Abstract
A highly specific antiserum was prepared against purified cauliflower mosaic virus viroplasm-protein (VmP). A virus specific in vitro major translation product (TPmaj), encoded by the 19S poly(A)+ RNA fraction from cauliflower mosaic virus infected turnip leaves, was recognized by this antiserum. The N-terminal sequence of TPmaj corresponds to the sequence following the first in-phase initiation codon in gene VI of the cauliflower mosaic virus genome. Both VmP and TPmaj have blocked termini and probably start from the same AUG codon.
Keywords: cauliflower mosaic virus, viroplasm, gene, in vitro, translation, immunopreciptation
Full text
PDF

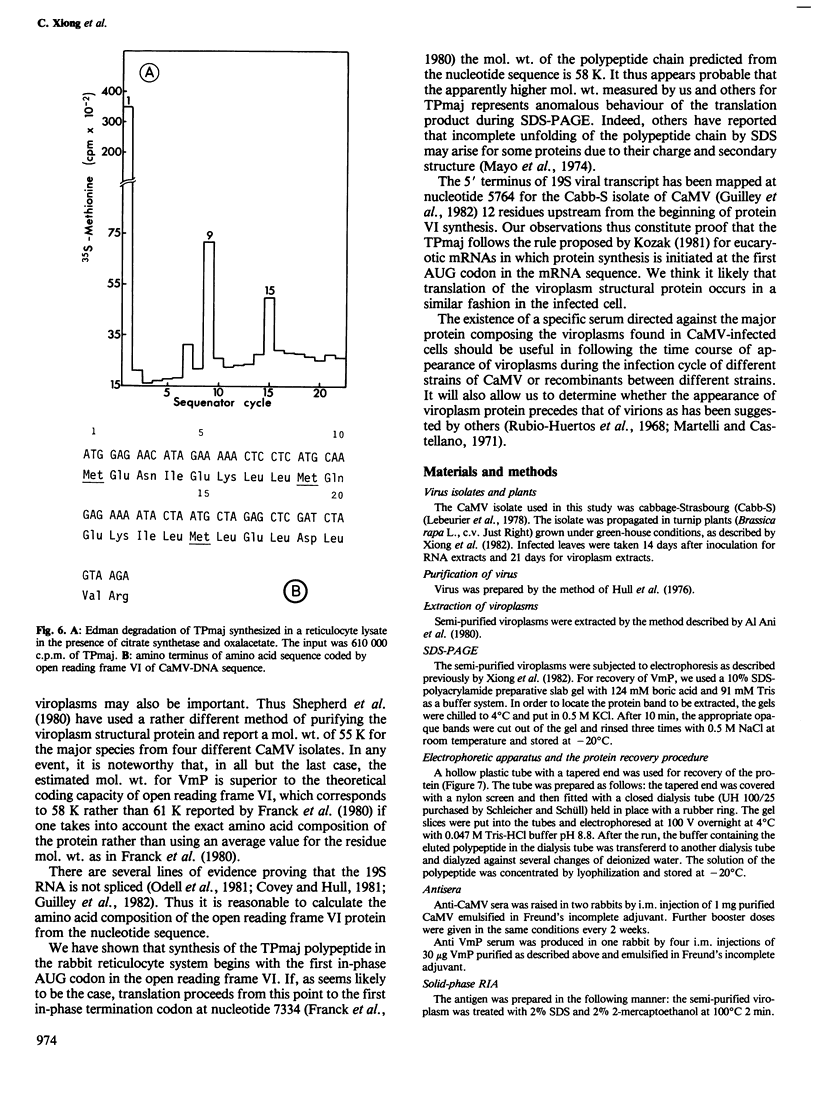
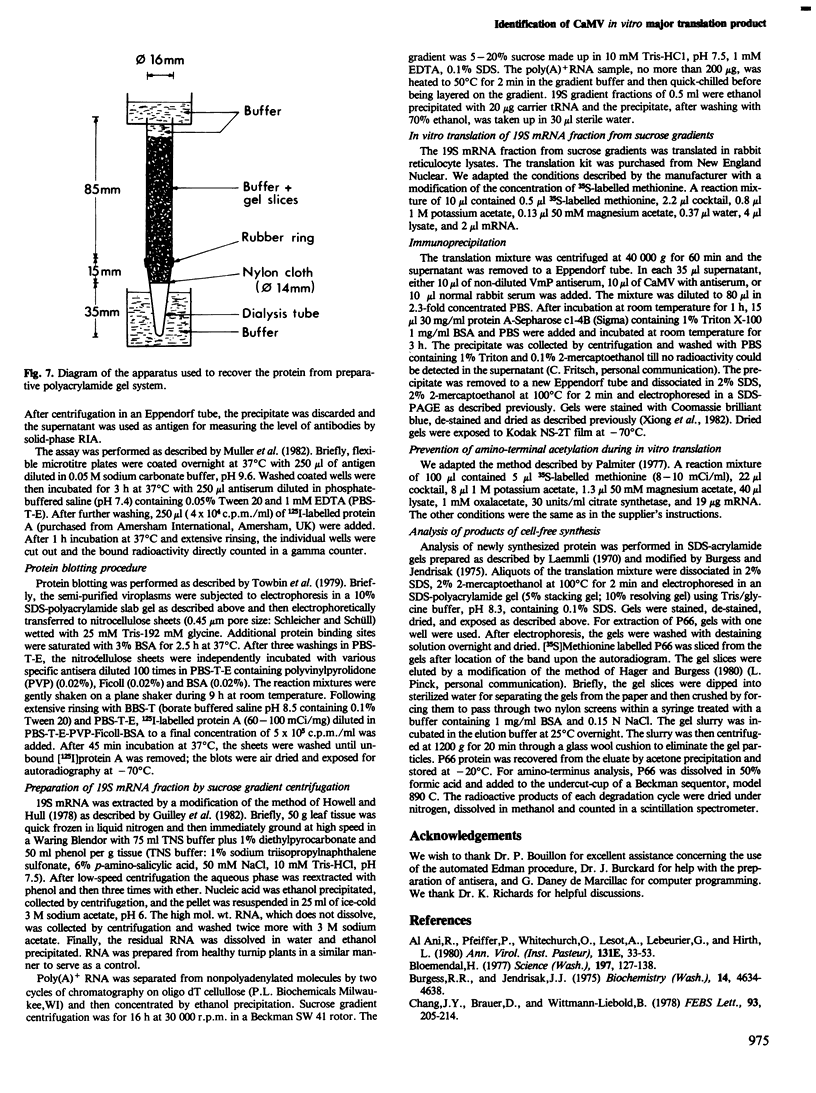

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloemendal H. The vertebrate eye lens. Science. 1977 Jul 8;197(4299):127–138. doi: 10.1126/science.877544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franck A., Guilley H., Jonard G., Richards K., Hirth L. Nucleotide sequence of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Richards K., Geneviève-Lebeurier Cauliflower mosaic virus on its way to becoming a useful plant vector. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;96:194–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. H., Hull R. Replication of cauliflower mosaic virus and transcription of its genome in turnip leaf protoplasts. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):468–481. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebeurier G., Hirth L., Hohn B., Hohn T. In vivo recombination of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2932–2936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebeurier G., Whitechurch O., Lesot A., Hirth L. Physical map of DNA from a new cauliflower mosaic virus strain. Gene. 1978 Nov;4(3):213–226. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martelli G. P., Castellano M. A. Light and electron microscopy of the intracellular inclusions of cauliflower mosaic virus. J Gen Virol. 1971 Oct;13(1):133–140. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-1-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo M. A., Robinson D. J., Pérombelon M. C. Some properties of a bacterial protease with a specific effect on the protein in tobacco rattle virus particles. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Nov;85(1):121–129. doi: 10.1099/00221287-85-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller S., Himmelspach K., Van Regenmortel M. H. Immunochemical localization of the C-terminal hexapeptide of histone H3 at the surface of chromatin subunits. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):421–425. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Prevention of NH2-terminal acetylation of proteins synthesized in cell-free systems. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):8781–8783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]