Abstract
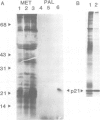
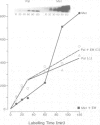
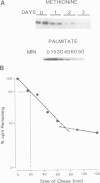
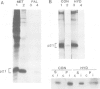
To study the acylation of p21N-ras with palmitic acid we have used cells which express the human N-ras gene to high levels under control of the steroid-inducible MMTV--LTR promoter. Addition of [3H]palmitate to these cells resulted in detectable incorporation of label into p21N-ras within 5 min, which continued linearly for 30-60 min. Inhibition of protein synthesis for up to 24 h before addition of [3H]palmitate had no effect on acylation of p21N-ras, suggesting that this can occur as a late post-translational event. Acylated p21N-ras with a high SDS--PAGE mobility is found only in the membrane fraction, whereas approximately 50% of the [35S]methionine-labelled p21N-ras is cytoplasmic and has a lower mobility. Conversion of the acylated high mobility form to a deacylated form of slightly lower mobility can be achieved with neutral hydroxylamine, which is known to cleave thioesters. This treatment also results in partial removal of p21N-ras from the membranes. A remarkably high rate of turnover of the palmitate moiety can be demonstrated by pulse--chase studies (t1/2 approximately 20 min in serum-containing medium) which cannot be attributed to protein degradation. The data suggest an active acylation--deacylation cycle for p21N-ras, which may be involved in its proposed function as a signal transducing protein.
Full text
PDF
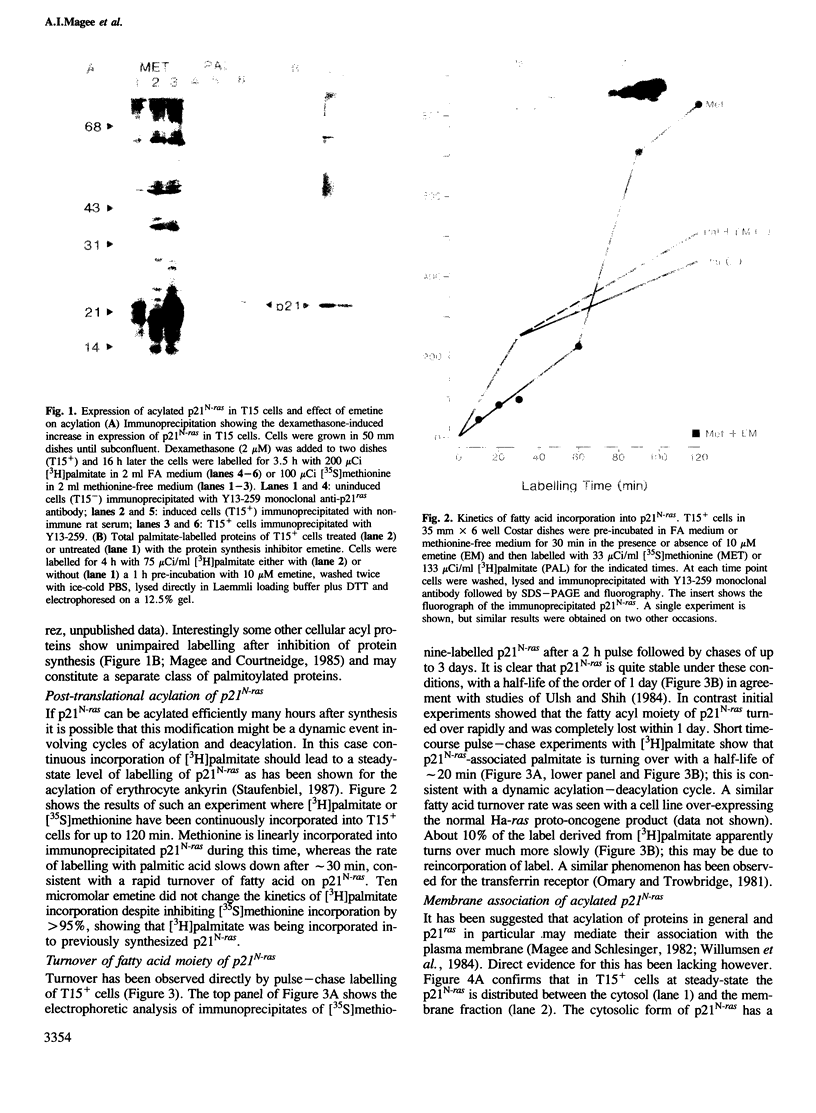
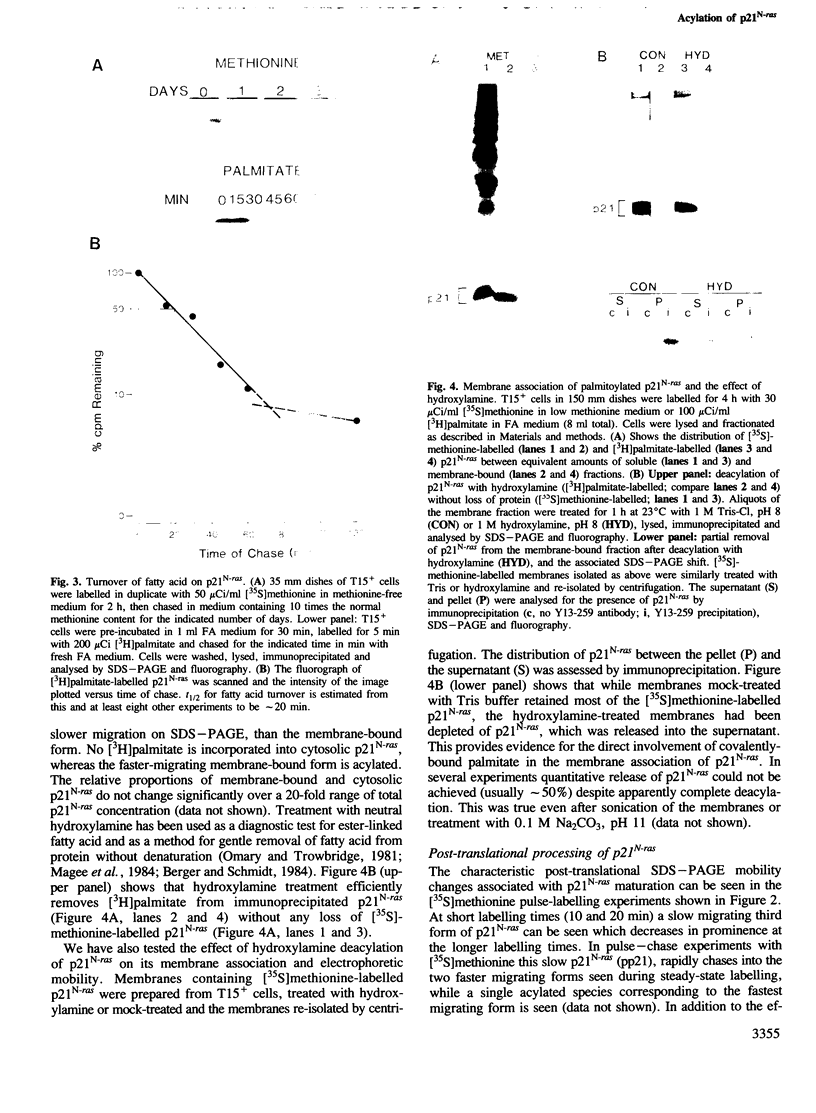


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Induction of membrane ruffling and fluid-phase pinocytosis in quiescent fibroblasts by ras proteins. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1061–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.3090687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M., Schmidt M. F. Cell-free fatty acid acylation of Semliki Forest viral polypeptides with microsomal membranes from eukaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7245–7252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. GTP-binding proteins. One molecular machine can transduce diverse signals. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):814–816. doi: 10.1038/321814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Direct identification of palmitic acid as the lipid attached to p21ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):116–122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Q., Ulsh L. S., DuBois G., Shih T. Y. Posttranslational processing of p21 ras proteins involves palmitylation of the C-terminal tetrapeptide containing cysteine-186. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):607–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.607-612.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote T. E., Frey E. A., Sekura R. D. Altered activity of the inhibitory guanyl nucleotide-binding component (Ni) induced by pertussis toxin. Uncoupling of Ni from receptor with continued coupling of Ni to the catalytic unit. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8693–8698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Fries E., Urbani L. J., Rothman J. E. Early and late functions associated with the Golgi apparatus reside in distinct compartments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7453–7457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Gross M., Kamata T., Rosenberg M., Sweet R. W. Microinjection of the oncogene form of the human H-ras (T-24) protein results in rapid proliferation of quiescent cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman L. F., Chahwala S. B., Cantley L. ras-transformed cells: altered levels of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate and catabolites. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):407–410. doi: 10.1126/science.3001936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Fong H. K., Teplow D. B., Dreyer W. J., Simon M. I. