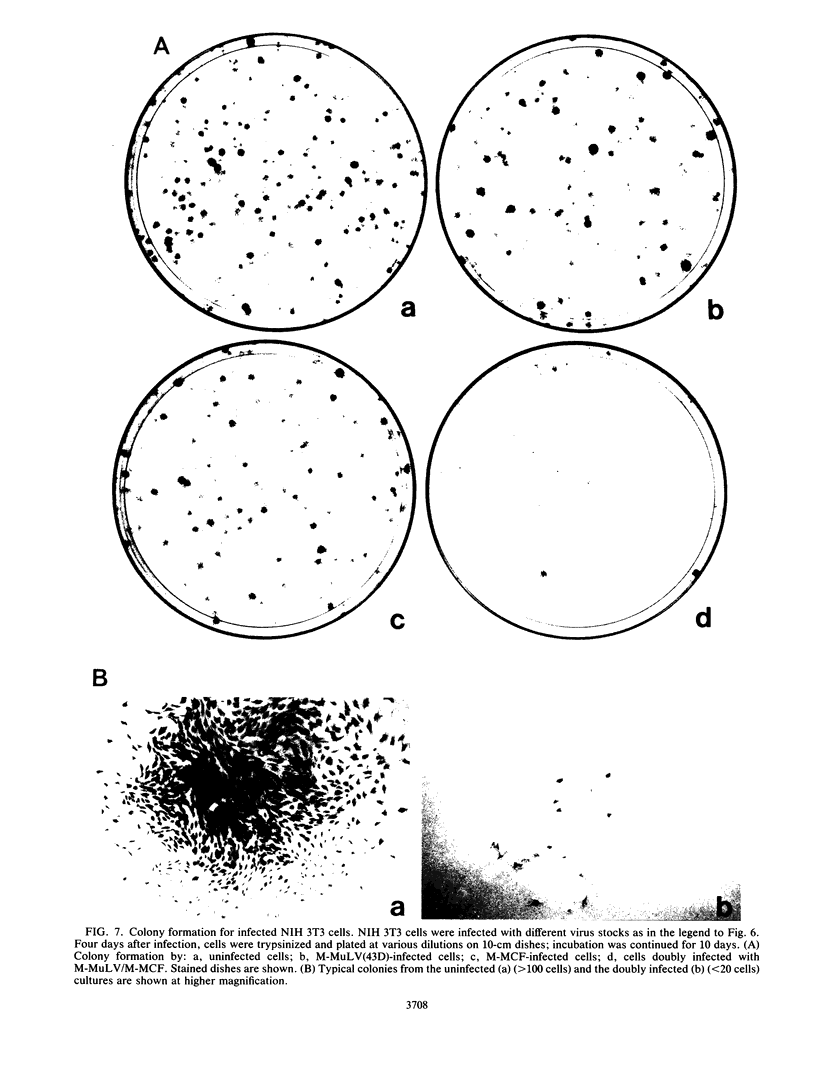
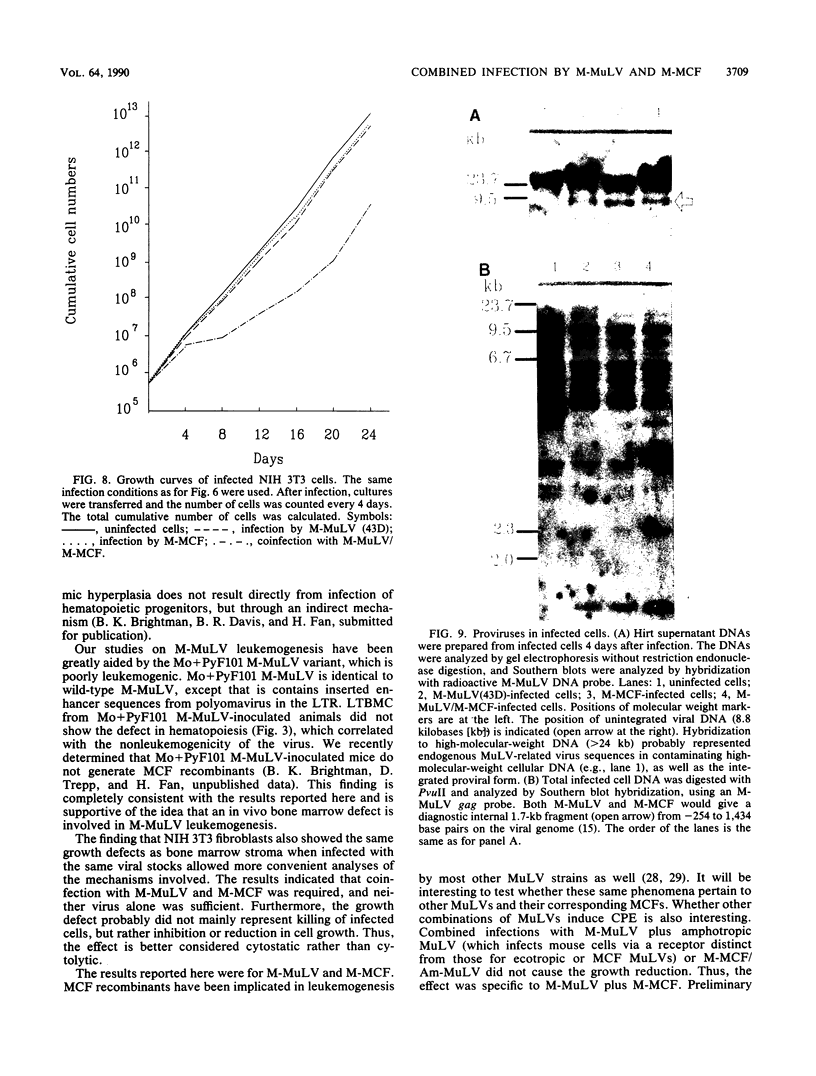
We described previously a preleukemic state in mice inoculated with Moloney murine leukemia virus (M-MuLV) characterized by generalized hematopoietic hyperplasia in the spleen. To investigate this further, long-term bone marrow cultures (LTBMC) from preleukemic mice were established. Surprisingly, LTBMC from M-MuLV-inoculated preleukemic mice showed less hematopoiesis than LTBMC from control mice. This resulted from a quantitative defect in establishment of bone marrow stromal cells in the LTBMC. This phenomenon could also be observed in LTBMC from normal mice infected in vitro with a stock of M-MuLV containing a mink cell focus-forming virus (MCF) derivative (M-MCF), but not in LTBMC infected with M-MuLV alone. This implicated MCF derivatives in the reduction in bone marrow stromal cells. The phenomenon could also be detected in infected NIH 3T3 cells. Combined infection of M-MuLV plus M-MCF resulted in fewer cells, in comparison to uninfected cells or cells infected with either virus alone. Further studies indicated that this was predominantly due to an inhibition in cell growth rather than to cell lysis. The cytopathic effect did not appear to result from overreplication of viral DNA, as measured by Southern blots. Thus, combined infection with M-MuLV and an MCF derivative had cytostatic effects on cell growth. This phenomenon might also contribute to the leukemogenic process in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler S. S., Trobauch F. E., Jr, Knospe W. H. Hemopoietic stem cell dynamics in 89Sr marrow-ablated mice. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Mar;89(3):592–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albritton L. M., Tseng L., Scadden D., Cunningham J. M. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen T. D., Dexter T. M. Long term bone marrow cultures: an ultrastructural review. Scan Electron Microsc. 1983;(Pt 4):1851–1866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asjö B., Skoog L., Palminger I., Wiener F., Isaak D., Cerny J., Fenyö E. M. Influence of genotype and the organ of origin on the subtype of T-cell in Moloney lymphomas induced by transfer of preleukemic cells from athymic and thymus-bearing mice. Cancer Res. 1985 Mar;45(3):1040–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselman R. A., van Straaten F., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M., Vogt M. Analysis of the env gene of a molecularly cloned and biologically active Moloney mink cell focus-forming proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):19–31. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.19-31.