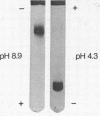
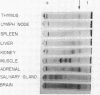
Abstract
A polypeptide of 8500 molecular weight is described that induces the differentiation of T (thymus-derived) cell and B (bone-marrow-derived) cell immunocytes in vitro, apparently via beta-adrenergic receptors and adenylate cyclase activation. This polypeptide shows a high degree of evolutionary conservation, exhibiting close structural, functional, and immunological similarity when isolated from such diverse origins as cells of mammals and higher plants. This polypeptide was detected in animal cells, yeast, bacteria, and higher plants, and so may well be a universal constituent of living cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S. Coupling of enzymes to proteins with glutaraldehyde. Use of the conjugates for the detection of antigens and antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C., Patrick R., Nussenzweig V. A population of lymphocytes bearing a membrane receptor for antigen-antibody-complement complexes. I. Separation and characterization. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):702–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitensky M. W., Gorman R. E. Cellular responses to cyclic AMP. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1973;26:409–461. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(73)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Aurbach G. D. Use of polyethylene glycol to separate free and antibody-bound peptide hormones in radioimmunoassays. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Nov;33(5):732–738. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-5-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix J. A., Diamond J. M., Kivelson D. Translational diffusion coefficient and partition coefficient of a spin-labeled solute in lecithin bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):474–478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROBSTEIN C. Some transmission characteristics of the tubule-inducing influence on mouse metanephrogenic mesenchyme. Exp Cell Res. 1957 Dec;13(3):575–587. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(57)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G. Isolation of bovine thymin: a polypeptide hormone of the thymus. Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):11–14. doi: 10.1038/247011a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G. The thymus and neuromuscular function. A substance in thymus which causes myositis and myasthenic neuromuscular block in guineapigs. Lancet. 1968 Jul 20;2(7560):119–122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90414-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komuro K., Boyse E. A. In-vitro demonstration of thymic hormone in the mouse by conversion of precursor cells into lymphocytes. Lancet. 1973 Apr 7;1(7806):740–743. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komuro K., Boyse E. A. Induction of T lymphocytes from precursor cells in vitro by a product of the thymus. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):479–482. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid M. P., Hoffmann M. K., Komuro K., Hämmerling U., Abbott J., Boyse E. A., Cohen G. H., Hooper J. A., Schulof R. S., Goldstein A. L. Differentiation of T cells induced by preparations from thymus and by nonthymic agents. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):1027–1032. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yust I., Wunderlich J., Mann D. L., Rogentine G. N., Jr, Leventhal B., Yankee R., Graw R. Human lymphocyte-dependent antibody mediated cytotoxicity and direct lymphocyte cytotoxicity against non-HL-A antigens. Nature. 1974 May 17;249(454):263–265. doi: 10.1038/249263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yust I., Wunderlich J., Mann D. L., Rogentine G. N., Jr, Leventhal B., Yankee R., Graw R. Human lymphocyte-dependent antibody mediated cytotoxicity and direct lymphocyte cytotoxicity against non-HL-A antigens. Nature. 1974 May 17;249(454):263–265. doi: 10.1038/249263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]