Abstract
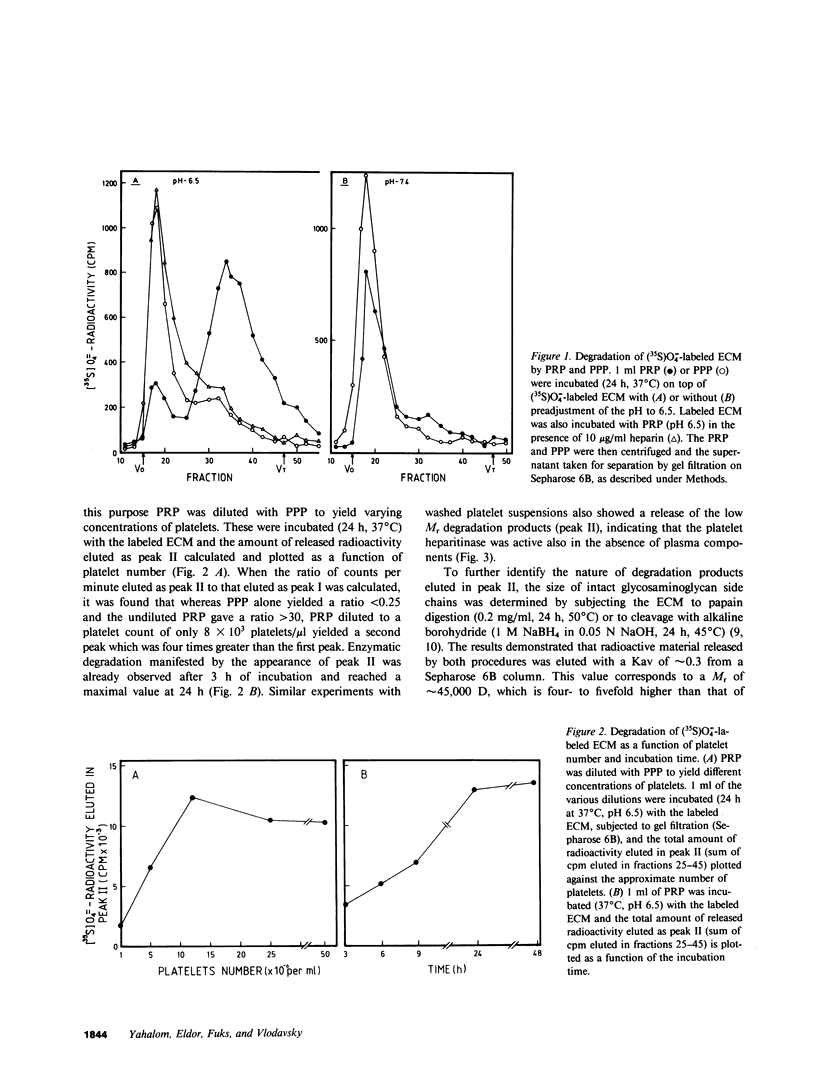
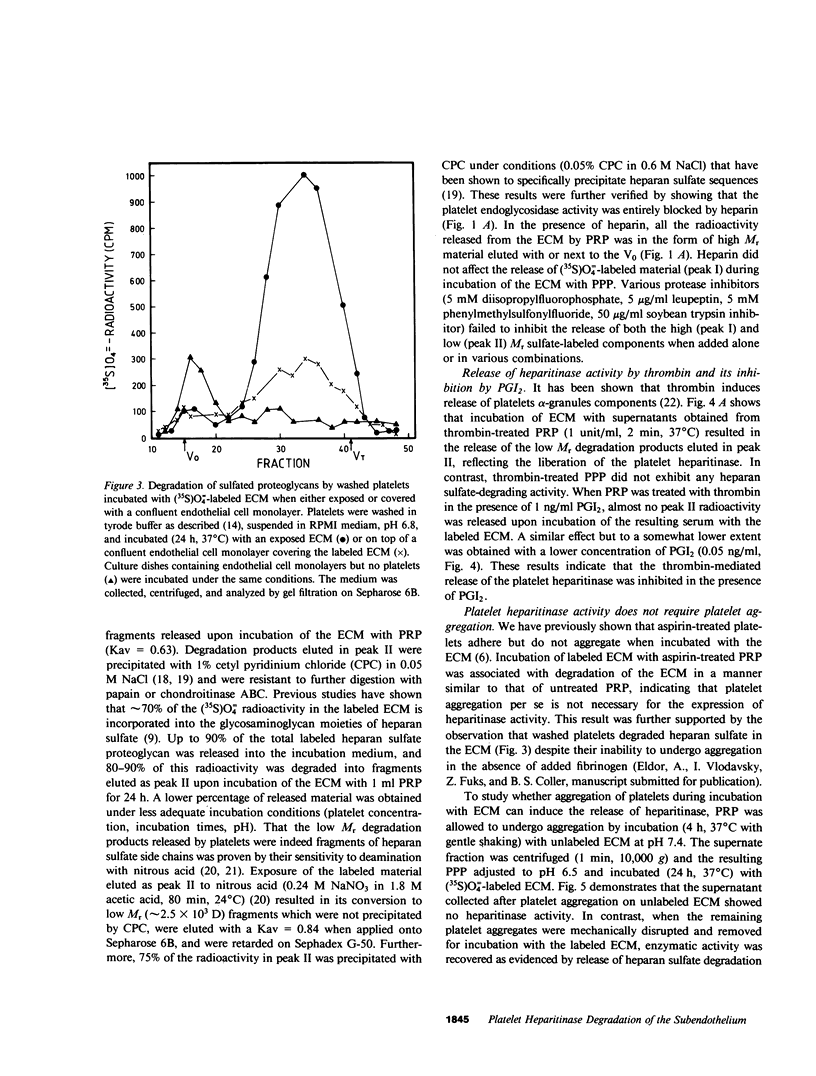
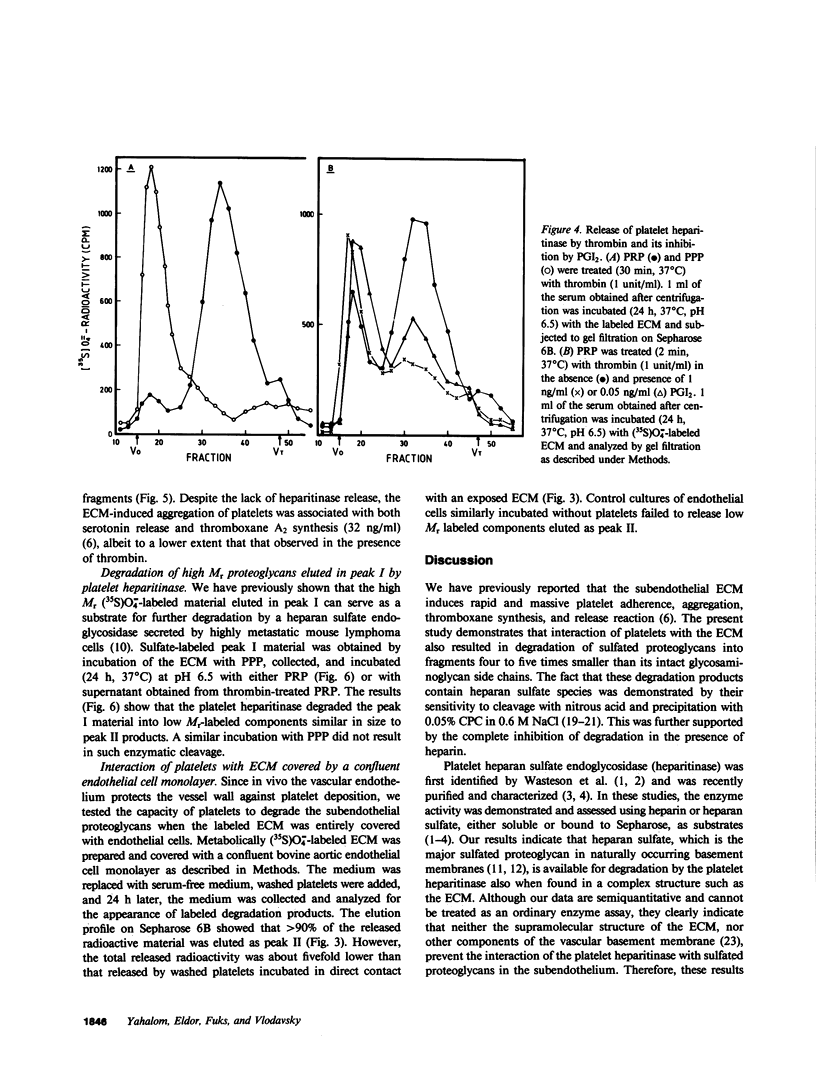
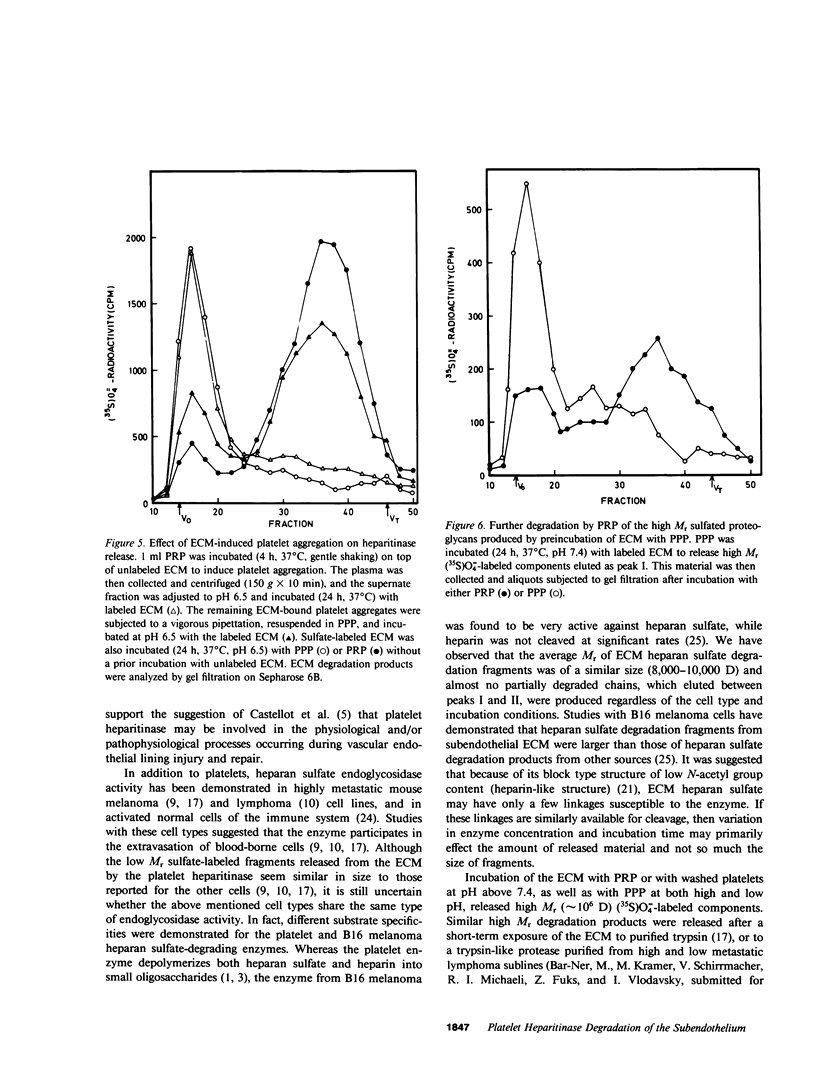
Cultured vascular and corneal endothelial cells produce an underlying extracellular matrix (ECM) which induces platelet adherence, aggregation, and release reaction. Incubation of a metabolically (35S)O = 4-labeled ECM with platelet-rich plasma or washed platelets, but not with platelet-poor plasma, resulted in degradation of its heparan sulfate-containing proteoglycans into labeled fragments four to five times smaller than intact glycosaminoglycan side chains. These fragments were sensitive to deamination with nitrous acid and were not produced in the presence of heparin, indicating that heparan sulfate in the ECM is susceptible to cleavage by the platelet heparitinase. This degradation required adhesion of platelets to the ECM rather than aggregation since it was not inhibited by aspirin, which prevented platelet aggregation but not adherence. The enzyme was not released during aggregation of platelets on the ECM but was readily liberated upon their exposure to thrombin. This liberation was inhibited in the presence of prostacyclin (PGI2). Isolated high molecular weight proteoglycans first released from the ECM by incubation with platelet poor plasma served as a substrate for further degradation by the platelet heparitinase, suggesting a cascade mechanism for degradation of heparan sulfate in the ECM. Heparitinase, although to a lower level, was also active when washed platelets were added on top of a confluent endothelial cell monolayer covering the (35S)O = 4-labeled ECM. It is suggested that the platelet heparitinase may be involved in the impairment of the integrity of the vessel wall and thus facilitate the extravasation of blood-borne cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Favreau L. V., Karnovsky M. J., Rosenberg R. D. Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell growth by endothelial cell-derived heparin. Possible role of a platelet endoglycosidase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11256–11260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasic G. J., Gasic T. B., Galanti N., Johnson T., Murphy S. Platelet-tumor-cell interactions in mice. The role of platelets in the spread of malignant disease. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):704–718. