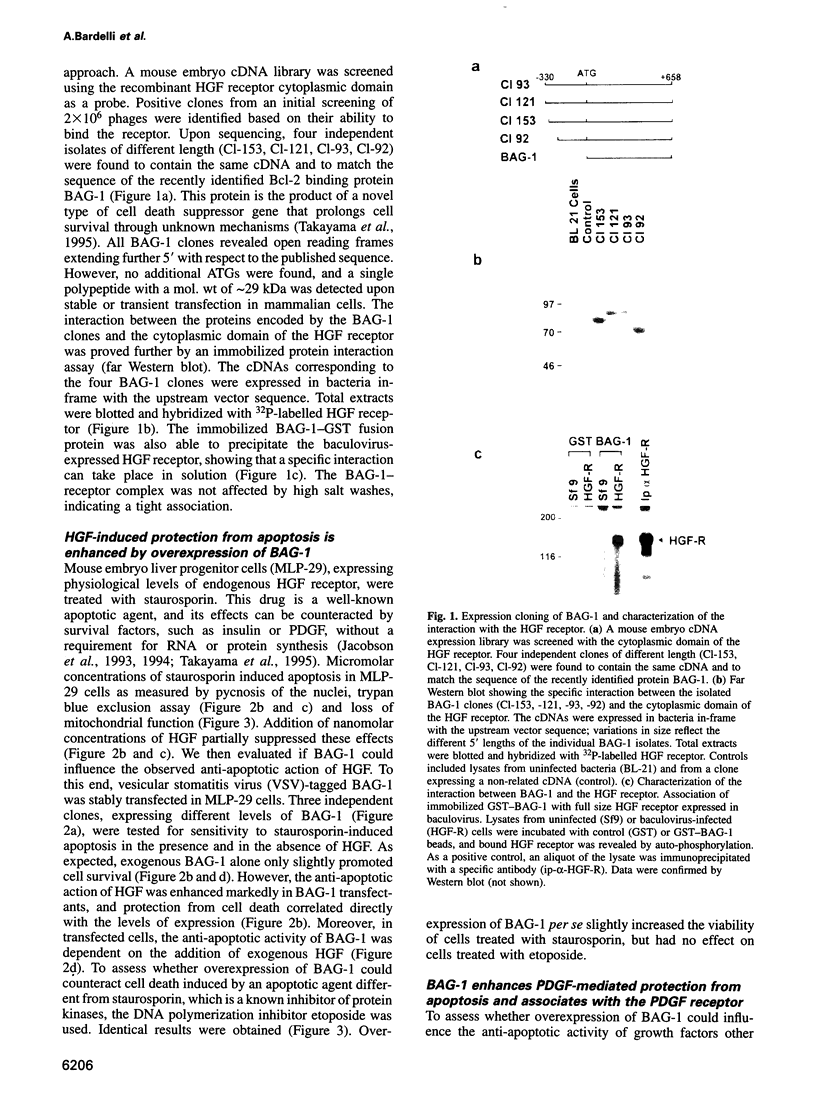
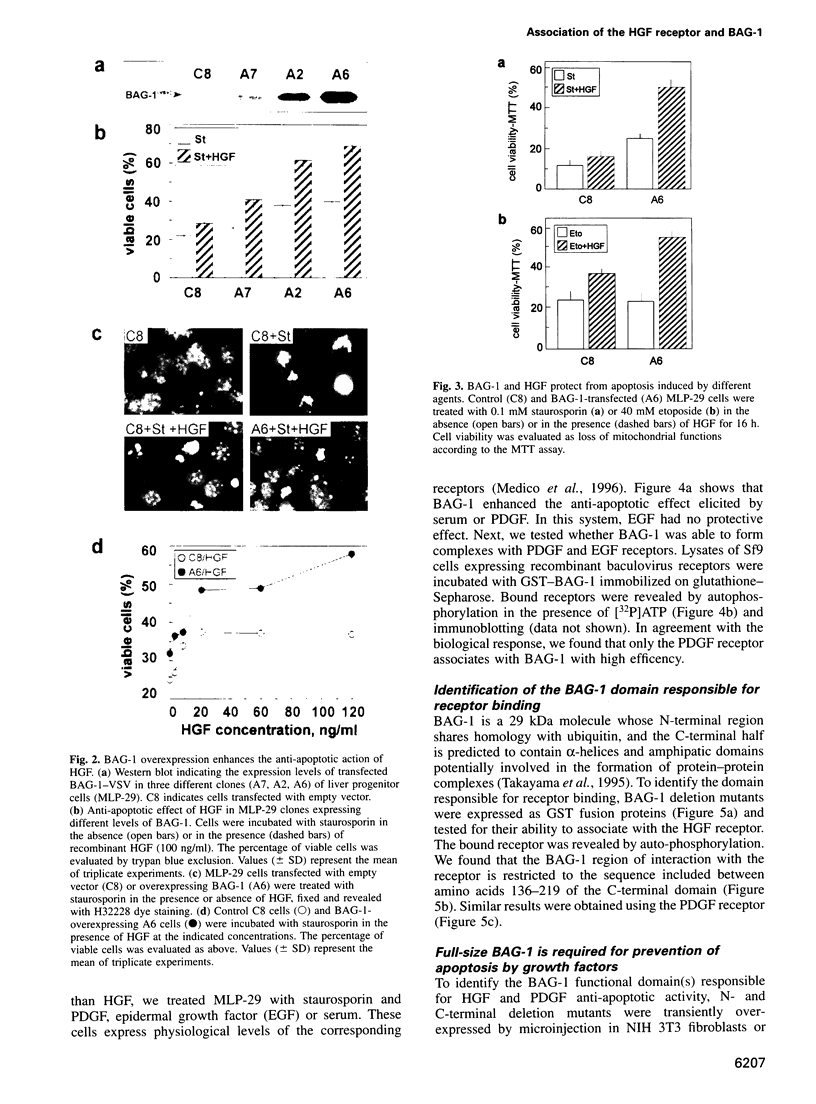
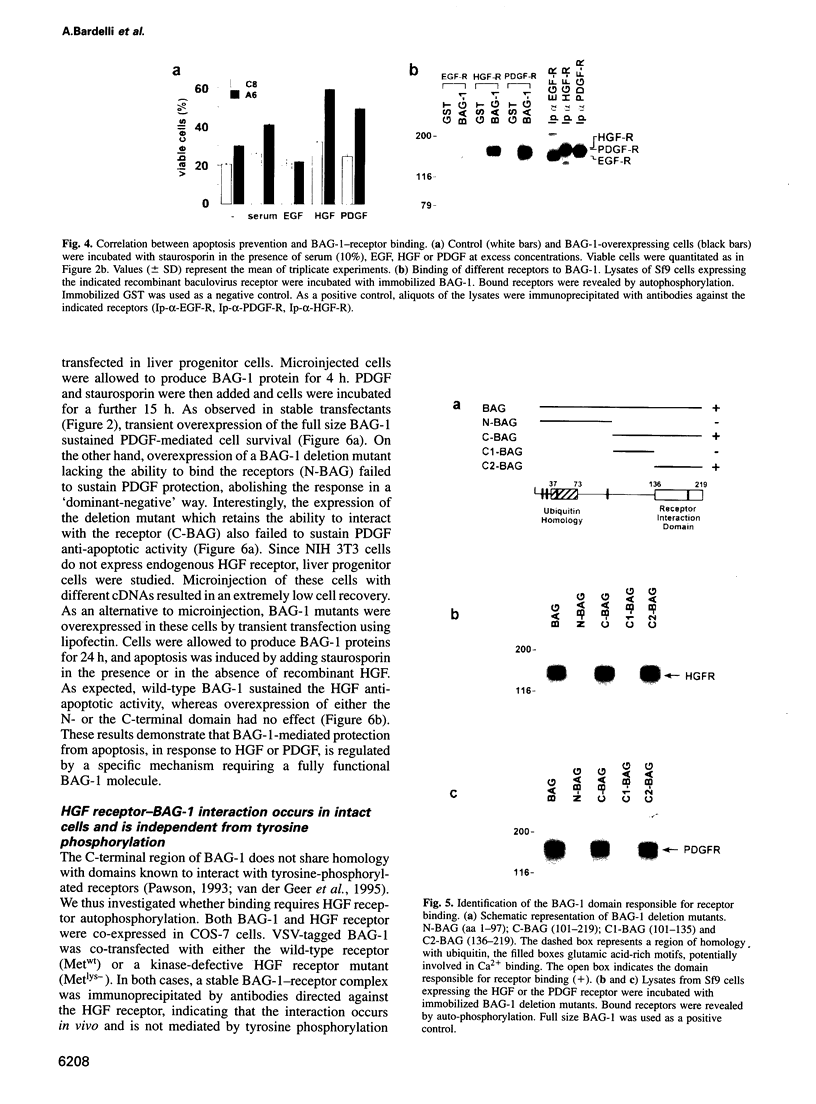
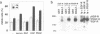Abstract
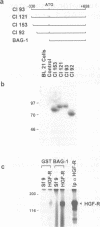
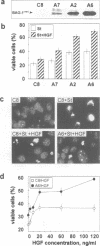
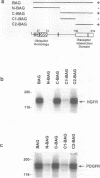
The mechanisms by which apoptosis is prevented by survival factors are largely unknown. Using an interaction cloning approach, we identified a protein that binds to the intracellular domain of the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) receptor. This protein was identified as BAG-1, a recently characterized Bcl-2 functional partner, which prolongs cell survival through unknown mechanisms. Overexpression of BAG-1 in liver progenitor cells enhances protection from apoptosis by HGF. Association of the receptor with BAG-1 occurs in intact cells, is mediated by the C-terminal region of BAG-1 and is independent from tyrosine phosphorylation of the receptor. Formation of the complex is increased rapidly following induction of apoptosis. BAG-1 also enhances platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-mediated protection from apoptosis and associates with the PDGF receptor. Microinjection or transient expression of BAG-1 deletion mutants shows that both the N- and the C-terminal domains are required for protection from apoptosis. The finding of a link between growth factor receptors and the anti-apoptotic machinery fills a gap in the understanding of the molecular events regulating programmed cell death.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardelli A., Maina F., Gout I., Fry M. J., Waterfield M. D., Comoglio P. M., Ponzetto C. Autophosphorylation promotes complex formation of recombinant hepatocyte growth factor receptor with cytoplasmic effectors containing SH2 domains. Oncogene. 1992 Oct;7(10):1973–1978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Faletto D. L., Chan A. M., Kmiecik T. E., Vande Woude G. F., Aaronson S. A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.1846706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann V., Foroutan H., Sachs M., Weidner K. M., Birchmeier W. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor induces a variety of tissue-specific morphogenic programs in epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 1):1573–1586. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Di Renzo M. F., Ziche M., Bocchietto E., Olivero M., Naldini L., Gaudino G., Tamagnone L., Coffer A., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor is a potent angiogenic factor which stimulates endothelial cell motility and growth. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):629–641. