Abstract
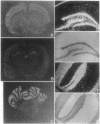
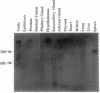
We have identified a member of the steroid receptor superfamily and cloned it from human and rat hypothalamus, prostate, and testis cDNA libraries. The open reading frame between first ATG and terminator TGA can encode 615 (human) and 596 (rat) amino acids with calculated molecular mass of 67.3 (human) and 65.4 (rat) kDa. The amino acid sequence of this protein, called TR4 orphan receptor, is closely related to the previously identified TR2 orphan receptor. The high homology between TR2 and TR4 orphan receptor suggests that these two orphan receptors constitute a unique subfamily within the steroid receptor superfamily. These two orphan receptors are differentially expressed in rat tissues. Unlike TR2 orphan receptors, the TR4 orphan receptor appears to be predominantly located in granule cells of the hippocampus and the cerebellum, suggesting that it may play some role(s) in transcriptional regulation in these neurons.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adan R. A., Cox J. J., Beischlag T. V., Burbach J. P. A composite hormone response element mediates the transactivation of the rat oxytocin gene by different classes of nuclear hormone receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Jan;7(1):47–57. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.1.8383287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adan R. A., Cox J. J., van Kats J. P., Burbach J. P. Thyroid hormone regulates the oxytocin gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3771–3777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman J., Das G. D. Post-natal origin of microneurones in the rat brain. Nature. 1965 Aug 28;207(5000):953–956. doi: 10.1038/207953a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Towle H. C., Young W. S., 3rd Spatial and temporal expression of alpha- and beta-thyroid hormone receptor mRNAs, including the beta 2-subtype, in the developing mammalian nervous system. J Neurosci. 1992 Jun;12(6):2288–2302. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-06-02288.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Kokontis J., Acakpo-Satchivi L., Liao S., Takeda H., Chang Y. Molecular cloning of new human TR2 receptors: a class of steroid receptor with multiple ligand-binding domains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 15;165(2):735–741. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Kokontis J. Identification of a new member of the steroid receptor super-family by cloning and sequence analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):971–977. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80591-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Kokontis J., Liao S. S., Chang Y. Isolation and characterization of human TR3 receptor: a member of steroid receptor superfamily. J Steroid Biochem. 1989;34(1-6):391–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(89)90114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney A. J., Tsai S. Y., O'Malley B. W., Tsai M. J. Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor (COUP-TF) dimers bind to different GGTCA response elements, allowing COUP-TF to repress hormonal induction of the vitamin D3, thyroid hormone, and retinoic acid receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4153–4163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer C., Krey G., Keller H., Givel F., Helftenbein G., Wahli W. Control of the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway by a novel family of nuclear hormone receptors. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Hopkins B., Powell S. J., Danks P., Briggs I. Isolation and characterisation of the human lung NK-2 receptor gene using rapid amplification of cDNA ends. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 31;177(1):8–16. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91940-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor-COUP-TF interactions modulate retinoic acid signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1448–1452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokontis J., Liao S., Chang C. Transcriptional activation by TR3 receptor, a member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Receptor. 1991;1(4):261–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Conneely O. M., DeMayo F. J., O'Malley B. W. Identification of a new brain-specific transcription factor, NURR1. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Dec;6(12):2129–2135. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.12.1491694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydon J. P., Power R. F., Conneely O. M. Differential modes of activation define orphan subclasses within the steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily. Gene Expr. 1992;2(3):273–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietus-Snyder M., Sladek F. M., Ginsburg G. S., Kuo C. F., Ladias J. A., Darnell J. E., Jr, Karathanasis S. K. Antagonism between apolipoprotein AI regulatory protein 1, Ear3/COUP-TF, and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 modulates apolipoprotein CIII gene expression in liver and intestinal cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1708–1718. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. The steroid receptor superfamily: more excitement predicted for the future. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):363–369. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palkovits M. Isolated removal of hypothalamic or other brain nuclei of the rat. Brain Res. 1973 Sep 14;59:449–450. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power R. F., Mani S. K., Codina J., Conneely O. M., O'Malley B. W. Dopaminergic and ligand-independent activation of steroid hormone receptors. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1636–1639. doi: 10.1126/science.1749936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Wright G. E., Resh M. D., Pearson R. C., Snyder S. H. Brain-specific src oncogene mRNA mapped in rat brain by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9831–9835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Lehmann J., Hoffmann B., Dawson M. I., Cameron J., Graupner G., Hermann T., Tran P., Pfahl M. Homodimer formation of retinoid X receptor induced by 9-cis retinoic acid. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):587–591. doi: 10.1038/358587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]