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. D., Stemerman M. B., Handin R. I. Vascular permeation of platelet factor 4 after endothelial injury. Science. 1980 Aug 1;209(4456):611–612. doi: 10.1126/science.6994228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Bialecki H., Greenburg G. Purification of the fibroblast growth factor activity from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3736–3743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Mescher A. L., Birdwell C. R. Stimulation of corneal endothelial cell proliferations in vitro by fibroblast and epidermal growth factors. Exp Eye Res. 1977 Jul;25(1):75–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(77)90248-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J., Braun D., Birdwell C. Clonal growth of bovine vascular endothelial cells: fibroblast growth factor as a survival agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Vlodavsky I., Savion N. The extracellular matrix and the control of proliferation of vascular endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(3):339–372. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassell J. R., Robey P. G., Barrach H. J., Wilczek J., Rennard S. I., Martin G. R. Isolation of a heparan sulfate-containing proteoglycan from basement membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4494–4498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawker R. J., Hawker L. M., Wilkinson A. R. Indium (111In)-labelled human platelets: optimal method. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Mar;58(3):243–248. doi: 10.1042/cs0580243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honn K. V., Cicone B., Skoff A. Prostacyclin: a potent antimetastatic agent. Science. 1981 Jun 12;212(4500):1270–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.7015512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., De Clerck Y. A. Extracellular matrix destruction by invasive tumor cells. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1982;1(4):289–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00124214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K. L., Broekman M. J., Chernoff A., Lesznik G. R., Drillings M. Platelet alpha-granule proteins: studies on release and subcellular localization. Blood. 1979 Apr;53(4):604–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpatkin S., Pearlstein E. Role of platelets in tumor cell metastases. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Nov;95(5):636–641. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-5-636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A., Alper R., Clark C. C. Biochemistry and metabolism of basement membranes. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;61:167–228. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61998-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. H., Vogel K. G., Nicolson G. L. Solubilization and degradation of subendothelial matrix glycoproteins and proteoglycans by metastatic tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2678–2686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Bäckström G., Jansson L., Hallén A. Biosynthesis of heparin. II. Formation of sulfamino groups. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7234–7241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcum J. M., McGill M., Bastida E., Ordinas A., Jamieson G. A. The interaction of platelets, tumor cells, and vascular subendothelium. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Dec;96(6):1046–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima M., Irimura T., Di Ferrante N., Nicolson G. L. Metastatic melanoma cell heparanase. Characterization of heparan sulfate degradation fragments produced by B16 melanoma endoglucuronidase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2283–2290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldberg A., Heldin C. H., Wasteson A., Busch C., Hök M. Characterization of a platelet endoglycosidase degrading heparin-like polysaccharides. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 9;19(25):5755–5762. doi: 10.1021/bi00566a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosta G. M., Favreau L. V., Beeler D. L., Rosenberg R. D. Purification and properties of human platelet heparitinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11249–11255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham M. A., Cazenave J. P., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Mustard J. F. Drug effects on platelet adherence to collagen and damaged vessel walls. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;109:253–276. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-0967-3_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savion N., Vlodavsky I., Fuks Z. Interaction of T lymphocytes and macrophages with cultured vascular endothelial cells: attachment, invasion, and subsequent degradation of the subendothelial extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Feb;118(2):169–178. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041180209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Ariav Y., Atzmon R., Fuks Z. Tumor cell attachment to the vascular endothelium and subsequent degradation of the subendothelial extracellular matrix. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jul;140(1):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Eldor A., HyAm E., Atzom R., Fuks Z. Platelet interaction with the extracellular matrix produced by cultured endothelial cells: a model to study the thrombogenicity of isolated subendothelial basal lamina. Thromb Res. 1982 Oct 15;28(2):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90260-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Fuks Z., Bar-Ner M., Ariav Y., Schirrmacher V. Lymphoma cell-mediated degradation of sulfated proteoglycans in the subendothelial extracellular matrix: relationship to tumor cell metastasis. Cancer Res. 1983 Jun;43(6):2704–2711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Lui G. M., Gospodarowicz D. Morphological appearance, growth behavior and migratory activity of human tumor cells maintained on extracellular matrix versus plastic. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):607–616. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren B. A., Vales O. The adhesion of thromboplastic tumour emboli to vessel walls in vivo. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Jun;53(3):301–313. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A. A method for the determination of the molecular weight and molecular-weight distribution of chondroitin sulphate. J Chromatogr. 1971 Jul 8;59(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A., Glimelius B., Busch C., Westermark H., Heldin C. H., Norling B. Effect of a platelet endoglycosidase on cell surface associated heparan sulphate of human culturei endothelial and glial cells. Thromb Res. 1977 Sep;11(3):309–321. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90184-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A., Hök M., Westermark B. Demonstration of a platelet enzyme, degrading heparan sulphate. FEBS Lett. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):218–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