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferracini R., Longati P., Naldini L., Vigna E., Comoglio P. M. Identification of the major autophosphorylation site of the Met/hepatocyte growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19558–19564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch S. M., Francis H. Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(4):619–626. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano S., Di Renzo M. F., Narsimhan R. P., Cooper C. S., Rosa C., Comoglio P. M. Biosynthesis of the protein encoded by the c-met proto-oncogene. Oncogene. 1989 Nov;4(11):1383–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano S., Ponzetto C., Di Renzo M. F., Cooper C. S., Comoglio P. M. Tyrosine kinase receptor indistinguishable from the c-met protein. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):155–156. doi: 10.1038/339155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani A., Gramaglia D., Cantley L. C., Comoglio P. M. The tyrosine-phosphorylated hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor associates with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22087–22090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani A., Gramaglia D., dalla Zonca P., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor stimulates the Ras-guanine nucleotide exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9165–9168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington E. A., Bennett M. R., Fanidi A., Evan G. I. c-Myc-induced apoptosis in fibroblasts is inhibited by specific cytokines. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3286–3295. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06630.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. D., Burne J. F., King M. P., Miyashita T., Reed J. C., Raff M. C. Bcl-2 blocks apoptosis in cells lacking mitochondrial DNA. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):365–369. doi: 10.1038/361365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. D., Burne J. F., Raff M. C. Programmed cell death and Bcl-2 protection in the absence of a nucleus. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 15;13(8):1899–1910. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06459.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longati P., Bardelli A., Ponzetto C., Naldini L., Comoglio P. M. Tyrosines1234-1235 are critical for activation of the tyrosine kinase encoded by the MET proto-oncogene (HGF receptor). Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Okazaki H., Nakamura T. Novel function of prostaglandins as inducers of gene expression of HGF and putative mediators of tissue regeneration. J Biochem. 1995 Feb;117(2):458–464. doi: 10.1093/jb/117.2.