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. R., Brightman B. K., Chandy K. G., Fan H. Characterization of a preleukemic state induced by Moloney murine leukemia virus: evidence for two infection events during leukemogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4875–4879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Linney E., Fan H. Suppression of leukaemia virus pathogenicity by polyoma virus enhancers. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):550–553. doi: 10.1038/314550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Allen T. D., Lajtha L. G. Conditions controlling the proliferation of haemopoietic stem cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jun;91(3):335–344. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Allen T. D., Testa N. G., Scolnick E. Friend disease in vitro. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):594–608. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Scott D., Teich N. M. Infection of bone marrow cells in vitro with FLV: effects on stem cell proliferation, differentiation and leukemogenic capacity. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M. Stromal cell associated haemopoiesis. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1982;1:87–94. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Cloyd M. W. Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses specifically recombine with different endogenous retroviral sequences to generate mink cell focus-forming viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Chute H., Chao E., Pattengale P. K. Leukemogenicity of Moloney murine leukemia viruses carrying polyoma enhancer sequences in the long terminal repeat is dependent on the nature of the inserted polyoma sequences. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):58–65. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Jaenisch R., MacIsaac P. Low-multiplicity infection of Moloney murine leukemia virus in mouse cells: effect on number of viral DNA copies and virus production in producer cells. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):802–809. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.802-809.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberger J. S., Shadduck R. K., Jaenisch R., Waheed A., Sakakeeny M. A. Effects of murine leukemia virus infection on long-term hematopoiesis in vitro emphasized by increased survival of bone marrow cultures derived from BALB/Mo mice. Cancer Res. 1981 Sep;41(9 Pt 1):3556–3565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Reshef T. Non-thymic malignant lymphomas induced in C57BL/6 mice by cloned dualtropic viruses isolated from hematopoietic stromal cell lines. Eur J Cancer. 1980 Jul;16(7):909–917. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(80)90329-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haran-Ghera N. Potential leukemic cells among bone marrow cells of young AKR/J mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2923–2926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Davis B., Overhauser J., Chao E., Fan H. Non-function of a Moloney murine leukaemia virus regulatory sequence in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):470–472. doi: 10.1038/308470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., Oliff I., Schmidt B., Famulari N. Isolation of immortal cell lines from the first stage of murine leukemia virus-induced leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5464–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A. Interference grouping of murine leukemia viruses: a distinct receptor for the MCF-recombinant viruses in mouse cells. Virology. 1982 Jul 15;120(1):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., Schultz A. Different recombinant murine leukemia viruses use different cell surface receptors. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):144–152. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90255-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Evans L., Nishio J., Wehrly K., Chesebro B. Analysis of two strains of Friend murine leukemia viruses differing in ability to induce early splenomegaly: lack of relationship with generation of recombinant mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):389–393. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.389-393.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Sola B., Evans L., Nishio J., Hayes S. F., Nathanson K., Garon C. F., Chesebro B. Hemolytic anemia and erythroleukemia, two distinct pathogenic effects of Friend MuLV: mapping of the effects to different regions of the viral genome. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):851–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90800-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt M. Properties of "mink cell focus-inducing" (MCF) virus isolated from spontaneous lymphoma lines of BALB/c mice carrying Moloney leukemia virus as an endogenous virus. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):226–236. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90290-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman A., Chang N. C., Strausbauch P. H., Morahan P. S. Differential effects of chronic monocyte depletion on macrophage populations. Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;49(3):291–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Joy A. E., Temin H. M. Correlation between cell killing and massive second-round superinfection by members of some subgroups of avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):494–506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.494-506.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Putten H., Quint W., van Raaij J., Maandag E. R., Verma I. M., Berns A. M-MuLV-induced leukemogenesis: integration and structure of recombinant proviruses in tumors. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]