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for the gamma subunit of bovine retinal transducin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6948–6952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Simon M. I., Teplow D. B., Robishaw J. D., Gilman A. G. Homologies between signal transducing G proteins and ras gene products. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):860–862. doi: 10.1126/science.6436980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nagata S., Nakamura S., Katada T., Ui M., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of cDNAs for alpha subunits of the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins Gs, Gi, and Go from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3776–3780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotwal G. J., Ghosh H. P. Role of fatty acid acylation of membrane glycoproteins. Absence of palmitic acid in glycoproteins of two serotypes of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4699–4701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochrie M. A., Hurley J. B., Simon M. I. Sequence of the alpha subunit of photoreceptor G protein: homologies between transducin, ras, and elongation factors. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):96–99. doi: 10.1126/science.3856323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Courtneidge S. A. Two classes of fatty acid acylated proteins exist in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1137–1144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03751.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Koyama A. H., Malfer C., Wen D., Schlesinger M. J. Release of fatty acids from virus glycoproteins by hydroxylamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 10;798(2):156–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Schlesinger M. J. Fatty acid acylation of eucaryotic cell membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 30;694(3):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90008-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Comparative biochemical properties of normal and activated human ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):644–649. doi: 10.1038/310644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlhinney R. A., Pelly S. J., Chadwick J. K., Cowley G. P. Studies on the attachment of myristic and palmitic acid to cell proteins in human squamous carcinoma cell lines: evidence for two pathways. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1145–1152. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay I. A., Marshall C. J., Calés C., Hall A. Transformation and stimulation of DNA synthesis in NIH-3T3 cells are a titratable function of normal p21N-ras expression. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2617–2621. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrdal S. E., Auersperg N. p21ras. Heterogeneous localization in transformed cells. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Aug;159(2):441–450. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(85)80017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Towler D. A., Glaser L. Specificity of fatty acid acylation of cellular proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3784–3790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omary M. B., Trowbridge I. S. Covalent binding of fatty acid to the transferrin receptor in cultured human cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4715–4718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Fine structural mapping of a critical NH2-terminal region of p60src. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1623–1627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Malfer C. Cerulenin blocks fatty acid acylation of glycoproteins and inhibits vesicular stomatitis and Sindbis virus particle formation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):9887–9890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F. Fatty acid binding: a new kind of posttranslational modification of membrane proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;102:101–129. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68906-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schlesinger M. J. Relation of fatty acid attachment to the translation and maturation of vesicular stomatitis and Sindbis virus membrane glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3334–3339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Papageorge A. G., Stokes P. E., Weeks M. O., Scolnick E. M. Guanine nucleotide-binding and autophosphorylating activities associated with the p21src protein of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):686–691. doi: 10.1038/287686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Weeks M. O., Gruss P., Dhar R., Oroszlan S., Scolnick E. M. Identification of a precursor in the biosynthesis of the p21 transforming protein of harvey murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):253–261. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.253-261.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Kung H. F. Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells by microinjection of Ha-ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):508–511. doi: 10.1038/310508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staufenbiel M. Ankyrin-bound fatty acid turns over rapidly at the erythrocyte plasma membrane. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2981–2984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Nukada T., Nishikawa Y., Sugimoto K., Suzuki H., Takahashi H., Noda M., Haga T., Ichiyama A., Kangawa K. Primary structure of the alpha-subunit of transducin and its relationship to ras proteins. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):242–245. doi: 10.1038/315242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ui M., Katada T., Murayama T., Kurose H., Yajima M., Tamura M., Nakamura T., Nogimori K. Islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin: a specific uncoupler of receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:145–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulsh L. S., Shih T. Y. Metabolic turnover of human c-rasH p21 protein of EJ bladder carcinoma and its normal cellular and viral homologs. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1647–1652. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dop C., Yamanaka G., Steinberg F., Sekura R. D., Manclark C. R., Stryer L., Bourne H. R. ADP-ribosylation of transducin by pertussis toxin blocks the light-stimulated hydrolysis of GTP and cGMP in retinal photoreceptors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):23–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Davies S. A., Houslay M. D., McKay I., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Normal p21N-ras couples bombesin and other growth factor receptors to inositol phosphate production. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):173–176. doi: 10.1038/323173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. E., Jr, Moss J., Vaughan M., Liu T., Liu T. Y. Pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of transducin. Cysteine 347 is the ADP-ribose acceptor site. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14428–14430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Banks-Schlegel S. P., Pastan I. H. Immunocytochemical localization in normal and transformed human cells in tissue culture using a monoclonal antibody to the src protein of the Harvey strain of murine sarcoma virus. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Nov;149(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90387-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Norris K., Papageorge A. G., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R. Harvey murine sarcoma virus p21 ras protein: biological and biochemical significance of the cysteine nearest the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2581–2585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfman A., Macara I. G. Elevated levels of diacylglycerol and decreased phorbol ester sensitivity in ras-transformed fibroblasts. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):359–361. doi: 10.1038/325359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]