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medico E., Mongiovi A. M., Huff J., Jelinek M. A., Follenzi A., Gaudino G., Parsons J. T., Comoglio P. M. The tyrosine kinase receptors Ron and Sea control "scattering" and morphogenesis of liver progenitor cells in vitro. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Apr;7(4):495–504. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Matsumoto K., Nakamura T., Orci L. Identification of a fibroblast-derived epithelial morphogen as hepatocyte growth factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Teramoto H., Ichihara A. Purification and characterization of a growth factor from rat platelets for mature parenchymal hepatocytes in primary cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6489–6493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Vigna E., Bardelli A., Follenzi A., Galimi F., Comoglio P. M. Biological activation of pro-HGF (hepatocyte growth factor) by urokinase is controlled by a stoichiometric reaction. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):603–611. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassar N., Horn G., Herrmann C., Scherer A., McCormick F., Wittinghofer A. The 2.2 A crystal structure of the Ras-binding domain of the serine/threonine kinase c-Raf1 in complex with Rap1A and a GTP analogue. Nature. 1995 Jun 15;375(6532):554–560. doi: 10.1038/375554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Signal transduction--a conserved pathway from the membrane to the nucleus. Dev Genet. 1993;14(5):333–338. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020140502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Bardelli A., Maina F., Longati P., Panayotou G., Dhand R., Waterfield M. D., Comoglio P. M. A novel recognition motif for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding mediates its association with the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4600–4608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Bardelli A., Zhen Z., Maina F., dalla Zonca P., Giordano S., Graziani A., Panayotou G., Comoglio P. M. A multifunctional docking site mediates signaling and transformation by the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor family. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90318-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat M., Narsimhan R. P., Crepaldi T., Nicotra M. R., Natali P. G., Comoglio P. M. The receptor encoded by the human c-MET oncogene is expressed in hepatocytes, epithelial cells and solid tumors. Int J Cancer. 1991 Sep 30;49(3):323–328. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910490302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Barres B. A., Burne J. F., Coles H. S., Ishizaki Y., Jacobson M. D. Programmed cell death and the control of cell survival: lessons from the nervous system. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):695–700. doi: 10.1126/science.8235590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):397–400. doi: 10.1038/356397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C., Bladt F., Goedecke S., Brinkmann V., Zschiesche W., Sharpe M., Gherardi E., Birchmeier C. Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor is essential for liver development. Nature. 1995 Feb 23;373(6516):699–702. doi: 10.1038/373699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider W. D. Functions of the neurotrophins during nervous system development: what the knockouts are teaching us. Cell. 1994 Jun 3;77(5):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Gish G., Mbamalu G., Pawson T., Cantley L. C. A single point mutation switches the specificity of group III Src homology (SH) 2 domains to that of group I SH2 domains. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 3;270(44):26029–26032. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.44.26029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H. Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1445–1449. doi: 10.1126/science.7878463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker M., Gherardi E., Perryman M., Gray J. Scatter factor is a fibroblast-derived modulator of epithelial cell mobility. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):239–242. doi: 10.1038/327239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama S., Sato T., Krajewski S., Kochel K., Irie S., Millan J. A., Reed J. C. Cloning and functional analysis of BAG-1: a novel Bcl-2-binding protein with anti-cell death activity. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90410-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo D., Persico M., Alcalay M. A "housekeeping" gene on the X chromosome encodes a protein similar to ubiquitin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):851–855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijay-Kumar S., Bugg C. E., Cook W. J. Structure of ubiquitin refined at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):531–544. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90679-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhen Z., Giordano S., Longati P., Medico E., Campiglio M., Comoglio P. M. Structural and functional domains critical for constitutive activation of the HGF-receptor (Met). Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1691–1697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Geer P., Wiley S., Lai V. K., Olivier J. P., Gish G. D., Stephens R., Kaplan D., Shoelson S., Pawson T. A conserved amino-terminal Shc domain binds to phosphotyrosine motifs in activated receptors and phosphopeptides. Curr Biol. 1995 Apr 1;5(4):404–412. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]